Shifting marking trends, customer expectations, and innovative technology ensure the business world is constantly in flux.
With change the only constant, today’s organizations understand that embracing digital transformation is the key to sustaining long-term success.
Embracing technology has become a key characteristic of these transformations. Businesses industry-wide have long relied on the latest tech solutions to expedite core processes. Without it, companies will lack the means to adapt and outpace competitors.
Innovations in AI are the latest tech trend, helping businesses capture value. Companies use AI systems that mimic human intelligence to augment various functions.
AI in business can be part of a digital transformation initiative, wherein AI adoption is simply a component of the wider strategy.
This article will explore AI in business, its involvement, and how it impacts organizations sector-wide. We’ll also provide examples of AI in action, taking a look at the top applications leading the charge.
What is AI in business?
AI in business enhances core business processes and functions by strategically adopting and implementing AI-powered technologies.
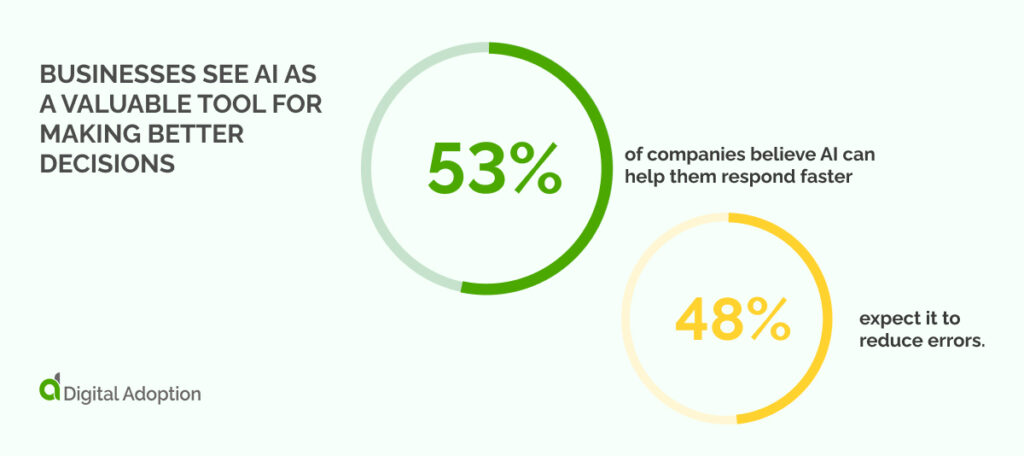
These systems use data as fuel, trained to perform sophisticated tasks, detect hidden patterns, and inform decision-making. They can also self-improve over time by continuously learning from input data.
Machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), computer vision (CV), and natural language processing (NLP) are distinct subsets of AI that empower most modern solutions.
ML is the discipline of teaching machines to recognize patterns within data. By training algorithms and statistical models, ML enables computers to produce independent outputs based on the data they process.
Deep learning (DL) is a sophisticated form of ML that goes a step further. It employs an interconnected network of algorithms often likened to the human brain’s neural network. These artificial nodes learn and adapt from data, improving DL solutions for more nuanced tasks like image recognition and natural language processing.
RPA and computer vision are upending traditional production processes in the manufacturing sector. In customer service, NLU enables intuitive chatbots and virtual assistance to enhance businesses’ experiences.
These are just some examples of the dedicated technologies underpinning today’s industry-leading AI solutions.
How is AI impacting businesses?
The AI market’s value exceeded $184 billion U.S. in 2024, a $50 billion increase compared to the previous year. Forecasts indicate further growth to surpass $826 billion by 2030.
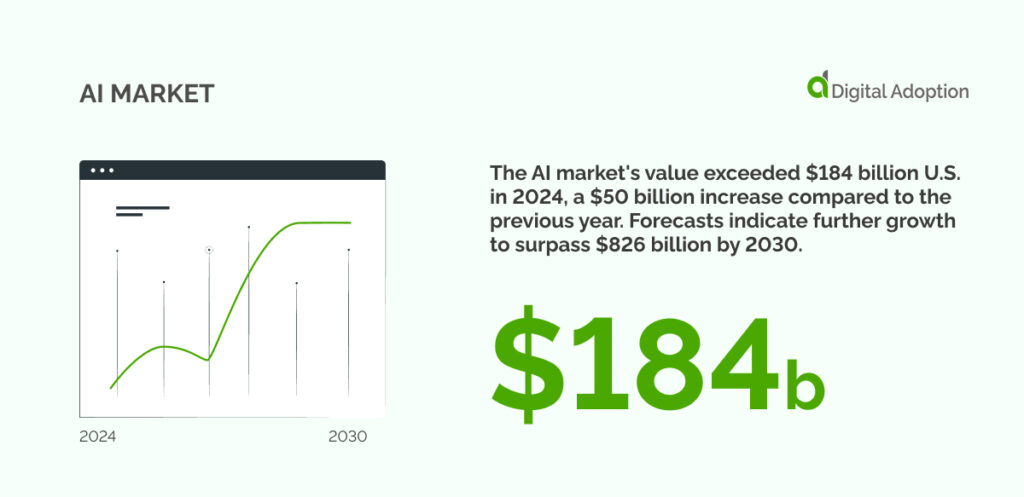
Those unafraid to assume first-mover status today will be better positioned to sustain success long into the future. This understanding is universal, and its impact has been quickly embraced across business spheres. So, how is AI being used in business today?
Let’s explore some of the ramifications felt following the onset of AI.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity relies on watertight system protocols and mechanisms to protect against external threats. CISOs, CSOs, and other human employees typically assume these day-to-day responsibilities. AI can augment key operational tasks traditionally handled by employees.
ML algorithms can synthesize recommended outputs and actions in response to threats they detect. These models scan for anomalous instances and mitigate attacks by learning from input data. Incident response mechanisms also become automated through AI, ensuring that all fronts are guarded.
Security is the territory of CISOs and CSOs. Because of this, they must understand the material risks associated with AI and the need for responsible implementation more than most.
IT operations
Operational reliance on technology makes AI perfectly suited to augment traditional IT processes. IT professionals don’t excel at monitoring and maintenance. The cognitive ability required to forecast system disruptions and downtime may be beyond our human reach.
Predictive maintenance is a notable AI capability that delivers efficiency across IT operations. This predictive power allows for improved response times and remedial action. AI can also use operational data to make analytical insights. This unveils an intricate picture of system performance, at-risk areas, and other key statistics.
With responsible implementation, IT professionals can leverage AI to innovate operations and develop a more reliable and efficient IT infrastructure.
Marketing and sales
Big businesses previously did not have access to large amounts of customer information. Insights into purchasing history, product preferences, or demographic information like age, gender, and location were analog. Today, siloed data is no longer the norm, providing marketing and sales teams with a mountain of customer data to leverage.
AI takes all this data and repurposes it for various marketing and sales functions. It can segment customer audiences, creating tailored campaigns and unique product offerings that cater to diverse demographics. Personalized customer interactions at different touch points throughout the sales lifecycle fuel engagement and brand loyalty.
Ultimately, AI drives sales growth and improves marketing efficiency,
allowing businesses to connect with their customers in more meaningful ways.
Manufacturing and production
Much like IT operations, predictive maintenance facilitated AI overhauls of manufacturing and production processes. AI gleans data from physical machines and robots in manufacturing settings.
It can analyze prior downtimes, recorded incidents, and faults to predict when maintenance is needed. This minimizes downtime and extends equipment lifespan. Real-time AI monitoring enhances efficiency and ensures a high-quality control standard in production.
For example, in retail production, AI can spot faults in pattern design and halt the production process to rectify the issue.
Healthcare
If done right, AI has the potential to usher in a new age of world-leading healthcare. As far as their medical expertise has got them, there are just some limits to healthcare professionals’ abilities.
For instance, in disease detection, AI can leverage patient data, medical history, and other key information (E.g., gender, age, allergies) to detect, diagnose, and prevent disease.
AI’s speed and accuracy can often outpace those of human healthcare professionals. This creates consistent and reliable results, allowing doctors to tailor patient care and treatment planning.
AI’s benefits for healthcare professionals span from enhancing operational processes to inventing life-saving products and services. This cuts expenditures, improves efficiency, and helps to advance progress in the life sciences.
Financial services
AI is kicking operations in various domains across the financial services sector into high gear. Money makes the world go round, so a failure to protect it may just bring it all down. Those in the financial industry know this all too well.
AI can augment cybersecurity infrastructure by detecting threats in real-time across internal systems, customer-facing platforms, and IoT networks. Traditional Fintech cybersecurity measures required constant oversight and optimization from programmers. AI ensures systems improve and self-iterate to adapt to evolving threats.
Elsewhere, AI-powered tools can perform algorithmic trading and provide up-to-date financial advice. Robo-advisors use AI to analyze market trends and customer data to tailor investment recommendations.
Implementing AI in finance requires an incremental and responsible approach. Curating the most dynamic solution will ensure asset protection and continuous improvement in operational security.
Human Resources
HR recruitment processes have historically been bogged down by manual processes that make finding talent a chore. Today, AI allows HR professionals to fast-track these essential processes through AI.
From candidate sourcing to onboarding, AI systems scan resumes, match candidates to job requirements, and streamline the hiring process. This efficiency allows HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives, nurture the workforce, and improve overall talent management.
AI’s impact on HR doesn’t stop at hiring. Advanced algorithms can analyze employee performance data, predict future talent needs, and identify areas for professional development. This data-driven approach helps HR departments proactively manage their workforce, ensuring employees are engaged and aligned with company goals.
AI Applications in Business
We’ve explored what AI in business is and how it’s making impacts sector-wide.
Now, let’s delve into some common use cases and application areas where AI is making strides.
Improved operational productivity and efficiency
Operational productivity underpins a successful business. If systems are siloed and processes are slow, business speed and productivity can be severely impacted. Artificial intelligence helps to fast-track operational productivity and efficiency by optimizing intricate workflows and automating redundant tasks.
ML algorithms learn from input data to identify patterns, inefficiencies, and potential security risks. From workflow management to cybersecurity needs and people processes, AI can augment capabilities across various operational domains.
For example, in manufacturing, AI systems provide predictive maintenance that ensures long-term operational agility. Data from factory machinery is analyzed to forecast future repairs and breakdowns, which mitigates downtime. In logistics, AI optimizes routing and inventory management, reducing costs and delivery times.
Ultimately, businesses that leverage AI can achieve higher accuracy, faster execution, and reduced operational costs.
Leveraging AI for industry-specific challenges
The mutable nature of AI technology means highly specific solutions can be developed to address various industry needs. AI is accelerating drug discovery, disease detection, and patient care in healthcare.
Leveraging large stores of medical data, AI can analyze molecular structures to identify potential drug candidates, significantly accelerating new medication development. It can use computer vision to scan medical images and detect diseases like cancer earlier, improving treatment outcomes. AI can also analyze patient data, such as geographical location, demographics, and environmental factors, to identify patterns and predict potential disease outbreaks, enabling proactive prevention measures.
Elsewhere, financial institutions are minimizing fraud through AI. These models flag suspicious activity by analyzing transaction patterns and monitoring systems in real-time. In agriculture, AI-driven drones monitor crop health and optimize irrigation.
Each industry benefits from AI’s ability to process and analyze specialized data, providing actionable insights that enhance decision-making, efficiency, and innovation.
Using Artificial intelligence for decision-making support
Decisions become a lot easier when backed up by extensive statistical analysis. This is how AI supports business decision-making. AI can make future predictions and key forecasting insights by using organizational data as fuel.
Decision-makers face immense pressure to make sound, data-driven choices that shape a company’s future. Errors can have far-reaching consequences. AI can enhance decision-making by uncovering hidden trends and patterns, increasing confidence and accuracy.
For instance, in finance, AI models predict market movements and investment risks, aiding in strategic planning. Retailers use AI to analyze consumer behavior, optimizing inventory and marketing strategies.
In healthcare, AI assists in patient diagnosis and treatment plans by analyzing medical records and research data. Incorporating AI into decision-making processes enables businesses to make informed, timely choices, reduce risks, and capitalize on opportunities with greater precision and assurance.
AI-driven quality control and assurance
Implementing AI can provide a new level of quality control and assurance for manufacturing and production processes. AI-powered visual inspection systems detect product defects with higher accuracy than human inspectors.
Machine learning algorithms learn from data to continuously improve inspection criteria and adapt to new product variations. For instance, AI systems in the automotive manufacturing sector meticulously examine components, reducing defects and enhancing vehicle safety.
In the aerospace industry, AI can analyze complex sensor data from aircraft components to predict failures before they occur, preventing catastrophic incidents and optimizing maintenance schedules.
By incorporating AI into quality control, businesses can enhance product reliability, reduce waste, and increase customer satisfaction, leading to a stronger brand.
Personalizing customer interactions with AI
Businesses with huge customer bases often rely on complex CRMs to better understand their customers. AI personalizes customer interactions and experiences by learning from individual preferences and behaviors. AI solutions can even integrate with legacy CRMs to leverage existing customer data and derive new value from it.
AI-driven chatbots provide instant customer support, answering questions and resolving issues 24/7. eCommerce platforms can use AI to recommend products tailored to each customer. This personalizes the shopping experience and increases sales opportunities by bringing customers closer to the products they like.
AI can also segment audiences and develop targeted marketing strategies, which helps turn idle leads into interested opportunities. Financial services employ AI to offer personalized financial advice and product recommendations. By reimagining customer service through the help of AI, businesses can strengthen B2C relationships, increase sales, and create returning customers.
Automating routine cognitive tasks
AI automates routine cognitive tasks, freeing employees to focus on higher-value activities. AI systems handle data entry, report generation, and customer inquiries with speed and accuracy.
In finance, AI processes transactions and detects anomalies, reducing the risk of errors and fraud. In customer service, AI chatbots provide immediate responses, improving user satisfaction.
AI also assists in drafting emails and summarizing documents, saving professionals time. Automating tasks unlocks greater efficiency, reduces operational costs, and frees employees to focus on strategic initiatives. This unleashes a wave of overall productivity and innovation.
AI as a creative collaborator
AI is a creative collaborator that generates content and ideas across various domains. In marketing, AI designs personalized ad campaigns and creates engaging content.
Artists use AI to compose music, produce visual art, and even write literature. In software development, AI assists in writing code and debugging. AI-driven design tools generate logos, layouts, and prototypes, accelerating the creative process.
AI integration in creative pursuits promotes innovation, accelerates time to market, and unlocks new artistic frontiers. AI collaboration fosters creativity, enabling teams to push the boundaries of what’s possible and deliver unique, impactful results.
AI for upskilling employees
AI tools enhance employee skills by providing real-time feedback and personalized learning experiences.
Language processing tools like Grammarly suggest improving grammar and stylistic changes and refining writing skills. AI-driven platforms offer coding assistance, helping developers learn new languages and techniques.
Training programs use AI to create adaptive learning paths, catering to individual needs and knowledge levels. For instance, AI-powered simulations provide hands-on practice in fields like healthcare and aviation.
Skill development programs with AI tools equip businesses to cultivate continuous employee growth, resulting in a more competent and adaptable workforce prepared for evolving industry demands.
AI applications for safer operations
AI enhances operational safety by monitoring environments and predicting risks. In construction, AI-powered drones and sensors assess site conditions, identifying potential hazards. AI systems in manufacturing monitor equipment for signs of wear, preventing accidents.
AI analyzes driver behavior and vehicle performance in transportation to ensure safe operations. It also aids in cybersecurity by detecting threats and vulnerabilities in real time. Implementing AI-driven safety measures helps businesses minimize risks, comply with regulations, and protect their workforce and assets.
Enhanced safety protocols prevent accidents and contribute to a culture of safety and reliability, strengthening overall operational integrity.
Boosting learning and training effectiveness with AI
AI revolutionizes learning and training by creating adaptive, personalized educational experiences.
AI-driven platforms assess individual learning styles and knowledge levels, tailoring content to meet specific needs. In corporate training, AI analyzes performance data to recommend targeted development programs.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies powered by AI provide immersive training simulations, enhancing hands-on learning. Medical professionals, for example, use AI-driven VR simulations for surgical training.
Training programs powered by AI boost learning effectiveness, ensure skills stay relevant, and embed a culture of continuous learning and adaptation within the workforce.
AI-driven innovations, products, and services
AI fuels innovation by enabling the development of new products and services.
Companies use AI to create advanced technologies, such as autonomous vehicles and smart home devices. In telecommunications, AI enhances communication platforms by improving voice and video quality.
Retailers leverage AI to develop personalized shopping experiences and custom products. AI also drives innovation in financial services with robo-advisors and automated trading systems.
AI empowers businesses to explore new markets, address evolving customer needs, and secure a lasting edge. AI-driven innovation accelerates growth, opening up opportunities for differentiation and sustained success in dynamic industries.
The future of AI in business
The future of AI in business holds immense promise and potential. As we look ahead, we can anticipate AI continuing to evolve, integrating even deeper into various sectors and offering more sophisticated solutions.
To prepare, businesses should invest in robust AI infrastructures and promote continuous learning. This involves upskilling employees to work alongside AI systems and ensuring ethical and responsible AI use. Strategic planning and collaboration with AI experts will be crucial in navigating privacy concerns. Companies should stay informed about AI advancements by subscribing to industry journals, participating in AI research forums, and attending technology conferences like the AI Summit and NeurIPS. They should be adaptable to new technologies by regularly updating their tech stacks, implementing pilot programs to test emerging AI solutions, and nurturing a culture of innovation.













