Artificial intelligence (AI) is a top driver of business transformation industry-wide.
AI adoption has seen businesses globally rush to capture its value to address a wide range of demands. From automating key processes to predicting patterns in data and strengthening decision-making, AI has firmly positioned itself as an essential business asset.
All this innovation isn’t without a silver lining. The risks AI poses are proving too consequential to ignore. AI can hallucinate, show bias, and provide false or misleading information. Threat actors can also manipulate data, tricking AI into breaching systems.
Luckily, AI governance sets the rules for AI’s design, use, and sustainability. Without it, risks go unchecked, especially in high-stakes industries like healthcare and finance.
This article explores AI governance, why it matters, key frameworks, principles, and compliance strategies.
What is AI governance?
AI governance is a set of policies, mechanisms, and frameworks that guide the responsible development, deployment, and use of AI systems. It establishes legal and regulatory requirements to ensure AI solutions are ethical, transparent, and compliant with laws.
These regulations include frameworks such as the EU AI Act and the US AI Initiative Act, which provide strict policies, standards, and practices for AI use.
AI governance also involves strategies for managing AI systems, focusing on operational reliability, data integrity, and system security. It addresses the ethical and moral implications of AI, such as setting up accountability in decision-making and ensuring that system outputs are explainable, fair, and transparent.
These practices ensure that AI algorithms are embedded with ethical principles. AI governance promotes strong management practices that amplify AI’s benefits and mitigate risks while considering its impact on broader society.
Why is AI governance important?
The importance of comprehensive AI governance cannot be overstated. As many benefits as AI presents, it also brings an equal number of potential risks. AI’s applicability spans many different verticals, casting a wide net of material risks that businesses must be aware of.
Huge amounts of data underpin AI, enabling it to learn, make decisions, and generate reliable outputs. This may include users’ personal information learned from inputs or critical business data taught during training. If AI systems are breached or trained inadequately, this sensitive data can become public or fall into the wrong hands.
If AI models are trained on incomplete or biased data, they can produce unfair or discriminatory results, reinforcing human prejudices. AI governance helps prevent this by setting strict rules on how AI works, how data is used and stored, and whether training data is clean, diverse, and accurate.
It also addresses the ethical side of AI, such as the risks of relying too much on AI without proper oversight. This can lead to job losses and more system errors. AI governance helps create clear rules, manage AI systems, and develop strategies for dealing with AI risks.
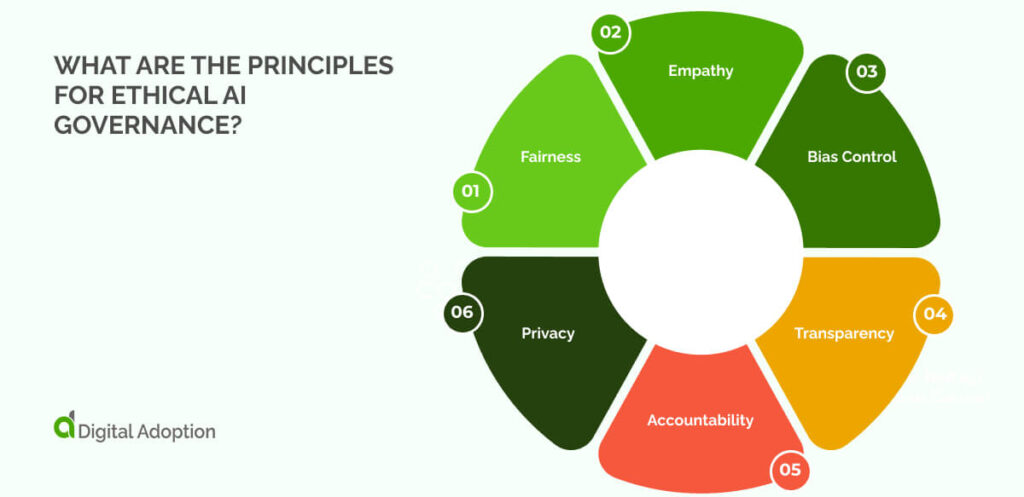
What are the principles for ethical AI governance?
Reliable AI governance requires assessing vendor reliability and data integrity while clearly defining the solution’s scope. It also means ensuring compliance and setting strict standards that comply with relevant laws and regulations.
With all this to consider, enterprises can adhere to some common principles to ensure solutions remain viable and ethical:
Fairness
Fairness means that AI systems treat everyone equally, without bias. It ensures that AI systems don’t favor any group based on gender, race, age, or other factors. This principle helps prevent AI from repeating harmful societal biases.
Empathy
Empathy ensures that AI decisions consider human needs and values. It guides AI to make choices that reflect respect for people and their well-being.
Bias Control
Bias control focuses on finding and removing unfair patterns in data or algorithms. It helps ensure AI results are fair, not biased or discriminatory.
Transparency
Transparency makes AI decisions clear and easy to understand. It also lets users track how AI arrives at its conclusions, promoting trust and accountability.
Accountability
Accountability ensures that the right people are responsible for AI’s actions. If AI causes harm, there are clear consequences for those involved.
Privacy
Privacy ensures that AI is protected when storing, using, or managing personal and sensitive data. It follows legal rules to keep information secure and private.
Examples of AI governance frameworks
AI risks can go unchecked without tangible guidance to help avoid them. The rush to explore AI’s upper limits and advance can lead to adopting solutions without the necessary oversight.
That’s why AI governance legal frameworks and regulations are in place. These ensure AI development and deployment are done correctly.
Let’s explore some of these below:
- EU AI Act: The EU AI Act, effective August 1, 2024, is the world’s first comprehensive AI regulation. It sets clear requirements for AI development and deployment and creates a uniform framework across the EU.
- National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Act of 2020: The 2020 National AI Initiative Act ensures U.S. leadership in AI research. The act promotes trustworthy AI systems, prepares the workforce for AI integration, and coordinates AI activities across civilian agencies.
- Executive Order 14110: Biden’s Executive Order 14110, signed on October 30, 2023, directs 50 federal entities to take 100 actions across eight policy areas to ensure safe, secure, and responsible AI development and use.
Who is responsible for enterprise AI governance?
Who is accountable when AI systems make mistakes that lead to real consequences? Figuring this out is negotiable for enterprises adopting AI in their operations.
Clear lines of responsibility need to be established, which means identifying the key players involved in ensuring enterprise AI governance.
Let’s explore who these key figures are:
- AI developers and engineers build and design AI systems. They must ensure that the technology functions as intended and is error-free.
- Data scientists handle AI’s data and ensure that it is accurate, complete, and free of biases that could affect the AI’s decisions.
- AI managers or governance teams oversee the whole AI process. They monitor and enforce rules, ensuring the AI meets legal, ethical, and safety standards.
- Legal and compliance officers ensure the AI meets regulatory standards, preventing legal issues related to privacy or security.
- Executives must take responsibility for AI’s impact and ensure it aligns with company goals and public expectations.
How are organizations deploying AI governance?
With the long-term impacts of AI still unknown, there’s ample room for today’s enterprises to make missteps with their investments. The rush to transform can lead to sporadic purchases that don’t fully consider long-term impacts.
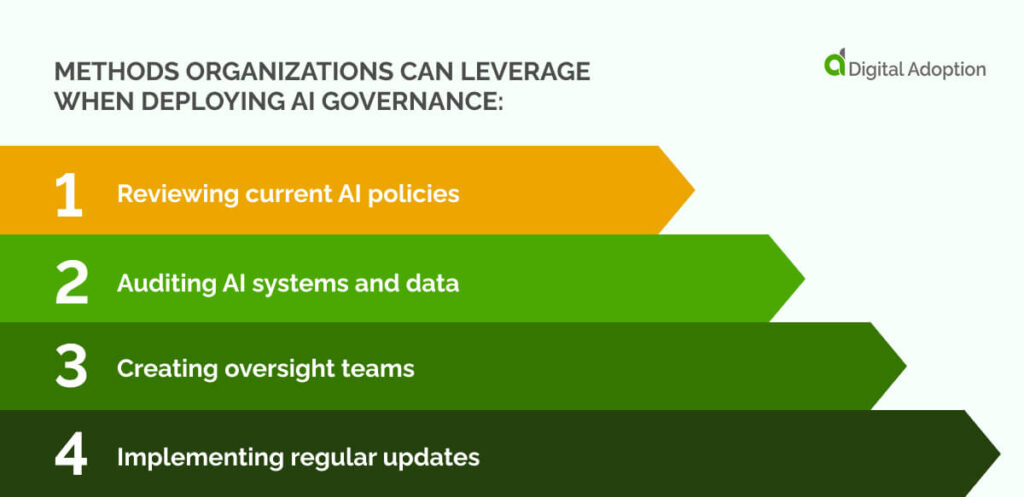
To mitigate these risks, here are a few methods organizations can leverage when deploying AI governance:
- Reviewing current AI policies: Organizations check the rules and practices they follow for AI to ensure they meet legal, ethical, and safety standards.
- Auditing AI systems and data: Consistent checks are made on how AI systems operate, how data is used, and their security. External experts are brought in to identify any biases or inaccuracies.
- Creating oversight teams: Organizations form teams to ensure AI follows the rules. These teams monitor fairness, transparency, and safety, with clearly defined roles for responsibility.
- Implementing regular updates: Organizations plan to update AI systems and stay informed about new laws, standards, and technology to address emerging risks and ensure ongoing improvement.
Futureproofing AI systems for enterprises
Unsecured AI systems can lead to serious risks, such as cyberattacks, data breaches, and manipulation of model outputs, which can damage data and AI performance. Implementing additional safeguards can mitigate these threats.
Businesses can develop risk frameworks like the Framework for AI Cybersecurity Practices (FAICP) from ENISA, which lays down harmonised rules for EU AI regulations. Tools like AI security posture management (AI-SPM), data encryption, and access controls fortify AI security.
Everyone who can access AI systems, including third parties and external partners, should be monitored. AI risk assessments can help avoid vendor management challenges and review how third parties manage security and protect AI systems.
Incorporating these measures ensures AI systems are both secure and compliant. A well-defined governance framework helps prevent risks while supporting the responsible use of AI across industries.
People Also Ask
-
What is Explainable AI (XAI)?Explainable AI (XAI) refers to AI systems that can explain how they make decisions. Instead of being a “black box,” where the decision process is unclear, XAI helps users understand why an AI reached a certain conclusion. This makes AI more trustworthy, as it’s easier to check if the system is fair and not biased. Explainable AI is needed in industries where accountability and transparency are important, such as healthcare or finance.
-
What defines trustworthy AI?Trustworthy AI is clear, fair, and reliable. It doesn’t show bias and explains how it makes decisions. Trustworthy AI keeps data safe, protects privacy, and follows all rules. It’s also accountable, meaning you can determine who’s responsible for its actions.
-
What are the different levels of AI governance?AI governance works on three levels: enterprise-level, which governs AI use in companies; national-level, where laws like the EU AI Act apply; and global governance, which sets worldwide AI standards. Each level makes sure AI is developed, used, and managed responsibly.













