The digital transformation race continues to showcase a persistent trend of businesses gravitating towards increased digital adoption and acquiring innovative technology to remain future-ready.
The enterprise software market consistently demonstrates impressive growth, often surpassing 10 percent year on year, making it the most rapidly expanding segment within the broader IT industry, according to Statista. In 2022, global IT spending on enterprise software reached approximately 783 billion U.S. dollars, reflecting a 7.1 percent increase from the previous year.
This trend will continue as global sectors adapt to the macroeconomic changes of the Next Normal and geopolitical tensions between Russia and Ukraine escalate. Business and IT decision-makers may take a head-first approach to tech procurement without first establishing a well-defined buying process.
In their quest to gain a competitive advantage, this can lead to hasty decision-making on behalf of business leaders and investments in technology that may not provide value to the company or align with their prospects.
Discerning the most impactful solutions can be challenging and exhilarating, with many emerging technologies vying for attention. As such, IT decision-makers must deploy solutions for successfully navigating the intricate maze of the tech buying process.
In this article, we navigate the tech buying process, providing business and IT decision-makers with an essential guide for informing technology procurement.
We discuss aligning business goals with the tech-buying process, outline key steps to establish an effective approach, and identify vital stakeholders to involve. Additionally, we touch on the typical duration of the buying process and offer practical tips for choosing the right tech vendors, ensuring successful partnerships that drive innovation and growth.
A summary of the article’s key points includes the following:
- Aligning business goals with the technology buying process
- Steps for establishing the tech-buying process
- Who should be involved in the buying process?
- How long is the tech buying process?
- How to choose the right tech vendors?
Aligning business goals with the technology buying process
In the era of digitalization, organizations must ensure their technology acquisition process remains in harmony with wider business goals. This alignment ensures that the chosen solutions address immediate needs and support long-term growth and adaptability.
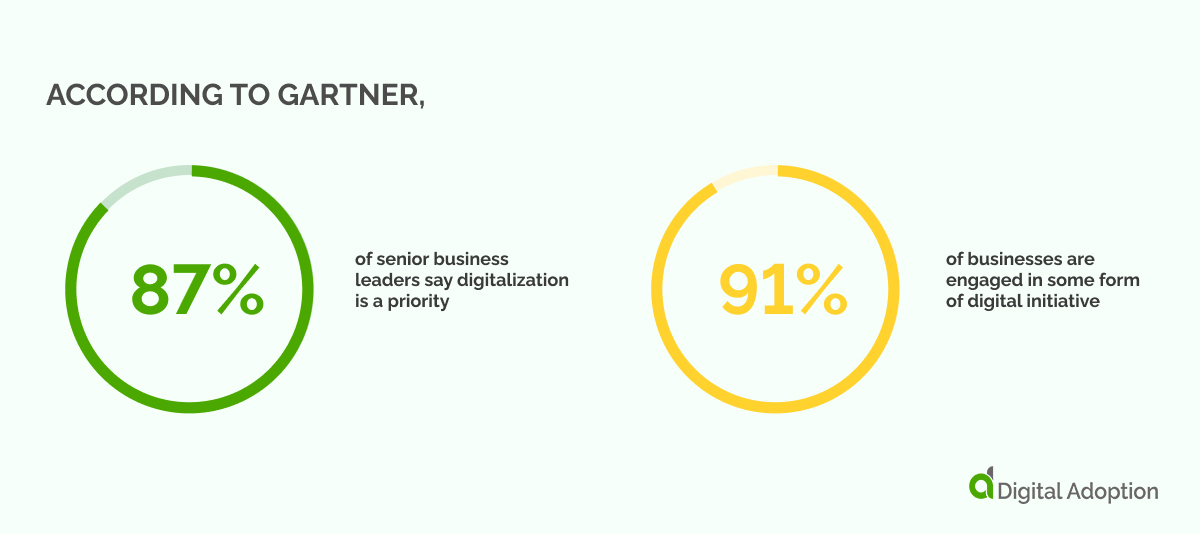
To achieve this, it is essential to cultivate a tailored purchasing strategy that enables executive and IT decision-makers to champion the broader technology adoption lifecycle. According to Gartner, 87% of senior business leaders say digitalization is a priority, and 91% of businesses are engaged in some form of digital initiative.
By embracing a culture of cross-functional collaboration among key stakeholders and continuously evaluating the effectiveness of technology investments, organizations can optimize their resources and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Streamlining technology adoption and procurement processes becomes even more pertinent when contrasted with research revealing that 93% of organizations have adopted or plan to adopt a digital-first business strategy.
Steps for establishing the tech-buying process
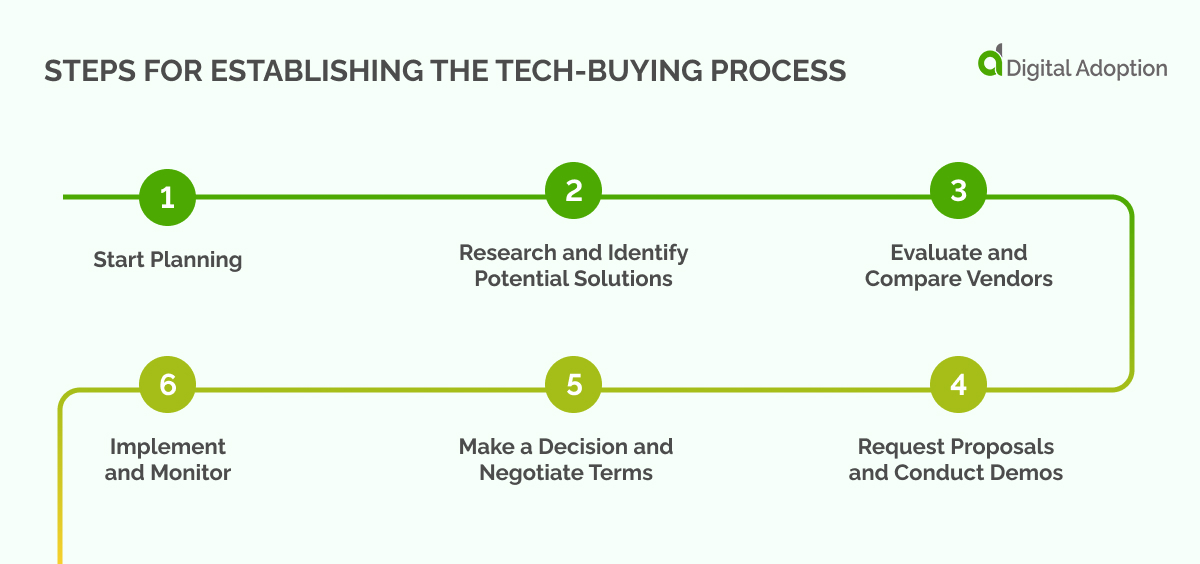
- Start Planning: To ensure a smooth and efficient tech-buying journey, it’s essential to begin with a well-thought-out planning process that sets the stage for success. This foundation involves identifying pain points, assembling a diverse buying team, setting a realistic budget, defining clear timelines, and aligning business objectives.
- Research and Identify Potential Solutions: Investigate various technology options that align with the organization’s needs and objectives. Look for industry trends, expert recommendations, and user reviews to gather valuable insights.
- Evaluate and Compare Vendors: Assess the strengths and weaknesses of each potential vendor based on factors such as product features, pricing, customer support, and integration capabilities. Create a shortlist of the most suitable options.
- Request Proposals and Conduct Demos: Reach out to the shortlisted vendors for detailed proposals and schedule product demonstrations to better understand their offerings. Encourage stakeholders to provide feedback and ask questions during the demos.
- Make a Decision and Negotiate Terms: Select the best-fit solution for the organization based on the feedback and evaluation. Negotiate contract terms, pricing, and support arrangements to ensure a mutually beneficial agreement
- Implement and Monitor: Roll out the chosen technology solution, providing necessary training and resources to facilitate a smooth adoption process. Continuously monitor performance and address issues, ensuring the solution delivers the desired outcomes.
Who should be involved in the buying process?
A successful technology buying process requires collaboration and input from various organizational stakeholders.
Involving the right individuals ensures that multiple perspectives are considered, fostering a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s needs and promoting buy-in from all parties involved.
Here are the key stakeholders who should be involved in the technology buying process:
- Executive Decision-Makers: C-suite executives, such as the CEO and COO, play a pivotal role in setting the strategic direction for technology investments. Their insights and understanding of overall business objectives are crucial in ensuring technology decisions align with the organization’s goals.
- Chief Information Officer (CIO) or IT Director: As the individuals responsible for overseeing the organization’s technology infrastructure, CIOs or IT Directors are instrumental in evaluating potential solutions, assessing compatibility with existing systems, and advocating for the necessary resources to support implementation.
- IT Professionals: Technical staff, such as network administrators, system analysts, and software developers, can provide valuable input on the feasibility, functionality, and integration of potential technology solutions. Their hands-on experience and expertise ensure the chosen technology is effective and efficient.
- End-Users: The individuals who will ultimately use the technology – employees or customers – should also be involved in the buying process. Their feedback and opinions can help identify specific requirements, uncover potential challenges, and ensure that the selected solution meets their needs and expectations.
- Finance and Procurement Teams: These stakeholders play a crucial role in assessing the financial viability of technology investments, negotiating contracts, and managing budgets. Their involvement ensures that technology decisions are fiscally responsible and adhere to organizational procurement policies.
- External Consultants and Vendors: Engaging with industry experts, consultants, and technology vendors can offer valuable insights into market trends, emerging technologies, and best practices. Their input can help organizations make informed decisions and select the most suitable vendor management solutions for their unique requirements.
Organizations can ensure a more holistic and collaborative approach to acquiring technology by involving these key stakeholders in the technology-buying process.
How long is the tech buying process?
The duration of the tech buying process varies significantly depending on several factors, such as the size and complexity of the organization, the technology being acquired, and the level of customization required.
Typically, smaller businesses with specific needs can complete the process within a few weeks to a few months. On the other hand, larger enterprises or those requiring highly specialized solutions may take several months or even over a year to navigate the process successfully.
It’s essential to remember that a well-executed tech buying process involves thorough research, evaluation, negotiation, and implementation. Rushing through these steps could lead to suboptimal decisions that may not align with the organization’s long-term goals.
Therefore, it is crucial to allocate sufficient time and resources to ensure a successful outcome, regardless of the specific timeline for each organization.
How to choose the right tech vendors?
Selecting the ideal tech vendors is a critical aspect of the tech-buying process, as it can significantly impact an organization’s performance and growth. To make informed decisions, consider the following strategies:
- Research and Shortlist: Conduct thorough research on various tech vendors in the market, exploring their reputation, product offerings, and customer feedback. Create a vendor shortlist that aligns with your organization’s goals and requirements.
- Evaluate Vendor Expertise: Assess each vendor’s industry expertise and experience working with similar organizations. Consider their knowledge of industry trends, best practices, and any unique challenges your organization might face.
- Analyze Product Features and Functionality: Compare the features and functionality of each vendor’s solution, ensuring they align with your organization’s needs. Pay close attention to scalability, integration capabilities, and user-friendliness.
- Consider Customer Support and Service: Evaluate each vendor’s commitment to customer support and service. Look for vendors that offer personalized assistance, prompt response times, and ongoing support for successfully implementing and maintaining their technology solutions.
- Weigh Pricing and Contract Terms: Analyze each vendor’s pricing structure and contract terms. Ensure they align with your organization’s budget and expectations for long-term value.
- Request Proposals and Demos: Engage with the shortlisted vendors to request detailed proposals and demonstrations of their solutions. Encourage stakeholders to participate and provide feedback during this stage.
- Check References: Reach out to existing clients of the shortlisted vendors to gather insights about their experiences and satisfaction levels. This step can help validate your decision and identify potential red flags.
Mastering the tech-buying process
In conclusion, navigating the tech buying process is crucial as it directly influences modern business operations, significantly impacting an organization’s performance and bottom line.
According to Oomnitza’s 2023 Snapshot Survey on SaaS and Cloud Spend Optimization & Automation, enterprises face challenges managing their software and cloud resources effectively. The survey reveals that 50% of enterprises waste a minimum of 10% of their yearly spending on underutilized software and SaaS applications. The survey also indicates that 53% of respondents spend over 10% of their budget on poorly managed or untracked cloud resources.
By highlighting the intricacies involved in this journey, this article aims to provide valuable insights to help businesses better navigate the tech buying process and make more informed decisions when procuring new technology.
Making better-informed technology investments ensures businesses remain at the forefront of innovation — ultimately contributing to their success in the long run.













