A transnational strategy represents the fusion of global efficiency and local responsiveness.
Companies using this strategy operate internationally, utilizing resources and competencies from their worldwide network to enhance digital innovation and IT efficiency. At the same time, they adapt their offerings to align with regional preferences, norms, and regulations, ensuring relevancy in each market they serve.
If you are employed by or considering joining a transnational company, it is beneficial to grasp the concept and its mechanisms. And, if you are a small business owner looking to expand globally, implementing a transnational strategy can give you the competitive advantage needed to succeed in international markets.
This article will dive deeper into transnational strategies and explore why it is a necessary tool for businesses in today’s globalized world.
- What is a Transnational Strategy?
- Why is a Transnational Strategy Important?
- What Are The Different Types of International Strategies?
- What Are The Benefits of a Transnational Strategy?
- What Are The Challenges of a Transnational Strategy?
- What Are Some Examples of a Transnational Strategy?
- What’s Next For Transnational Businesses?
What is a Transnational Strategy?
A transnational strategy is a global expansion approach used by businesses to balance both global integration and local responsiveness. It involves coordinating global activities and operations across international borders, leveraging a company’s worldwide resources, competencies, and understanding of local markets.
Transnational strategies enable companies to function across multiple geographical borders while catering effectively to local preferences and norms. They aim to create a unified international business that adapts and responds to diverse market conditions.
A transnational strategy’s essence lies in its dual focus: global integration and local customization. It allows businesses to leverage their global presence for maximum benefit while respecting and capitalizing on local market nuances.
The result is a competitive edge on the global stage, achieved by harmonizing international scale with local market resonance.
Why is a Transnational Strategy Important?
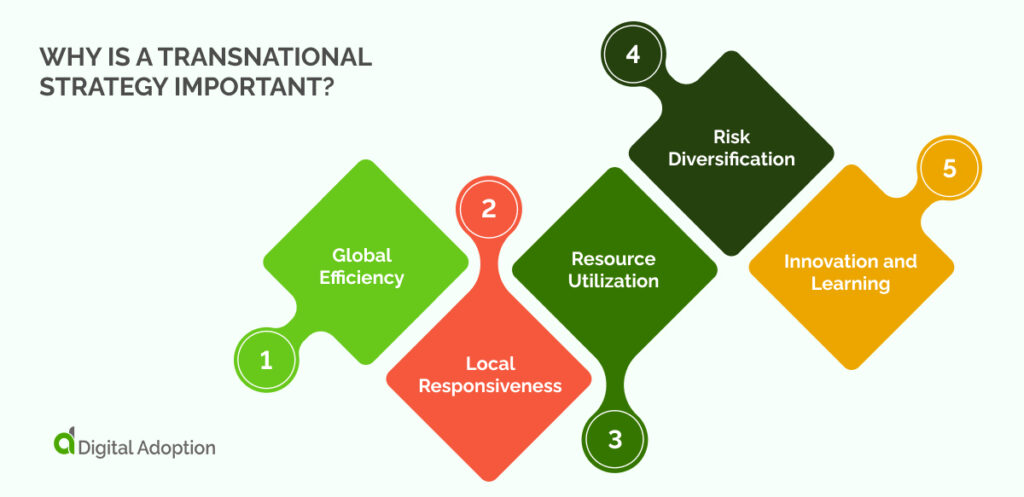
Understanding the importance of a transnational strategy is pivotal, as it masterfully intertwines universal efficiency with local market adaptability, creating a robust framework for enhanced international business success.
Here’s why having a transnational strategy is important:
- Global Efficiency: A transnational approach allows businesses to leverage their global presence for cost efficiencies. They can source materials from the cheapest or most available locations, manufacture in low-cost regions, and utilize economies of scale.
- Local Responsiveness: This strategy enables companies to adapt to local market conditions, tastes, and cultural nuances. It allows them to offer customized products or services that meet the specific needs and preferences of different regional markets.
- Resource Utilization: Companies can tap into the best resources – human, material, or knowledge-based – from across their global network, leading to improved products or services.
- Risk Diversification: Operating in multiple markets allows companies to spread their risks. If one market encounters economic instability or decline, the impact is mitigated by the company’s presence in other, more stable or growing markets.
- Innovation and Learning: Exposure to diverse markets promotes learning and innovation. The insights gained from operating in various regions can be shared and implemented across the company, fostering continual improvement and innovation.
What Are The Different Types of International Strategies?
It’s important to note that no one-size-fits-all approach to an international strategy exists.
Each company must evaluate its unique business objectives, resources, and capabilities when determining the most suitable type of international strategy for its goals.
Having said that, there are four different types of international strategies commonly used by businesses globally, with transnational being one of them:
Global Strategy
A global strategy is a company aiming to create and sell products or services standardized across all markets.
This approach is most effective for businesses that offer products or services with universal demand, such as technology or consumer goods. The primary advantage of a global strategy is the potential to achieve economies of scale and scope, which can lead to significant cost reductions.
It also allows companies to take advantage of market linkages and coordinate their strategies across different regions. However, a key challenge is the lack of flexibility to cater to local tastes and preferences.
Transnational Strategy
A transnational strategy seeks to strike a balance between global efficiencies and local responsiveness.
Companies using this strategy often have a dispersed yet interdependent network of operations and subsidiaries across numerous countries. They centralize some functions to reap the benefits of economies of scale and decentralize others to adapt to local market conditions.
This approach allows businesses to enjoy both cost advantages and differentiated products/services. However, managing the complexity of this strategy can be challenging due to conflicting pressures for cost efficiency and local adaptation.
Multidomestic Strategy
A multi-domestic strategy involves tailoring products or services to suit the needs and tastes of local markets.
This approach is common in industries where cultural factors, such as food and beverage or media, significantly influence consumer behavior. The main advantage of a multi-domestic strategy is its high responsiveness to local market conditions, which can lead to a better customer experience transformation and an increased market share.
However, this strategy can result in higher costs due to the lack of standardization and the need for multiple supply chains and manufacturing processes.
International Strategy
An international strategy involves leveraging domestic-based core competencies in international markets.
Companies using this strategy typically export products or services developed at home to foreign markets. The focus is on transferring and adapting the company’s existing knowledge and capabilities from the home country to overseas markets.
While this strategy allows businesses to use their strong domestic bases, it may limit their ability to adapt to local market conditions and preferences, potentially affecting their competitive position in those markets.
What Are The Benefits of a Transnational Strategy?
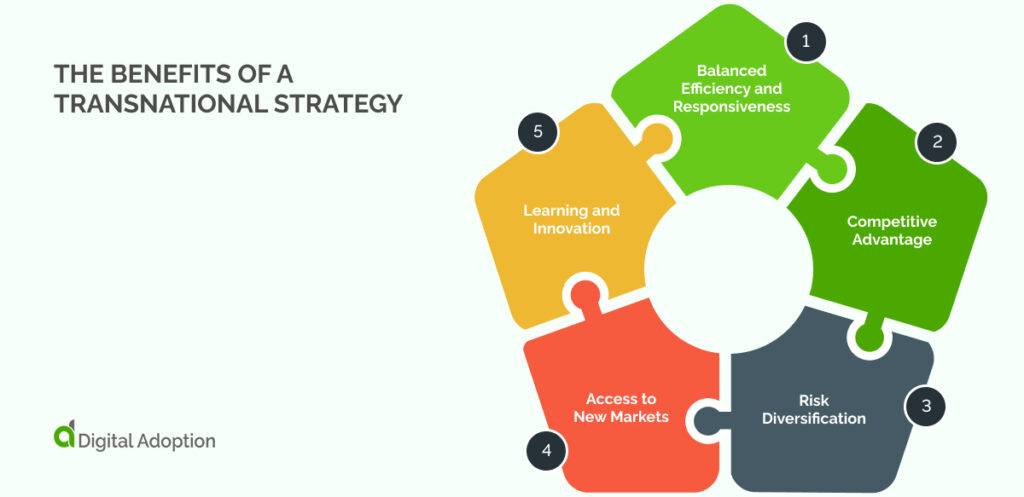
Exploring transnational strategies reveals benefits like global efficiency, risk diversification, and innovation, providing businesses with a competitive edge worldwide.
Let’s take a closer look:
Balanced Efficiency and Responsiveness
A transnational strategy provides the flexibility to balance global efficiency with local responsiveness.
This means companies can centralize some functions to benefit from economies of scale and scope, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
At the same time, they can decentralize other functions to adapt to specific local market conditions and customer preferences.
This dual focus allows businesses to optimize their operations while still effectively meeting the needs of diverse markets.
Competitive Advantage
Integrating resources and capabilities across various international markets allows companies to develop unique competencies, setting them apart from competitors.
This could include superior knowledge of local markets, unique product adaptations, or more efficient supply chains.
These advantages are often difficult for competitors to replicate, especially those operating solely in domestic markets or using a one-size-fits-all global approach.
Risk Diversification
A transnational strategy mitigates risk by spreading business operations and investments across multiple countries.
If one market experiences an economic downturn, political instability, or other adverse conditions, the impact on the overall business can be offset by the performance of units in other, more stable markets.
This diversification reduces the potential damage of localized risks and enhances the company’s resilience.
Access to New Markets
Transnational strategy allows businesses to enter and compete in new markets. This can increase market share, revenue growth, and brand recognition.
Additionally, it enables companies to cater to a larger and more diverse customer base, which can drive innovation and adaptation in products or services to meet varying customer needs and preferences.
Learning and Innovation
Operating in multiple countries exposes companies to different market conditions, consumer behaviors, and business practices.
This exposure can foster cross-border learning and innovation.
Companies can gather insights and best practices from each market and apply them across their global operations, leading to continuous improvement, innovation, and a stronger competitive position.
This strategy can also encourage sharing of knowledge and skills among employees from different backgrounds and cultures, further enhancing the company’s learning culture.
What Are The Challenges of a Transnational Strategy?
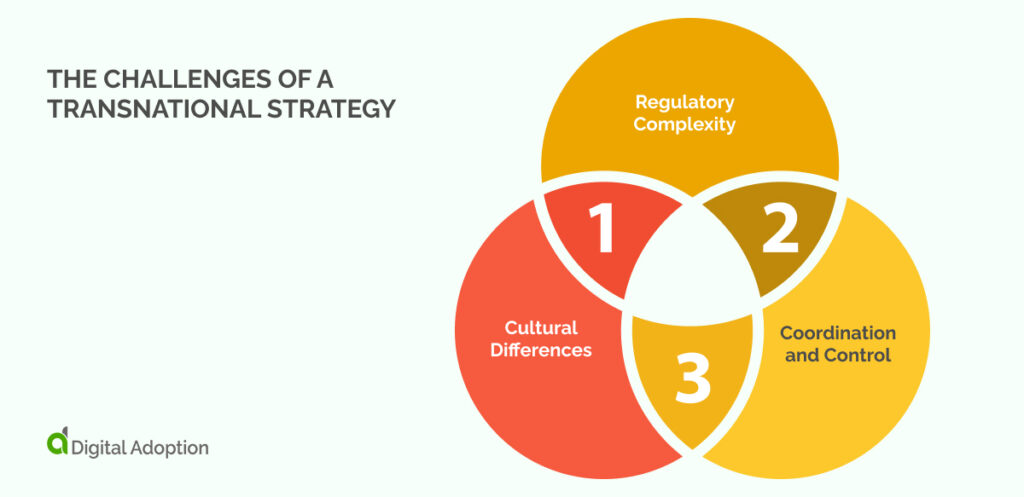
With all the potential benefits, it’s essential to consider the challenges of a transnational strategy.
Some of these include:
Cultural Differences
One of the significant challenges of a transnational strategy is dealing with cultural differences.
When a company expands its operations across various countries, it encounters diverse cultures, languages, and business practices.
This diversity can lead to misunderstandings, miscommunication, and potential conflicts. For instance, a marketing campaign that works well in one country may not resonate in another due to cultural nuances.
Therefore, businesses must invest time and resources into understanding and respecting these cultural differences to build strong relationships with local customers, employees, and partners.
Regulatory Complexity
Different countries have their unique sets of laws and regulations that govern business operations.
These can range from labor laws and tax regulations to environmental policies and data protection rules.
Navigating this regulatory complexity can be a daunting task for businesses employing a transnational strategy.
Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, legal issues, and damage to the company’s reputation.
Therefore, businesses must ensure they have a deep understanding of the local legal landscape and stay updated on any changes to avoid potential pitfalls.
Coordination and Control
Implementing a transnational strategy involves managing operations across various regions, which requires a high level of coordination and control.
Ensuring consistency in product quality, customer service, and brand image across all locations can be challenging.
There can be logistical hurdles in coordinating supply chains, managing international teams, and synchronizing processes.
Furthermore, controlling operations across borders can become difficult due to time zone differences, communication barriers, and varied operational standards.
Businesses need robust systems and processes in place to effectively manage these challenges and maintain operational efficiency.
What Are Some Examples of a Transnational Strategy?
We will delve deeper into the world of transnational business strategies as we explore how five global powerhouses, Unilever, Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, and Starbucks, have successfully merged global aspirations with local relevance.
Unilever
Unilever, a renowned multinational consumer goods company, is widely recognized as an exemplary transnational corporation. With its extensive presence in numerous countries worldwide, Unilever has honed its expertise in catering to diverse regional tastes and preferences.
Through a portfolio of carefully tailored brands, Unilever has successfully captured the essence of local markets while upholding global standards. This harmonious blend of adaptability and consistency showcases Unilever’s remarkable implementation of a transnational strategy, setting it apart as a true industry leader.
Procter & Gamble (P&G)
As one of the world’s largest consumer goods companies, P&G has established a strong presence across international borders with its diverse range of products.
From groundbreaking health care and personal care solutions to reliable household cleaning products, P&G has meticulously tailored its offerings to cater to the unique needs and preferences of customers worldwide.
P&G’s continuous adaptation of its products and marketing strategies has led to remarkable success, serving as a testament to the prowess of its transnational strategy.
Through a careful blend of innovation, adaptability, and market insight, P&G has solidified its position as a global leader in the consumer goods industry.
Coca-Cola
Operating in more than 200 countries, Coca-Cola has perfected the art of balancing global and local strategies by leveraging its deep understanding of diverse cultures.
While the brand maintains a strong global identity, it also adapts its products to cater to local tastes, preferences, and traditions.
Embracing this nuanced approach allows Coca-Cola to maintain its relevancy and a deep connection with the unique needs and desires of consumers in each market.
This commitment to understanding and embracing local nuances has made Coca-Cola a prime example of a highly successful transnational strategy, solidifying its position as a global leader in the beverage industry.
Starbucks
Starbucks‘ successful international expansion exemplifies a well-executed transnational strategy.
By maintaining a consistent global brand identity, Starbucks has created a sense of familiarity and trust among its customers worldwide. However, what sets Starbucks apart is its ability to adapt and cater to local preferences.
For example, in Japan, where matcha is a popular flavor, Starbucks offers matcha-flavored drinks that cater to the local taste buds. Similarly, in China, where red bean is a traditional ingredient, Starbucks has introduced red bean frappuccinos to capture the local market.
This strategic blend of global and local approaches has allowed Starbucks to establish itself as a beloved global brand and foster a deep connection with customers by offering a taste of familiarity while celebrating local flavors.
This attention to detail and commitment to delivering a personalized experience has been key to Starbucks’ continued success in the competitive coffee industry.
What’s Next For Transnational Businesses?
Transnational businesses are poised to shape the next wave of globalization.
Their focus is on leveraging entrepreneurial growth to expand their global influence and increase their share in worldwide GDP, exports, and employment once the current crisis dissipates.
To achieve this, transnational companies are:
- Adopting lean expansion strategies, focusing on well-defined product strategies and reinvestment cycles.
- Collaborating with other businesses across borders is also seen as a key strategy for internationalization.
- Utlizing digital adoption platforms as well as tools that provide data-driven insights into local market preferences, behaviors, and trends. This allows for customized digital experiences created based on local insights while still maintaining a consistent global brand image
- Strategizing to navigate the reshaping of global value chains due to rising demand and new industry capabilities in the developing world.
It’s evident that businesses with a global footprint are gearing up for a dynamic future.
They’re striking a harmonious balance between their expansive global presence and the essence of local relevance, positioning themselves to tap into unparalleled growth opportunities in the ever-evolving global landscape.













