Technology is a core asset for business success in the digital era. Alongside a clear vision and dedicated talent, the right tech mix can drive lasting innovation.
However, a good technology adoption strategy isn’t just about purchasing. It needs active management at every phase. Without this, tech stacks can become bloated and hurt performance.
Application performance management (APM) helps keep apps configured and efficient, keeping productivity flowing. Artificial intelligence (AI) driven transformation enhances APM even further, saving organizations time and resources by augmenting human-led tasks.
This article dives into why APM matters, its functions, and common enterprise use cases.
- What is application performance management?
- How does application performance management work?
- Key metrics tracked by application performance management
- APM vs. observability: What’s the difference?
- Use cases for application performance management
- Common features of application performance management tools
- APM in the context of digital transformation
- Choosing the right APM solution
- APM and the path to transformation
What is application performance management?
Application Performance Management (APM) is the process of monitoring and optimizing software applications to ensure they perform well, remain available, and deliver a good user experience. APM tools analyze data to detect and resolve issues, helping applications meet business requirements.
APM uses a proactive approach, predicting potential issues and fixing them before users are affected. By providing detailed insights, APM identifies the root causes of performance problems.
With AI, APM tools can self-learn, monitor applications, take corrective actions, and adjust automatically across the application’s lifecycle. Modern APM also includes applied observability, which uses AI for advanced data collection and analysis, making it ideal for businesses managing on-premises and cloud-based systems.
Why is application performance management important?
Many customer interactions now occur through digital touchpoints like websites, chatbots, and payment portals.
Keeping these touch-points optimized means firms can deliver swift user experiences and ensure customer needs are satisfied.
APM helps to achieve this. It’s also key for preventing performance issues before they occur, which is important for mitigating repairs and maintenance costs.
Let’s get into a few reasons why APM is important below:
Customer satisfaction
Keeping your customers happy is really important. APM closely watches how your essential apps work, ensuring users have a smooth, easy experience when using your website or apps. This helps you keep your current customers and get new ones, which is vital for repeat business.
Rapid diagnosis
When your apps go wrong, you need to fix it fast. APM tools let you quickly find and solve problems before they affect your customers. With real-time monitoring and smart data, APM helps you resolve issues quickly.
Reduced operating costs
Running a business costs a lot, but APM can save you money. APM reduces the need for expensive hardware upgrades or extra cloud storage by making your apps run better. Since it helps fix problems faster, your team spends less time troubleshooting and can focus on more important things.
Effective product development
Developing apps is an ongoing process, and APM can make it much easier. APM gives your development team detailed performance data and insights so they can quickly find ways to improve your apps. This helps them make your products better and more reliable, which keeps users happy.
How does application performance management work?
Application performance management (APM) helps ensure applications are healthy and reliable. It uses tools to monitor performance, measure digital transformation KPIs, and improve the user experience.
Here’s a closer look at how APM works:
Instrumentation and agents
APM tools use agents to collect data on applications. These small programs track performance metrics, like response times and error rates, sending this data to the APM system to catch problems early.
Metrics and alerts
Metrics measure how well an application runs. Common metrics include uptime and load times. APM tools monitor these metrics and send alerts when they fall below acceptable levels, allowing teams to fix issues before users notice.
Traces, logs, and analyses
APM gathers traces and logs to record application activities. Traces show requests moving through the app, while logs capture specific events. Analyzing this data helps teams identify bottlenecks or errors.
Synthetic monitoring
Synthetic monitoring simulates user actions in the application. APM tools run tests to find performance issues before real users encounter them. This proactive approach helps maintain a smooth user experience.
Real user monitoring
Real user monitoring tracks actual user interactions. It collects data on how users engage with the application, including load times. This method provides insights for teams to make improvements.
Key metrics tracked by application performance management
Now that we understand how APM works, several key APM metrics ensure applications perform as intended.
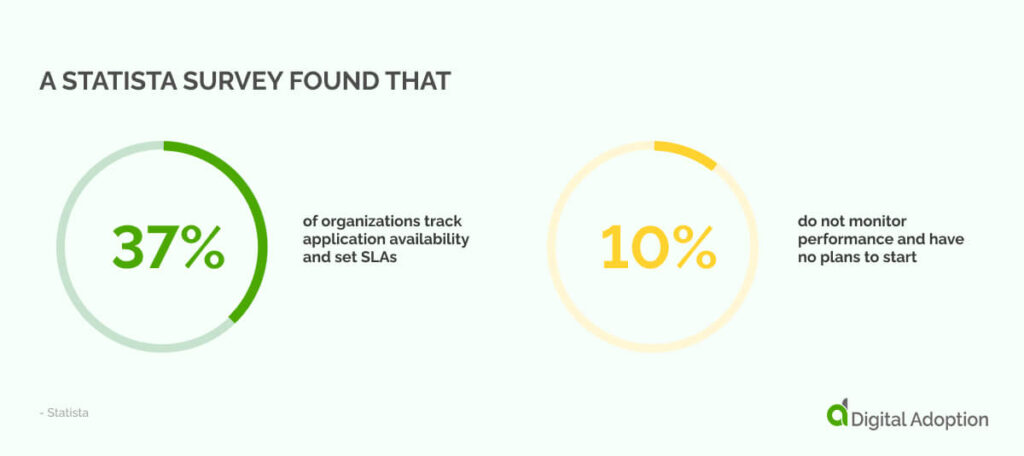
As such, it’s wise to have a basic understanding of the primary metrics monitored in APM:
Central processing unit (CPU) usage
CPU usage measures the server’s processing power. High CPU usage can slow down applications and affect user experience. Monitoring this helps identify performance issues early.
Response times
Response times track how quickly an application reacts to user requests. Maintaining fast response times is essential for a good UX. APM tools assess this metric to ensure speedy responses.
Error rates
Error rates indicate how often errors occur in an application. A high error rate can signal problems that need fixing. By identifying these potential issues, teams can improve application reliability.
Uptime
Uptime measures the amount of time an application is available and working. High uptime is essential for keeping users happy. APM tools ensure applications remain accessible without interruptions.
Transaction tracing
Transaction tracing follows user actions within the application. This helps teams understand how transactions flow and pinpoint any possible slowdowns or errors.
Requests
Requests track the volume of actions users take in the application. Monitoring requests help understand user activity and ensure the application can handle traffic effectively.
APM vs. observability: What’s the difference?
APM and observability are aimed at software monitoring but do different things.
APM tracks application performance, identifies problems, and ensures everything runs well. It is used when you need to monitor specific metrics, such as response times and error rates.
Use cases for APM
APM works best in areas where application performance matters. For example, it is great for eCommerce websites needing quick load times. APM tools track how fast a site responds to users, helping to fix slowdowns quickly.
When observability is more effective
Aggregating various data types, such as logs, metrics, and traces, improves observability for complex systems with many parts. If an app feature fails, observability helps understand why. It provides insights from multiple data sources, which is key for diagnosing problems in systems with many services.
Combining APM and observability
Combining APM and observability creates a stronger monitoring strategy. APM provides detailed performance insights, while observability offers a birds-eye view of the entire enterprise application and network.
Introducing AI and machine learning (ML) can enhance both solutions. AI can collect and analyze data, while ML cleverly finds patterns and predicts issues.
This added layer minimizes application downtime and improves reliability. It ensures that applications function well and can adapt throughout their lifecycle.
Use cases for application performance management
Increasing investments in digital tools and applications will require more reliable APM.
Let’s look at some use cases where APM is helping businesses:
Real user monitoring
Real user monitoring checks how real users experience an application. It tracks issues like slow loading times or errors. This helps engineering teams understand what users face and make improvements.
User-defined transaction profiling
User-defined transaction profiling allows users to customize their monitoring. They can focus on specific actions that are important to them, ensuring that essential processes are prioritized.
Infrastructure monitoring
Digital infrastructure monitoring keeps an eye on hardware and cloud components. It ensures that servers and networks run well. This helps catch problems before they affect users.
SLA monitoring
SLA monitoring checks if service level agreements (SLAs) are met. SLAs are promises about how well a service should perform. APM tools help companies track if they fulfill these promises to customers.
Common features of application performance management tools
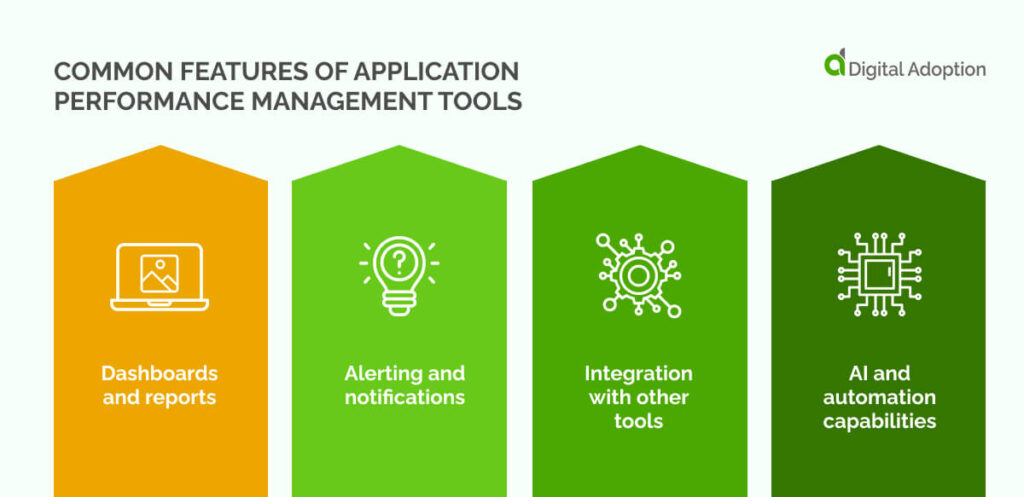
APM software boasts many features that help businesses sustain application performance.
Here are some common functions available with most APM solutions:
Dashboards and reports
APM tools provide dashboards and reports that show performance data. These visuals help teams understand how applications perform and spot issues quickly.
Alerting and notifications
APM tools send automatic alerts when problems occur. If something goes wrong, the team is notified right away. AI can make alerts smarter by predicting issues based on past data. This allows teams to fix problems before they affect users.
Integration with other tools
Most APM tools work well with other software, which means teams can keep using their favorite tools without changes. AI helps with these integrations by learning user habits, making work easier and faster.
AI and automation capabilities
Many APM tools use AI for insights and automation. AI analyzes large data sets to find patterns and predict future problems. Automation lets teams respond to alerts quickly, freeing up time for more important tasks.
APM in the context of digital transformation
In digital transformation, effective APM builds a solid base for business growth.
When software runs well, less time and fewer resources are needed to handle downtime and technical issues. This shift frees up focus for projects that drive growth and add value.
Let’s explore areas where it speeds up progress to see how APM boosts transformation:
Enabling agile development
APM tools generate loads of data about how applications perform in real time. They collect information on response times and user actions. This data helps developers find problems in the noise, allowing them to fix issues and add new features faster.
Enhancing IT operations
APM automates IT operations by monitoring systems and tracking key metrics, like CPU usage. AI identifies unusual patterns and raises the alarm with IT directors before problems affect users.
Ensuring cloud migration success
During cloud migrations, APM monitors both old and new cloud-based applications. AI’s predictive abilities flag low performance, ensuring smooth transitions to cloud environments and allowing adjustments as needed.
Supporting data-driven strategies
APM collects extensive performance data that AI then analyzes to find patterns in user behavior. This analysis reveals which features are popular, allowing teams to adjust and fine-tune user experiences based on insights gleaned.
AI and AIOps integration
APM tools increasingly integrate AI to enhance data analysis. Machine learning helps spot early warning signs and gives insights about potential future issues. This proactive stance enables teams to address problems before they disrupt services.
Choosing the right APM solution
Knowing what APM tool to invest in is essential. Without thorough research, companies risk problems with scalability, integration, and vendor lock-in with subpar solutions.
Here’s what to consider for the best choice.
Features
Look for core APM features like real-time monitoring, alerts, and user tracking to catch issues as they happen.
Advanced tools with AI can preemptively detect patterns or performance issues. Consider investing in tools that offer custom dashboards and reports so teams can quickly access relevant data without searching.
Cost requirements
APM pricing varies widely. In addition to initial costs, factor in expenses for add-ons, extra data, or advanced features.
Some tools offer tiered plans based on data or users, so compare costs against the features provided. Make sure it meets your needs without going over budget.
Vendor support
Vendor support is non-negotiable in case of technical issues. Some APM providers offer round-the-clock support or even dedicated account managers, which is helpful during critical events.
When quick fixes are essential, verify if the vendor provides specialized support during updates or heavy loads. The benefits of vendor management include decreased costs and more opportunities.
Integration Capabilities
Check that the APM tool integrates well with your existing systems.
Tools with built-in APIs or pre-configured integrations make it easier to connect data across platforms. A tool that integrates into your workflow with little to no issues saves time and reduces data silos.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
Choose an APM tool that can grow with your business. Scalable tools can handle increased data loads as your operations expand. Look for solutions with regular updates to stay compatible with the latest technology so your APM can adapt to your needs.
APM and the path to transformation
One thing is clear—digital adoption isn’t slowing anytime soon.
All this influx of new tech means businesses must find ways to maintain the quality and integrity of their app investments.
A revolving door of solutions can make choosing the right solution feel overwhelming. It may mean high software turnover, and users must quickly learn, understand, and adapt to new programs almost overnight.
Through trial and error, firms seek assurance that they can manage their applications effectively, no matter how new or quickly adopted.
The road to transformation is unpredictable, and there is no one-size-fits-all blueprint. Long-term success requires taking risks and venturing into unknown territory.
Providing your teams with the right tools can ensure the reliability of these ventures. APM can be the guiding force in making this happen.









