In the realm of digital transformation, AI Compliance is a term that’s gaining significant attention. But what is it, and why should you care?
Simply put, AI Compliance is the practice of ensuring that Artificial Intelligence systems adhere to legal, ethical, and societal norms. It’s a critical aspect of AI integration that cannot be overlooked, especially considering the rapid proliferation of AI technologies in various sectors.
AI Compliance is not just about ticking off regulatory checkboxes; it’s about fostering trust and transparency in AI systems. With increasing concerns around data governance, algorithmic bias, and responsible AI use, compliance has become a hot topic. It’s about ensuring that AI systems are being used responsibly, ethically, and with consideration for the potential implications on society.
Whether you’re a digital transformation leader, an AI developer, or simply a user of AI-powered services, understanding AI Compliance is crucial. Non-compliance can result in legal repercussions, damage to brand reputation, and even the potential misuse of AI technologies. Therefore, it’s vital to comprehend the importance of AI Compliance and how it impacts you and your organization.
As we venture deeper into the era of AI, embracing AI Compliance is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. This article will delve into the intricacies of AI Compliance, its growing importance in today’s digital world, and why it should be at the forefront of any AI implementation strategy.
What is AI compliance?
AI Compliance ensures that artificial intelligence (AI) systems adhere to all legal, ethical, and societal norms.
It’s essential in integrating AI technologies across various sectors, fostering digital trust and transparency in AI systems. But AI compliance extends beyond regulatory adherence – it’s about safeguarding against data theft, preventing tax evasion, and protecting against government-imposed fines.
New AI technologies are compelling compliance professionals to rethink operational models and risk management approaches. With AI playing a critical role in governance, risk management, and compliance efforts, unchecked AI holds the potential for harm. AI compliance, therefore, becomes a tool to identify risks, automate tasks, and investigate potential misconduct.
In this new era of compliance, AI is removing complex processes and replacing them with streamlined solutions, improving regulatory compliance. As AI continues to accelerate across industries, particularly financial, AI compliance becomes increasingly important in addressing regulatory challenges.
The delicate balance between innovation and regulation makes AI compliance crucial in our advancing digital world.
Why is AI compliance Important?
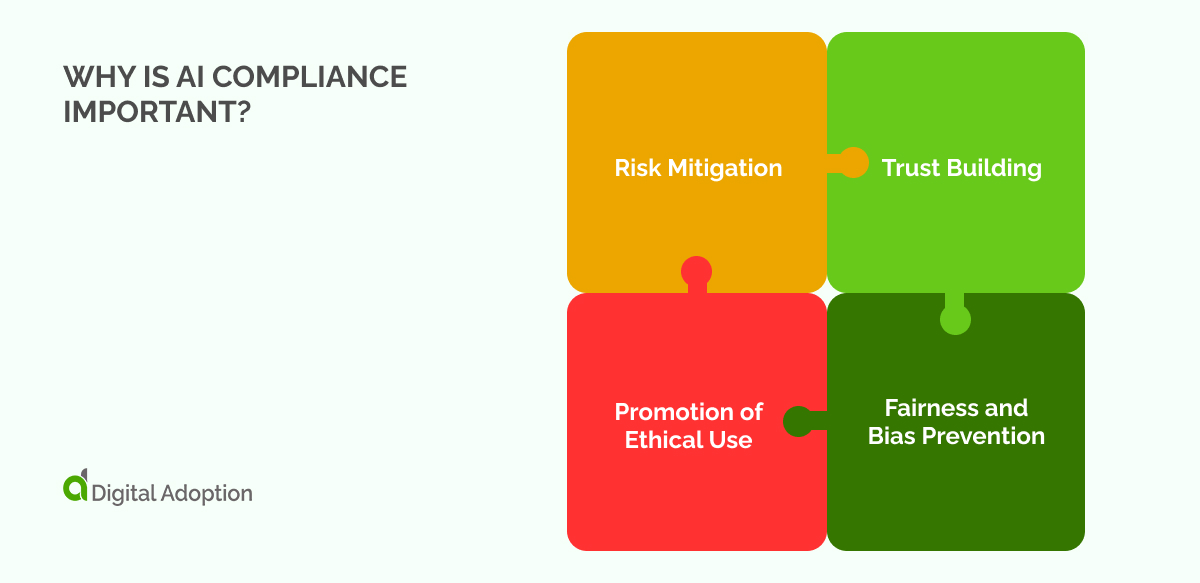
AI Compliance is vital in the digital world and essential in maintaining the balance between technological progress and ethical standards.
Here are some reasons why AI Compliance is of paramount importance:
- Risk Mitigation: Non-compliance can lead to significant legal repercussions, including substantial fines and court proceedings. These can severely impact a company’s financial standing and tarnish its reputation. AI compliance helps businesses avoid these risks by adhering to all necessary regulations.
- Trust Building: AI systems often handle sensitive data. By demonstrating robust compliance practices, companies can assure their customers that their information is secure and used ethically. This builds trust, which in turn enhances customer loyalty and engagement.
- Fairness and Bias Prevention: If not properly checked, AI algorithms can unintentionally perpetuate societal biases, leading to unfair outcomes. AI Compliance ensures these systems are equitable and unbiased, promoting fairness in AI-driven decisions.
- Promotion of Ethical Use: As AI capabilities continue to grow, so does the potential for misuse. AI Compliance safeguards against this possibility, ensuring that AI technologies are used responsibly and for the greater good of society.
Aside from the legal implications of non-compliance, AI Compliance is essential for upholding ethical standards and promoting trust in the digital world.
How to Comply with AI Regulations?
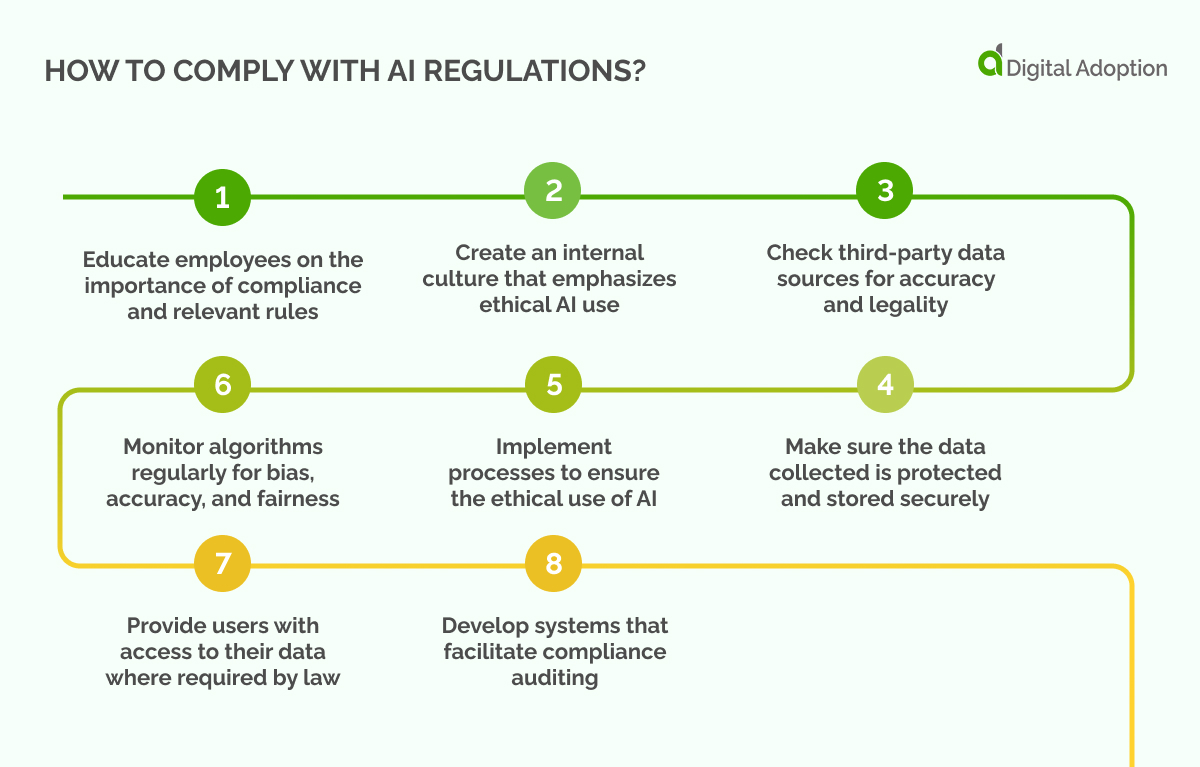
AI Compliance involves adhering to both general regulations, such as privacy laws, and industry-specific regulations that are more specific. Companies must be aware of these rules and ensure they comply with them.
Here are some steps companies should take to comply with AI regulations:
- Educate employees on the importance of compliance and relevant rules.
- Create an internal culture that emphasizes ethical AI use.
- Check third-party data sources for accuracy and legality.
- Make sure the data collected is protected and stored securely.
- Implement processes to ensure the ethical use of AI.
- Monitor algorithms regularly for bias, accuracy, and fairness.
- Provide users with access to their data where required by law.
- Develop systems that facilitate compliance auditing.
Examples of AI Non-Compliance
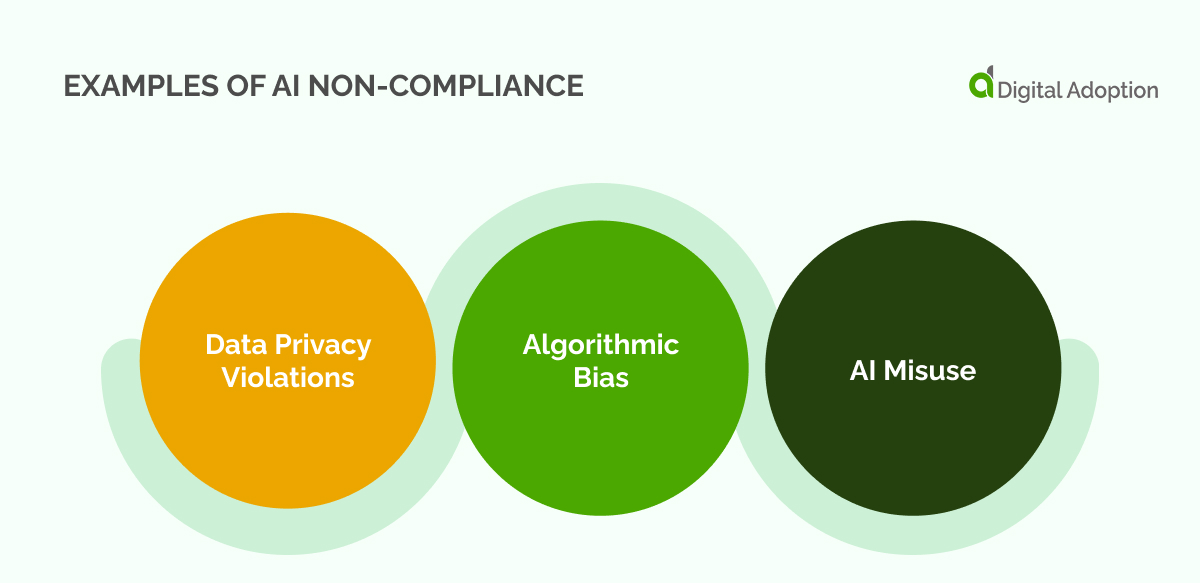
Non-compliance in AI can have significant implications, ranging from financial penalties to ethical concerns. Understanding some real-world examples of AI non-compliance is crucial to better grasp the importance of maintaining stringent compliance standards.
- Data Privacy Violations: In one instance, a popular social media platform was fined $5 billion for privacy violations related to its use of AI in ad targeting. The company had used AI algorithms to analyze user data and target ads without obtaining explicit user consent, a direct violation of data privacy regulations.
- Algorithmic Bias: A leading technology firm faced backlash when its AI-powered hiring tool was found to be biased against women. The algorithm used to screen resumes had learned to favor male candidates, demonstrating a clear case of non-compliance with equal employment opportunity laws.
- AI Misuse: A facial recognition software company was penalized for selling its technology to law enforcement agencies without proper oversight. This resulted in misuse of the technology, leading to false arrests and infringement of personal freedoms.
But that’s not all. Businesses have also been non-compliant when it comes to AI usage in areas such as automated decision-making, data analytics, and automation of customer services.
AI Non-Compliance: Business Use Cases

Understanding the potential pitfalls of AI non-compliance becomes clearer when we look at real-world examples from prominent businesses.
- Facebook and Data Privacy: In 2019, Facebook was fined a record $5 billion by the Federal Trade Commission for privacy violations. The company’s use of AI in ad targeting involved analyzing user data without obtaining explicit user consent, a direct violation of data privacy regulations.
- Amazon and Algorithmic Bias: Amazon faced significant backlash when it was discovered that its AI-powered hiring tool was biased against women. The algorithm used to screen resumes had learned to favor male candidates, resulting in a clear case of non-compliance with equal employment opportunity laws.
- Google and Misuse of AI: Google’s subsidiary, DeepMind, was involved in a controversy where it was accused of breaching the UK’s data protection laws. The company had shared the health data of 1.6 million patients with the Royal Free NHS Foundation Trust without explicit consent for testing its AI app.
Each of these examples underscores the importance of stringent AI compliance measures. They serve as reminders that even the most advanced tech giants are not immune to the risks associated with AI non-compliance.
The Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act)
In a bold move that’s making waves across the globe, the European Union has proposed the pioneering Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act). This trailblazing legislation establishes comprehensive rules on artificial intelligence and significantly modifies various Union legislative acts.
The AI Act brings with it a new classification system for AI, categorizing systems based on risk levels and laying down specific development and use guidelines. It outlines obligations not just for AI providers but also for users, depending on the level of risk posed by the AI system.
With its comprehensive set of rules, the AI Act stands poised to become a universal standard akin to the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The GDPR has been transformative in shaping global data privacy norms, and the AI Act could mirror this impact in the realm of artificial intelligence.
This regulatory ripple effect is already visible beyond European borders. A compelling case in point is Brazil. In September 2021, Brazil’s Congress passed a bill that establishes a legal framework for artificial intelligence. This swift action underscores the far-reaching influence of the EU’s regulatory initiatives and highlights the global recognition of the need for AI governance.
As the world grapples with the complexities of AI, the European Council’s endorsement of the AI Act sends a clear message – regulation is not just necessary. It’s imminent.
The Act could be the harbinger of a new era of responsible AI use, setting a precedent for countries worldwide.
Penalties imposed under the EU AI Act will reach elevated levels, reflecting the gravity of the violations committed:
- Companies may face fines of up to 30 million Euros or 6% of their annual global revenue (whichever is higher) for using a prohibited AI system as per Article 5 of the AI Act or not meeting the quality standards for high-risk AI systems outlined in Article 10.
- Non-compliance with establishing and documenting a risk management system, technical documentation, and standards concerning accuracy, robustness, and cybersecurity for high-risk AI systems (Article 9) can lead to penalties up to 20 million Euros or 4% of annual global turnover (whichever is higher).
- Providing misleading, insufficient, or inaccurate information in response to an information request from competent authorities can result in a fine of 10 million Euros or 2% of the company’s annual worldwide turnover (whichever is larger).
Updates on the EU Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act)
In a significant development on June 14, 2023, the European Parliament articulated its position on a number of critical issues related to Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The lawmakers expressed apprehension about AI systems capable of identifying individuals in public spaces in real-time or retrospectively. They proposed that such identification should be exclusively reserved for law enforcement agencies in serious crime scenarios, and even then, they must obtain judicial approval.
The Parliamentarians also raised concerns about AI systems that classify people based on sensitive attributes such as gender or race, predictive policing models that profile individuals based on geolocation or past conduct, systems capable of emotion detection used in contexts like law enforcement or educational institutions, and indiscriminate collection of personal data from sources like social media or CCTV for facial recognition databases. They fear these practices could infringe upon individuals’ rights and privacy.
The Parliament underscored the need for heightened diligence concerning AI technologies that pose potential harm to health, safety, fundamental human rights, or the environment. This includes AI that could manipulate electoral behavior or influence the content users encounter on major social media platforms.
Businesses developing AI technologies, such as the human-like language generator GPT, are expected to ensure their innovations respect human rights, health, safety, and environmental standards. These firms must demonstrate proactive measures to prevent adverse outcomes, adhere to design and information standards, and register with the EU’s database. They also need to disclose when their content is AI-generated rather than human-created.
In a bid to balance technological advancement with the safeguarding of individual rights, the Parliament proposed exemptions for research and open-source AI components. They also endorsed the concept of “regulatory sandboxes,” controlled environments where AI can be safely tested before wider deployment.
Lastly, the Parliament seeks to empower individuals with more avenues to raise complaints about AI systems and seek explanations when high-risk AI systems significantly impact their rights. They also aim to bolster the role of the EU AI Office to ensure strict compliance with these AI regulations.
How do you ensure AI compliance?
To ensure complete compliance with AI standards, organizations should consider the following set of best practices:
- Formulate well-defined rules and guidelines for the operation of AI systems.
- Construct a thorough program that ensures adherence to all relevant regulations.
- Regularly scrutinize AI systems to ensure they meet all legal and regulatory standards.
- Design a governance structure specifically tailored for AI operations.
- Prioritize the safeguarding of data privacy and security.
- Set up a system to audit AI operations regularly.
- Devise a procedure for identifying, reporting, and addressing compliance concerns.
- Initiate a program to manage potential risks associated with AI.
- Educate staff about the necessary compliance requirements related to AI.
- Leverage automated technology for continuous monitoring of AI compliance.
The Future of AI Compliance

Looking to the future, it becomes evident that AI compliance is on the cusp of a substantial shift. The symbiotic relationship between technology and regulation is changing, necessitating smarter, more strategic approaches.
With AI systems growing increasingly intricate and widespread, the urgency for robust, adaptable compliance structures escalates. These aren’t just needed to protect data privacy, maintain security, and uphold ethical norms while fostering innovation.
This future landscape calls for a new breed of professionals – those well-versed in AI and regulatory compliance. Their role will be critical in understanding the intricacies of AI, assessing its potential risks and benefits, and ensuring adherence to the ever-evolving regulatory landscape.
Alongside this, the tools used for monitoring AI compliance will need an upgrade. Automation, with its ability to provide continuous, real-time oversight, will become a cornerstone of this process.
An equilibrium is crucial to responsibly and ethically harness the vast potential of AI. As we navigate this course, one thing stands clear: the future of AI compliance is a thrilling journey that is only beginning to unfold.













