As enterprises scale, they often struggle with manual processes left over from their early growth stages. These old ways of working waste time and reduce efficiency.
To solve these problems, enterprises must embrace automation. Digital tools like AI and integrated software help companies streamline their operations. This makes the entire organization more flexible and responsive.
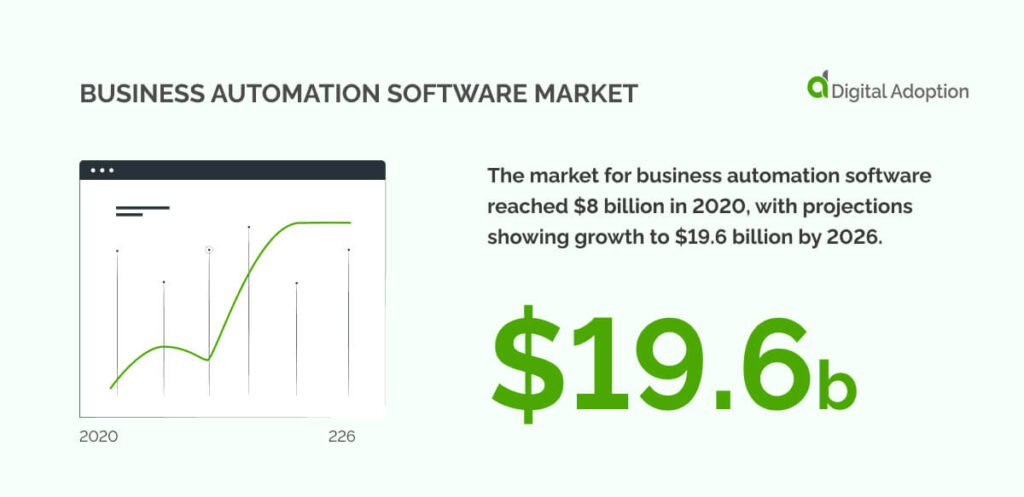
The market for business automation software reached $8 billion in 2020, with projections showing growth to $19.6 billion by 2026. This surge reflects how enterprises are investing more in automation to keep their competitive edge.
This article shows how enterprises can use automation to work smarter. We examine the different ways to automate tasks, share real examples, and guide you through building a strategy that works on an enterprise level.
What is enterprise automation?
Enterprise automation is the use of technology to make business processes run smoother across large companies. It combines software, AI, and digital tools to work faster and reduce manual work.
For enterprises, this makes a real difference in how well they perform and embrace digital adaptation to respond to change. Think about how your team spends hours doing the same tasks over and over. When you automate these jobs, your staff can focus on more important work.
Automated systems make fewer mistakes than humans, leading to better results. As your company grows, performance tracking is key.
Automation also helps you grow without needing to hire more people. For example, automating invoice processing enables you to pay invoices quicker and with fewer errors.
Companies that want to be responsive to market shifts must embrace automation.
What are the different types of enterprise automation?
Understanding how automation can help on the enterprise level is important before you start using it.
Take customer care, for example. Automated responses can handle ticket responses faster. Or look at data entry, where robotic process automation (RPA) software can fill out forms automatically.
When you use the right type of automation for each task, you get better results and spend less money.
Let’s take a look at the different types of enterprise automation:
Basic automation
Basic automation uses technology to handle simple, repeated tasks without human help. This allows companies to progress faster and make fewer mistakes. For example, in customer service, tools like Zendesk or Salesforce respond to clients quickly and reliably.
Intelligent automation
Intelligent or business analysis automation uses data and AI to make quick decisions as needed. This helps companies stay nimble and accurate, especially in areas like banking. For example, banks watch transactions as they happen and use AI to spot possible fraud. This keeps money safer and ensures compliance.
Business process automation (BPA)
BPA smooths complex workflows by connecting multiple tasks. It automates end-to-end processes, reducing manual intervention and eliminating bottlenecks in workflow execution.
Integration automation
Integration automation helps different computer systems work together and share information. This gives companies better access to their data and smoother operations. For instance, Shopify stores can automatically track items across their online and physical shops, helping keep inventory counts accurate.
Artificial intelligence (AI) automation
AI automation uses machine learning (ML) algorithms to handle tasks requiring human thinking. This gives companies better insights and helps predict future trends. In healthcare, tools like IBM Watsonx quickly analyze medical scans, assisting doctors in making better diagnoses and treatment plans.
What are some enterprise automation use cases?
Now that you understand the different types of enterprise automation, let’s move on to some real-world use cases. These examples will help you see how automation can be applied across various industries in an enterprise context.
Let’s take a closer look at some enterprise automation use cases:
Customer service automation
Enterprises can use automation to respond faster and better to customer needs. Smart systems and chatbots answer basic questions at any time of day. Take Vodafone, for example. They use their automated system, Tobi, to handle billing questions and common problems. This helps them serve more customers at once while their staff handles more complex issues. The result is happier customers and lower costs for the business.
Supply chain management automation
Supply chain automation improves ordering, storage, and delivery. Companies like Amazon use it to run their warehouses and plan delivery routes. These systems monitor product levels and collaborate with suppliers based on current needs. This helps get products to customers faster and keeps the right amount of stock on hand. Enterprises can save money and can track their supplies more clearly when they invest in supply chain digital transformation.
Financial process automation
Financial automation handles regular financial tasks like bills, payroll, and expenses. Enterprises use systems like SAP to manage payments coming in and going out. When they process bills automatically, they pay vendors faster and make fewer mistakes. This makes money flow better through the business and keeps things accurate. It also helps enterprises follow financial governance, risk, and compliance regulations.
HR process automation
HR automation makes hiring and managing staff easier. Companies use smart HR systems to look through job applications and find the best people. Google, for example, uses automation to screen candidates and set up interviews. These systems also handle employee benefits and talent management. This frees HR teams to work on more important things, like keeping employees happy and helping them grow.
Marketing process automation
Marketing automation helps run campaigns across many channels at once. Tools like HubSpot help send emails, post on social media, and stay in touch with customers. Enterprises use it to suggest products based on what customers bought before. This gets better results from marketing efforts while saving time. It also ensures all marketing messages work together and reach the right people.
How to build an enterprise automation strategy

Understanding how to build an enterprise automation strategy is crucial for enterprises to drive efficiency, scalability, and innovation.
A well-planned strategy enables businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making by leveraging real-time data. It also helps align automation initiatives with business goals, ensuring a competitive edge in evolving markets.
Let’s take a look at how to build an enterprise-level automation strategy:
Review your goals
Start by examining your company’s digital transformation goals. Ensure your automation plans match these priorities, whether cutting costs or serving customers better. Look for places where ideas get stuck or mistakes happen often, and set clear targets you can measure. This helps you focus on automation that will make the biggest difference to the whole enterprise.
Setting goals helps teams see how they’re doing. Use simple charts to show progress and post the results so everyone can see them. This gets people excited about the changes and helps them understand how their work matters to the bigger plan.
Develop an implementation plan
Create a clear plan for implementing automation—list which tasks you’ll automate first and when you’ll do each step. Plan for testing, rollout, and training your team. Start small and grow gradually to avoid disrupting digital workflows. This approach lets you fix problems early and adjust your plans as needed, helping automation work better in the long term.
Run small tests with a few trusted users before big rollouts. Pick workers who aren’t afraid to tell you what’s wrong. Let them try the new tools and tell you what needs to change. Then, fix those issues before more people start using the system.
Obtain stakeholder support
Get support from key people in your company before starting automation. Leaders and team heads need to see how it will help the business. Show them real numbers about savings and better results. Share examples of where it’s worked before. When everyone agrees on the plan, you’ll get the resources you need and face fewer problems later.
Build a team of champions across different departments and train them well in the new systems. These helpers can teach others and fix small problems quickly. They also help spread the good news about how the changes improve work processes.
Invest in valuable automation
Choose automation that gives you the best return on your money. Pick systems that can grow with your business and adapt to new needs. Look for tools that use smart office technology to spot trends and make better choices. Compare costs and benefits carefully. This helps you spend money on automation that brings the most value to your business.
Look for tools that can teach themselves and get better over time. Systems that learn from their own data often work better than basic ones. They might cost more initially, but they save money by fixing their mistakes and finding better working practices.
Integrate with existing systems
Make sure new automation works well with your current systems. Your tools need to connect with existing software and databases. Use connection tools to link new and old systems smoothly. Technology integration information flows across your company without extra work. When systems work together well, you get better insights and fewer problems.
Set up a simple way for workers to report problems with the system. Make it easy for them to tell you when something isn’t working right. Quick fixes keep small issues from growing into big ones that could stop work from progressing.
Evaluate success
Check how well your automation is working regularly. Track important numbers like time saved and fewer errors. Ask your team how the systems are working for them. Look for new places to use automation or fix parts that aren’t working well. Regular checks help you improve your automation and keep it valuable for your business.
Turn your findings into a report that shows wins and areas to fix. Share these results in team meetings every month. Look at how other companies score with similar tools. This helps you highlight new ways of improving and shows stakeholders your progress. When employees see results, they’re more likely to suggest new ideas for automation.
How to choose enterprise automation software
Enterprises should choose automation tools that fit their needs. First, list the big tasks you want to automate, like supply chain logistics or financial reporting. Then, set clear goals to measure whether the tools are working well.
Ensure the enterprise automation software can grow with your company and handle more work as you grow. The new tools must integrate with your current systems, so all your company data stays correct across teams. Look for strong safety features that keep your information safe.
Check if the software is fit for purpose and reputable in helping enterprises. It should offer special support for large firms and have positive testimonials.
Think about all the costs—not just buying the software but also setting it up and running it. This helps you pick tools that will be worth the money for years to come.
Transform your business with enterprise automation
Enterprises are changing how they work through automation. Leading firms like Siemens now automate production monitoring systems, which helps catch problems early and keeps equipment running longer. DHL even uses smart warehouse systems to handle orders faster, making customers more satisfied with quicker deliveries.
Finance teams use auditing tools to find mistakes and follow best practices. When HR departments use automation for hiring and paying workers, they can focus more on helping the business grow. Enterprise automation gives leaders real facts to make smarter choices quicker.
Enterprises that use automation will stay ahead of the competition and can better handle new market changes. They will keep improving their processes, helping them remain competitive in the face of adversity.
People Also Ask
-
What are the differences between RPA and enterprise automation?RPA is a small part of enterprise automation that copies human tasks like filling forms or moving data between programs. Enterprise automation is much bigger. It changes how whole companies operate by connecting all parts of the business. It makes entire processes run on their own, from start to finish.
-
What is enterprise automation software?Enterprise automation software helps big companies run tasks independently. These tools connect different departments and handle complex jobs without needing people to supervise them. They can run many business tasks simultaneously, like tracking orders, paying bills, and helping customers.