The dawn of the digital era has given birth to a myriad of innovative technologies, but none have created quite a stir as Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Today, we stand at the cusp of a new era – AI as a Service (AIaaS). This novel concept is transforming the landscape of modern businesses, democratizing access to advanced machine-learning models and algorithms.
AIaaS is a cloud-based model that enables companies to leverage AI capabilities without investing in expensive hardware, specialized talent, or time-consuming development processes. It’s like renting an AI powerhouse on demand, which can be customized and scaled according to business needs.
This paradigm shift is empowering even small enterprises to harness the power of AI, once a privilege of tech giants.
The potential applications are vast and varied, from predictive analytics and customer segmentation to natural language processing and image recognition. With AIaaS, businesses can make data-driven decisions, optimize operational resilience, and create personalized customer experiences like never before.
This unprecedented access to AI is not just revolutionizing business operations; it’s reshaping entire industries. Healthcare, insurance, banking, publishing – no sector is immune to this wave of change.
As we delve into the world of AIaaS, we will explore its transformative potential, its implications, and how businesses can adapt to this promising field.
What is AI as a Service (AIaaS)?
AI as a Service (AIaaS) refers to the provision of artificial intelligence (AI) outsourcing, enabling individuals and companies to access AI capabilities without substantial investment in digital infrastructure or technical expertise. It is a cloud-based model that offers machine learning algorithms and AI computing through APIs, web portals, or software applications.
Users can harness advanced AI tools for data analysis, predictive modeling, natural language processing (NLP), and more. AIaaS allows rapid adoption and scalability of AI technologies, fostering innovation and efficiency in diverse sectors.
How does AI as a Service work?
AI as a Service (AIaaS) is a rapidly evolving sector in the tech industry. This model allows businesses to leverage artificial intelligence capabilities without needing extensive in-house expertise or high upfront costs.
AIaaS refers to the outsourcing of artificial intelligence functionalities to cloud-based platforms. It’s a business model where companies provide AI tools as services over the internet, similar to Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
How AIaaS Works
- Data Collection and Preparation: The first step in AIaaS is gathering and preparing data. This involves cleaning, sorting, and structuring data sets in a format suitable for machine learning training.
- Model Training and Validation: The cleaned data is then used to train machine learning models. The models are validated and tested to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Deployment: Once the models are trained and validated, they are deployed on the cloud. Users can access these AI services via APIs or web interfaces.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: AIaaS systems are designed to continuously learn and improve over time. They adapt to new data and feedback, enhancing their performance and capabilities.
Key Components of AIaaS
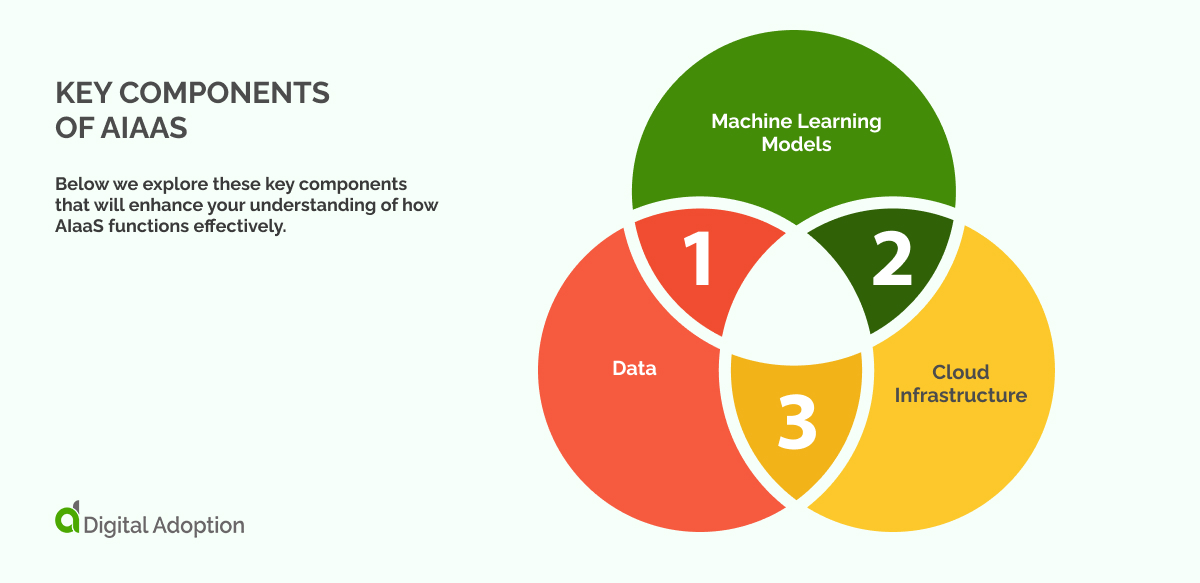
As we continue our discussion, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental components that form the backbone of AIaaS. These elements work together, creating a system capable of making accurate predictions, learning from experiences, and offering scalable solutions.
Below we explore these key components that will enhance your understanding of how AIaaS functions effectively.
- Data: The foundation of any AI system is data. Data sets to train machine learning models, enabling them to make accurate predictions and decisions.
- Machine Learning Models: These are the algorithms that learn from the data. They are essentially the ‘brain’ of an AI system.
- Cloud Infrastructure: AIaaS leverages cloud computing for storage and processing. This allows for scalability and accessibility, providing businesses with flexible AI solutions.
What are the benefits of using AIaaS platforms?
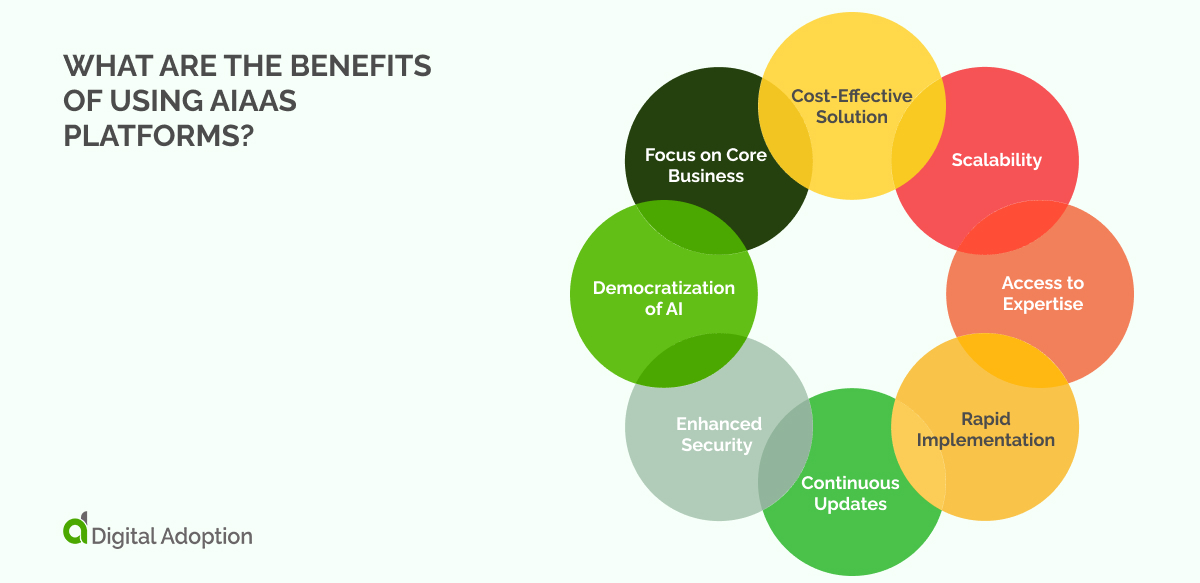
While the potential applications of AIaaS are vast and varied, there are certain key benefits to using these platforms.
We’ve listed a few of the key advantages below:
- Cost-Effective Solution: AI as a Service (AIaaS) is a cost-effective solution that bypasses the need for large-scale investments in hardware and software. Traditionally, implementing AI technology requires substantial financial resources to procure the necessary equipment and develop systems from scratch.
With AIaaS, businesses can leverage advanced AI technology on a subscription basis, reducing upfront costs and transforming them into predictable operational expenses.
- Scalability: AIaaS can scale AI operations according to fluctuating business demands. This scalability is vital as AI workloads can vary significantly, depending upon the tasks’ complexity and the data volume.
AIaaS allows businesses to easily scale up or down their AI usage, ensuring optimal resource allocation and cost efficiency.
- Access to Expertise: AIaaS offers businesses access to an extensive pool of AI specialists. These experts deeply understand AI algorithms, machine learning models, and neural networks.
Their expertise can provide valuable insights, help troubleshoot issues, and guide businesses in maximizing the benefits derived from AI technologies.
- Rapid Implementation: AIaaS providers offer pre-trained models and ready-to-use AI solutions that can be swiftly integrated into existing business processes.
This rapid deployment capability reduces time to market, enabling businesses to leverage AI’s benefits in a shorter timeframe.
- Continuous Updates: AI is a rapidly evolving field, constantly emerging with new advancements and improvements. AIaaS ensures that businesses are always at the forefront of these developments.
Providers regularly update their AI models and algorithms, ensuring clients can access the latest and most effective AI solutions.
- Enhanced Security: Security is critical when dealing with sensitive data and AI. Many AIaaS providers incorporate robust security measures into their platforms, including end-to-end encryption, secure data storage, and strict access controls. These features help protect against data breaches and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
- Democratization of AI: AIaaS democratizes access to AI technology, making it available to companies of all sizes, not just large corporations with substantial resources.
This democratization fosters innovation by enabling smaller firms to experiment with AI, develop novel applications, and compete on a more level playing field.
- Focus on Core Business: By outsourcing AI-related tasks to AIaaS providers, businesses can free up internal resources to focus on their core competencies. Rather than diverting time and effort towards managing complex AI operations, they can concentrate on improving their products, services, and overall customer experience. This strategic focus can enhance competitiveness and drive business growth.
What are the challenges of using AIaaS platforms?
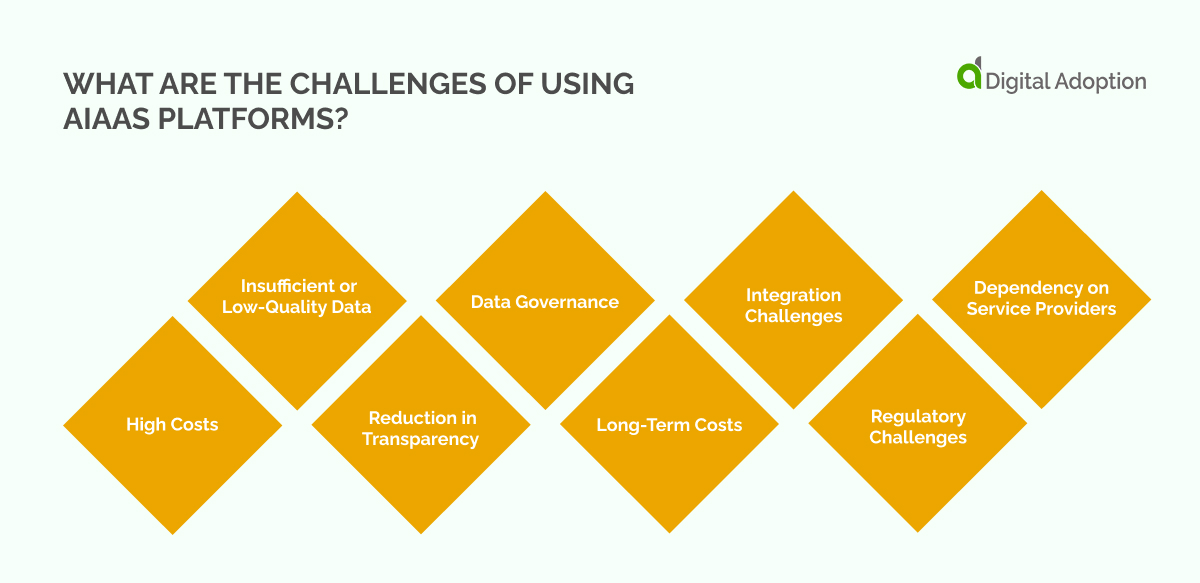
If businesses want to reap the full benefits of AIaaS, they must first address a few potential challenges. If these problems are not properly managed, they can limit the effectiveness of AIaaS platforms and cost organizations precious resources.
With that in mind, we’ve listed a few of the primary challenges associated with AIaaS below:
- High Costs: While AI as a Service (AIaaS) can be cost-effective in the long run, the initial investment can be substantial.
This financial hurdle includes the subscription fee and the costs associated with manpower for deployment and maintenance, hardware upgrades for accommodating AI workloads, and data storage and security measures expenses. Potential hidden costs, such as those for ongoing technical support and fine-tuning the AI model, can add to the overall financial burden.
- Insufficient or Low-Quality Data: AI systems thrive on high-quality, relevant data for training. The effectiveness of AIaaS solutions is directly proportional to the quality and quantity of available data.
If data is scarce, poorly structured, or irrelevant, the system’s learning ability will be compromised, leading to inaccurate predictions or flawed decision-making. Therefore, businesses must invest considerable resources in data collection, cleaning, and structuring to ensure the efficiency of their AIaaS solutions.
- Reduction in Transparency: AIaaS often operates as a black box, where the inner workings of the AI models are not visible to the end-users. This lack of transparency can lead to trust issues, as organizations may find it difficult to understand how the AI made a particular decision.
Furthermore, the opaque nature of these systems can make troubleshooting and fine-tuning more challenging, requiring reliance on the service provider for problem resolution.
- Data Governance: With AIaaS, managing large volumes of data becomes a significant concern.
Data governance involves ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, maintaining data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and ensuring ethical use of data. Inadequate data governance can lead to legal penalties and damage the organization’s reputation.
- Long-Term Costs: The long-term costs of AIaaS can accumulate over time. While the initial outlay may seem manageable, ongoing expenses can add up.
These include recurring subscription fees, costs associated with scaling up the service to meet growing business needs, additional data storage and enhanced security measures, and potential costs for integrating new AI functionalities or upgrading existing ones.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating AIaaS solutions into existing business systems and workflows can be complex. There may be compatibility issues between the AIaaS platform and the existing IT infrastructure.
Overcoming these integration challenges may require technical expertise, custom software development, and significant time, adding to the overall cost of AIaaS adoption.
- Regulatory Challenges: AI technology is advancing rapidly, outstripping the development of regulatory frameworks. Compliance with existing and emerging regulations related to AI use, data privacy, and cybersecurity is a major challenge.
Navigating this complex regulatory landscape requires a thorough understanding of the laws and standards applicable in different jurisdictions and sectors.
- Dependency on Service Providers: Adopting AIaaS creates a dependency on the service provider. This dependency can pose a risk if the provider ceases operations, changes its terms of service, or significantly increases prices.
Organizations must have contingency plans to mitigate these risks, including maintaining in-house AI capabilities or having agreements with multiple AIaaS providers.
What are the various types of AI as a Service?
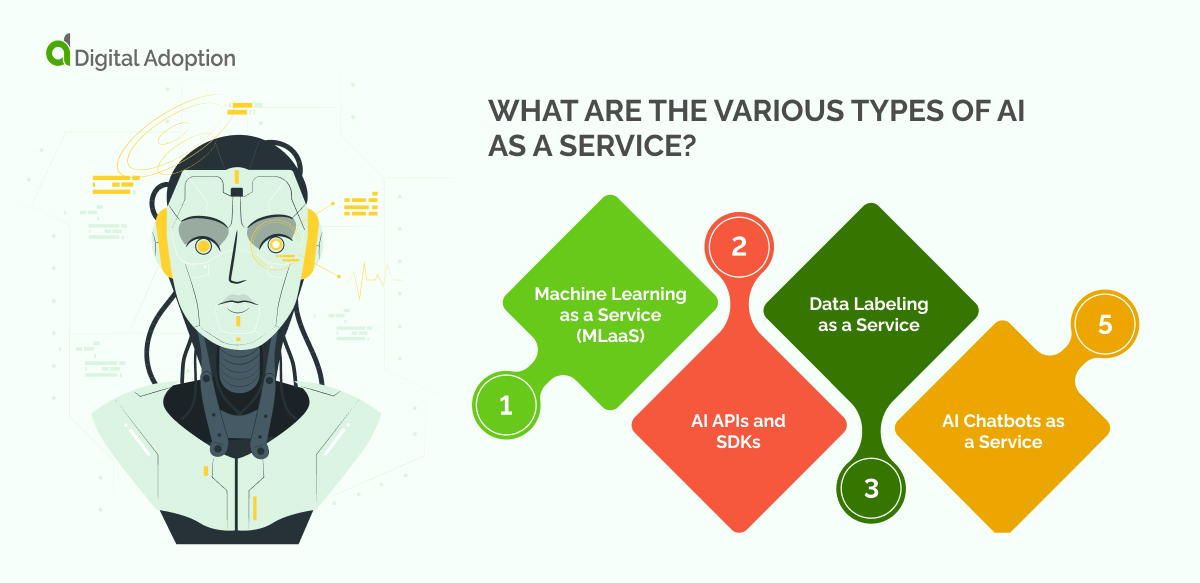
Depending on their specific needs, different types of AI as a Service (AIaaS) are available to organizations. Some of the most popular AIaaS solutions are outlined below:
Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS)
- Definition: MLaaS offers machine learning tools as part of cloud computing services. These tools include data visualization, APIs, face recognition, natural language processing, predictive analytics, and more.
- Benefits: It allows businesses to utilize machine learning algorithms without requiring extensive data science knowledge.
- Examples: Microsoft Azure’s Machine Learning Studio, Google Cloud Machine Learning Engine, and IBM Watson Machine Learning.
AI APIs and SDKs
- Definition: AI APIs and SDKs are protocols and tools for building AI-powered software applications.
- Benefits: They provide developers with pre-trained models and the capability to customize them for specific tasks, thus saving development time and resources.
- Examples: Google Cloud Vision API, Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services, and IBM Watson APIs.
Data Labeling as a Service
- Definition: This service annotates, categorizes, or tags data to train and improve machine learning models.
- Benefits: It ensures high-quality, accurate data for training AI and ML models, leading to better performance and accuracy.
- Examples: Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth, Google Cloud AI data labeling service, and Microsoft Azure Data Labeling.
AI Chatbots as a Service
- Definition: AI chatbots as a service provide conversational interfaces that can understand and respond to human inputs, typically used in customer service.
- Benefits: They can handle multiple customer queries simultaneously, provide 24/7 support, and deliver consistent customer experiences.
- Examples: IBM Watson Assistant, Google Dialogflow, and Microsoft Azure Bot Service.
AI as a Service vendors
Vendors play an important role in making AIaaS solutions available to organizations. It is important to research the features of each vendor before selecting a solution that best meets your needs.
We’ve outlined the key features of each vendor’s AIaaS offerings below:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leader in providing cloud services and has a wide array of AIaaS solutions. The platform offers a plethora of AI services, including machine learning, chatbots, forecasting, recommendation systems, and more. AWS’s AI services are designed to be user-friendly and accessible, with pre-trained AI services that require no machine learning expertise.
Developers can use these services to build, train, and deploy machine learning models quickly and at scale.
2. Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is another frontrunner in the AIaaS market. Its AI services empower developers by providing pre-built models and services to enhance applications with natural language processing, speech, vision, and decision-making capabilities.
Azure also offers a Machine Learning platform for building, training, and deploying models using the tools and frameworks of your choice. Azure’s AI services are designed to help businesses solve complex challenges and improve customer experiences.
3. Google Cloud
Google Cloud provides robust AIaaS solutions designed to help businesses leverage the power of AI and machine learning.
The platform offers pre-trained vision, speech, translation, and more models. Google Cloud’s AutoML allows businesses to create custom models with minimal machine learning expertise required. Google Cloud’s AI Platform is a unified tool for machine learning professionals to build, run, and manage models at scale.
4. IBM Watson
IBM Watson is renowned for its cognitive computing capabilities. Watson’s AIaaS offerings include Watson Assistant for building conversational interfaces, Watson Discovery for uncovering patterns and insights from unstructured data, and Watson Machine Learning for building, training, and deploying models at scale.
Watson’s AI services are designed to help businesses automate processes, improve decision-making, and create engaging customer experiences.
What does the future hold for AI as a Service?
The landscape of Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AIaaS) is projected to undergo a significant metamorphosis in the coming years.
Skyquest’s latest research shows that the global AIaaS market is expected to reach a staggering USD 187.98 billion by 2030, registering a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 48.2% between 2023 and 2023. This growth trajectory is primarily driven by the extensive adoption of AIaaS across diverse sectors such as healthcare, retail, transportation, and security.
In the realm of customer service, AIaaS is anticipated to facilitate more efficient and gratifying interactions. AI-powered solutions can expedite problem resolution, thereby enhancing user experience. Furthermore, the shift from customer service to customer engagement via AI capabilities can result in cost reduction and revenue augmentation.
Moreover, AIaaS is set to revolutionize various other sectors. In healthcare, it could enable predictive analytics for improved patient care. In finance, automated risk assessment and fraud detection would be possible. In manufacturing, AIaaS could optimize production processes, and in transportation, it could enable autonomous vehicles.
The future of AIaaS appears to be remarkably promising. It signifies a transformative phase in the digital era, poised to redefine operational efficiency across industries. While it’s important to remember these trends are subject to change, current projections based on market trends still forecast substantial growth for AIaaS.