By the end of this article, you’ll be an expert as you understand the role of digital transformation in manufacturing. Gain the confidence to choose new technologies and implement them for higher productivity and operational efficiency to beat competitors. You’ll be designing your future using digital transformation before you know it.
What is digital transformation in manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing involves adopting new digital technologies to enhance the entire manufacturing process. Organizations can optimize these processes wholesale or slowly over time. Software is one of the key drivers.
Critical areas include improving operations, customer experiences, and leveraging big data. Examples include robotic process automation (RPA), mobile apps for frontline management, 3D printing, ERP systems, and automating knowledge work.
What are some examples of digital transformation in manufacturing?
These three examples show how other manufacturing enterprises have successfully implemented digital transformations. Consider the lessons at the end of each one to see what you could apply to your organization’s transformation.
We will begin with Siemens and its innovative digital twin transformation.
Siemens: Digital twin technology
Siemens needed to solve the problem of inefficiency, unplanned downtime, and lengthy development cycles in their manufacturing processes as part of a large-scale business process transformation.
To address these challenges, Siemens implemented digital twin technology, creating virtual replicas of physical assets. These digital twins allowed Siemens to simulate, predict, and optimize the performance of their machinery and production systems in real-time.
Using digital twin technology, Siemens could monitor equipment health, predict maintenance needs, and test new processes and designs without physical trials.
This virtual modeling enabled them to identify potential issues before they occurred, significantly reducing unexpected downtime.
It also allowed for more efficient and effective product development by simulating various scenarios and outcomes, leading to optimized production processes and higher-quality products.
The positive outcomes of using digital twin technology at Siemens were substantial. They achieved a reduction in time-to-market for new products.
Additionally, the technology improved product quality and consistency, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced overall operational efficiency.
What can you learn from this example?
We can learn several lessons from Siemens’ manufacturing transformation, including:
- Digital twins are powerful in the design stage: Based on Siemens’ example, we can see the value of Implementing digital twins for predictive maintenance to minimize downtime.
- Real-time simulations are useful in manufacturing: Siemens’ use of real-time simulations optimizes processes and improves product quality.
- Virtual models can improve time to market: How Siemens used virtual models helped them accelerate their development cycles for new products and reduce time-to-market, saving time and money.
General Electric: Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The company sought a solution to enhance real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance across its vast machinery and equipment.
GE implemented the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) by connecting machines, sensors, and systems to a centralized platform.
This platform collected and analyzed real-time data as part of their data transformation, enabling predictive analytics and maintenance. By integrating IIoT, GE could continuously monitor the health of its equipment, predict failures before they occur, and optimize overall operational efficiency.
The implementation of IIoT led to significant improvements for GE. They reduced unplanned downtime, as predictive maintenance allowed timely interventions before equipment failures.
Operational efficiency improved as real-time data provided actionable insights for process optimization. Additionally, the data-driven approach helped GE streamline maintenance schedules, reduce costs, and improve asset utilization.
What can you learn from this example?
We can learn several lessons from GE’s manufacturing transformation, including:
- Real-time monitoring is essential: Implement real-time monitoring to gain immediate insights into equipment performance and health.
- Predictive maintenance ensures quality operations: Utilize predictive analytics to foresee and prevent equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Operational optimization guarantees high-level functionality: Leverage data analytics to optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and drive cost savings.
Bosch: Advanced robotics and automation
Bosch faced challenges in manufacturing related to precision, scalability, and efficiency. The company sought to address these issues by leveraging advanced robotics and automation technologies to streamline its production processes.
Bosch decided to integrate advanced robotics and automation systems into many different stages of their manufacturing operations.
They focused these innovative technologies on assembly, packaging, and quality control. The outcome was precise and efficient execution of tasks employees previously completed at higher cost and time.
By adopting advanced robotics and automation, Bosch achieved several significant benefits. These included increased productivity due to faster and more accurate production processes and improved product quality through consistent and standardized operations.
Additionally, the company experienced reductions in labor costs and human error, leading to overall cost savings and enhanced competitiveness in the market.
What can you learn from this example?
We can learn several lessons from Bosch’s manufacturing transformation, including:
- Customization and scalability are key to manufacturing success: Invest in robotics and automation solutions that you can tailor to specific manufacturing needs and easily scale up or down as needed.
- Employee training and integration support staff to succeed: Ensure proper training and integration of robotics with the existing workforce to maximize efficiency and productivity gains.
- Continuous improvement ensures consistency: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement to identify new automation opportunities and optimize manufacturing processes over time.
These examples highlight the diverse technologies driving digital transformation in manufacturing. From digital twins and IIoT to advanced robotics, these technologies significantly benefit efficiency, productivity, and cost savings.
Other companies can learn from these successes by adopting similar technologies tailored to their needs and challenges, ensuring a competitive edge in the evolving manufacturing landscape.
What are the benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing?
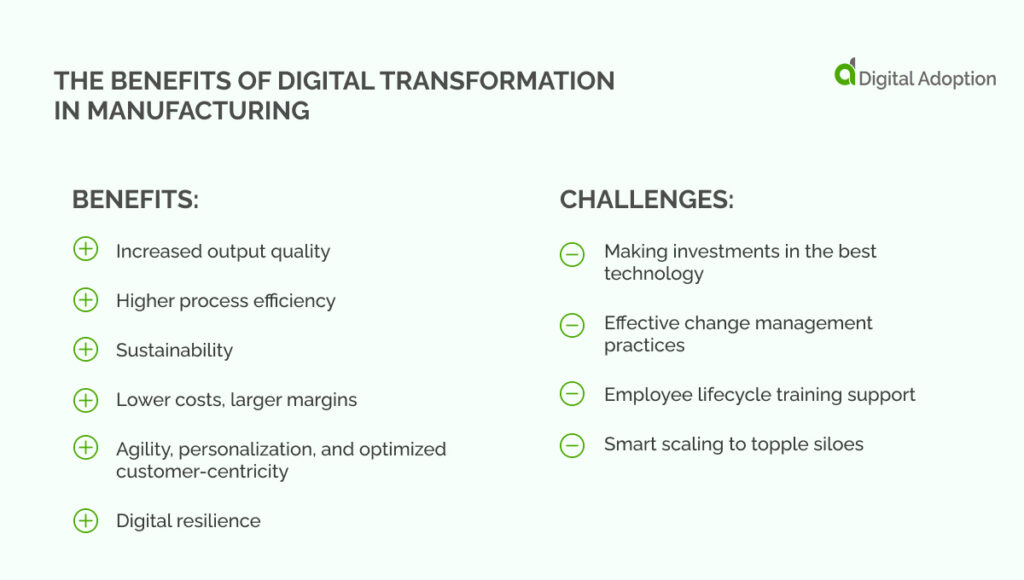
Planning and implementing a digital transformation in your manufacturing enterprise has many benefits. It can increase output quality, process efficiency, and sustainability. Let’s begin with the increased output quality.
Increased output quality
Enhanced sensors, automated testing, and quality control integrated throughout the manufacturing process can help manufacturers produce higher-quality products.
This integration allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments, ensuring that any deviations are promptly corrected. By applying the Pareto principle, manufacturers can focus on the most significant issues, leading to substantial improvements.
Additionally, leveraging machine learning allows for continuous learning and optimization, identifying patterns and solutions that might not be evident to human operators.
This holistic approach reduces errors and enhances overall process efficiency and product quality, leading to greater customer satisfaction and reduced waste.
Higher process efficiency
Hyperautomation significantly boosts process efficiencies by minimizing human errors in manufacturing. It integrates artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance and support human activities, leading to more accurate and consistent outputs.
This technology streamlines workflows, enabling faster production cycles and reducing the need for manual interventions.
A hyper-automation platform can support the automation of repetitive tasks, allowing workers to focus on more strategic and complex tasks, further driving efficiency.
The combination of AI and ML provides predictive analytics, optimizes processes, and preemptively addresses potential issues, resulting in a more agile and responsive manufacturing environment.
Sustainability
As consumers increasingly demand eco-positive practices, technology evolves to meet these needs. AI-driven and monitored machinery enhances efficiency, significantly reducing energy consumption.
Efficient machinery also uses fewer materials, leading to a positive environmental impact. These technological advancements support sustainable manufacturing practices, aligning with consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
The implementation of eco-positive technologies not only reduces the carbon footprint but also promotes resource conservation.
This approach saves costs. It also shows that manufacturers are responsible. It also shows that they are forward-thinking. It makes them leaders in sustainability. This benefit gives them a market edge.
Lower costs, larger margins
Digital transformation significantly reduces manufacturing costs. The Industrial Internet of Things enables monitoring in real-time. It also allows the diagnosis and fixing of issues in businesses. It happens before they cause major disruptions and minimizes manufacturing equipment downtime.
Connected machinery helps with predictive maintenance. It schedules repairs during non-peak times to avoid losses. This proactive approach ensures continuous production. It boosts productivity and profits.
IoT also cuts waste and operating costs by optimizing resource use. As a result, manufacturers have higher margins and a stronger position against rivals. These efficiencies drive business growth and make businesses resilient. The industrial landscape is changing fast.
Agility, personalization, and optimized customer-centricity
One of the biggest challenges for manufacturers is making custom products. They must do this at a large scale.
Customers are willing to pay more for personalized products. But they expect the same speed and responsiveness as generic ones. Agile manufacturing is key. It helps maintain a customer focus.
Makers can understand and use customization parameters. They do this by using data-driven production machinery. This action directly affects production lines.
This agility allows quick adjustments. It helps you respond to customer demands. It ensures your customers stay satisfied and loyal to your brand.
Using advanced tech, manufacturers can offer tailored products efficiently. This meets the growing demand for personalization, and it doesn’t sacrifice speed or quality.
Digital resilience
You need digital resilience. It’s essential for thriving in tough circumstances in which new tech emerges daily. In addition to operational resilience, digital adaptability is crucial for long-term success.
To keep up, manufacturers must expect and respond to digital challenges. Digital technologies improve resilience. They do this by enabling flexible automation, remote operations, and a connected supply chain through cloud infrastructure.
These technologies let manufacturers adapt quickly. They also help them keep continuity and use resources well.
Manufacturers can use digital tools to ensure strong, flexible operations. They can withstand and thrive amidst disruptions. This approach ensures they have sustained growth and competitiveness in the market.
What are the challenges of digital transformation in manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing is always changing. It presents unique challenges with each new advance. Manufacturers today must keep up with rapid changes. They must also help the business grow. This action requires overcoming many key challenges. They come up when implementing new digital tech.
Making investments in the best technology
A big challenge in manufacturing is investing in the right tech. Innovation and staying ahead of the competition are crucial. But, just using new tools is not enough.
The success of a company depends on choosing tools. The tools must work well. They must be able to change and grow. The tools must grow with the business. They must stay useful as the company evolves. Picking the wrong technology can waste resources. It can also cause missed chances to improve and grow.
Effective change management practices
Managing change is hard. It’s a big hurdle for companies that pursue digital transformation in manufacturing, which is moving toward automation. Companies must consider how their processes will change with the new technology.
Traditional manufacturing processes rely on human interaction. They may not be easily or quickly adaptable to automation. However, there is hope for those willing to re-examine their current systems.
Hiring a consultant for digital transformation can help with this. They help companies understand their needs for new systems. They do this before using them. Change is inevitable. However, you need careful planning and understanding for a smooth change.
Employee lifecycle training support
A big challenge in manufacturing is making an effective plan for digital transformation. The plan involves user onboarding and training employees on new tools. However, doing so is key to supporting employees. It will help them throughout their lives and improve their ability to survive change.
This action is often part of an organization’s broader digital adoption plan. New technologies often require employees to learn new skills and ways of working. This makes widespread adoption hard.
For example, new software or robots may need training. This step ensures all workers can use them well. Some companies have strong programs to aid this change. Others may struggle. This can lead to slower adoption and implementation.
Training is key and drives digital adoption. It lets manufacturers get a higher return on investment (ROI) from their technology and ensures that employees can use new tools well. This skill is essential and unlocks the potential of digital transformation.
Smart scaling to topple siloes
Silos in organizations are a big challenge. They hurt digital manufacturing. Digital transformations often fail. They can’t scale from departments to the whole company.
This failure is often due to the lack of a shared culture and shared business goals. These are lacking across the company. Digital transformation will likely falter, and teams can’t work together.
In summary, the journey to digital transformation in manufacturing is hard and full of challenges. By navigating these challenges carefully, manufacturers can fully use digital transformation. This will make us faster, and it will also help us make more and grow.
Design your future with digital transformation
Embrace digital transformation to revolutionize your manufacturing processes. It will lead to a future of better efficiency, quality, and innovation.
AI, IoT, and robotics can streamline operations, saving money and meeting the growing demand for custom products.
This strategic adoption boosts productivity and positions your business as an industry leader.
Seize the chance. It will help you stay competitive and sustainable, especially in a changing market landscape.









