For effective AI adoption, every sector has a unique set of opportunities, risks, and challenges.
So, while AI adoption has quickly grown across many industries, the sector-specific pathways to AI maturity are unique.
Globally, the financial services industries have emerged as the most significant early adopters of AI solutions. Healthcare and retail are hot on their tails.
This article delves into AI adoption across key industries. It examines factors affecting adoption rates, barriers to implementation, and AI’s impact on finance, healthcare, and retail operations.
Since the advent of generative AI in late 2022, businesses have had to prepare for an AI digital adoption process quickly. Now that we have detailed research from international foundations, we’re starting to understand how AI adoption might work.
Although we will mention “AI” in general, this article will focus on the new kid on the block generative AI – in other words, AI in the age of ChatGPT and Bard.
AI adoption rates: what makes a difference?
Why don’t more businesses use AI solutions?
After all, in many standard white-collar workplaces, AI has a clear support role for the workforce. Research has shown that AI software and hardware costs are dropping dramatically.
Although there are numerous technical risks and barriers, AI adoption depends on various factors. For example:
AI adoption can vary according to different business functions
As research from Statista shows, AI adoption rates are uneven across business functions and sectors, whether HR, marketing, sales, or logistics.
The term “AI” is a wide umbrella term
There are many types of artificial intelligence (and many types of generative artificial intelligence), and their adoption rates are not even. As US Census Bureau researchers demonstrated in a working paper, different types of tech are adopted at radically different rates. If you want to be sure about AI adoption, you must be clear about the specific AI tools and AI technologies you are interested in.
AI Adoption varies significantly depending on job role.
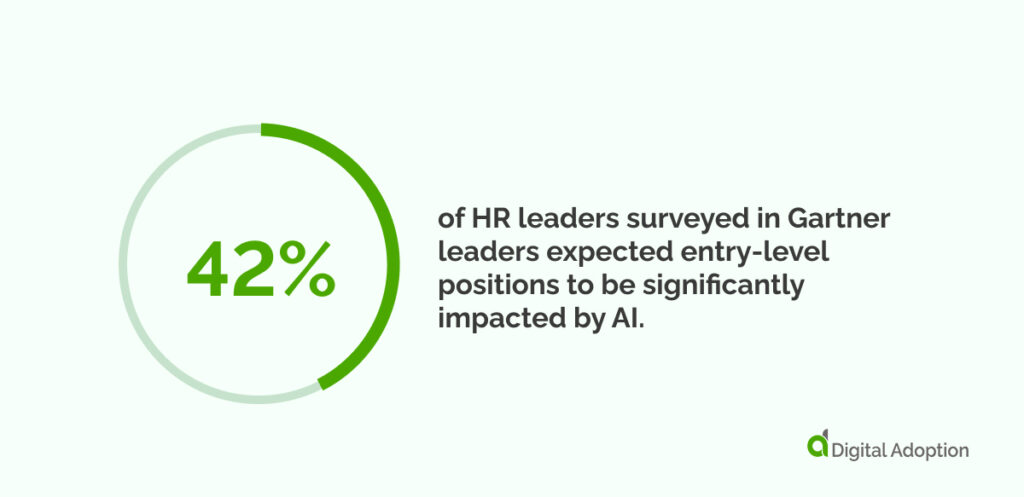
42% of HR leaders surveyed in Gartner leaders expected entry-level positions to be significantly impacted by AI. The same thing has, of course, happened before. The arrival of desktop word processing didn’t change things for CEOs. But in time, it resigned the secretarial “typing pool” that processed so many documents into history. AI adoption will be different at all levels of the company.
AI adoption rates vary by country, continent, and geographic region.
This connects with the relative cost of labor, the levels of digital transformation and digital maturity, and by industry.
These factors remind us that “AI adoption” is far more complicated than we might want. We’ll keep things simple in this article by focussing only on a sector analysis. We believe this is a useful choice, as sector-specific demands are likely to be a driving force for more extensive AI adoption in globalized industries.
Cross-sector barriers to AI Adoption
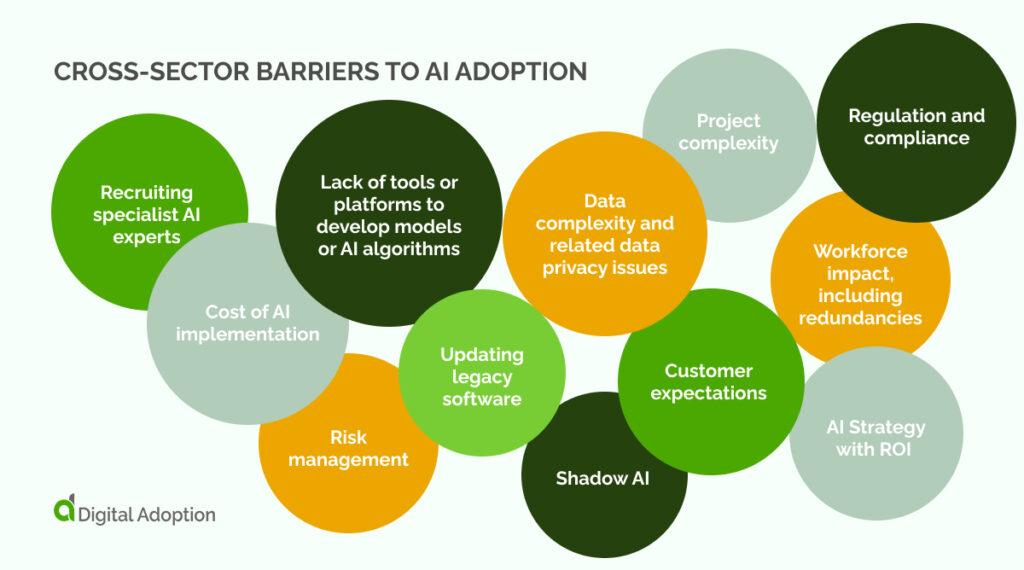
Some of the barriers to AI adoption are present across all industries.
After the past year of global excitement about ChatGPT, extensive research has revealed many challenges of adopting AI in different businesses.
Looking at research from Statista, KPMG’s Generative AI Survey, and McKinsey’s “State of AI” report, some of the common barriers are:
- Recruiting specialist AI experts
- Cost of AI implementation
- Lack of tools or platforms to develop models or AI algorithms
- Data complexity and related data privacy issues
- Project complexity
- Regulation and compliance
- Updating legacy software
- Customer expectations
- Workforce impact, including redundancies
- AI Strategy with ROI
- Risk management
- Shadow AI
With these in mind, let’s look at AI applications’ opportunities, risks, and futures in financial services, healthcare, and retail.
AI adoption in financial services
Financial services has been using AI more extensively than most other sectors. To understand the lay of the land, we’re lucky to have thorough research published by the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Examples of AI adoption in financial services
Generative AI has significant real-world applications for financial services business.
Companies are showing how it can enhance fraud detection, improve investment decisions, automate document processing, and power in-house software development.
These are proven, not speculative, use cases, with global companies harnessing generative AI to optimize their processes.
Risks
Amid the rapid AI adoption in finance, the sector grapples with well-acknowledged risks.
These include bias, privacy breaches, opacity, fragility, and cybersecurity threats. The sensitive nature of financial data magnifies these concerns, impacting wider financial security.
Legitimate fears of Shadow AI have led numerous institutions to ban ChatGPT and similar AI tools.
The future
The future of the financial sector’s AI use promises innovation but carries limitations.
Well-known problems with AI, like hallucinations and context comprehension, are especially significant. Vigilant monitoring is vital to ensure alignment with industry standards.
Continuous oversight is crucial to balance AI benefits and risk mitigation, maintaining precision, transparency, and security in financial services.
AI adoption in healthcare
The healthcare industry already has a clear track record of digital adoption. AI tools are the next step in the industry’s progress towards better outcomes.
However, for healthcare, the challenges of change management are especially precarious. Healthcare needs extremely careful change management; a mistake could have serious consequences.
So, it’s no surprise that a leading HBR article says AI adoption “won’t be easy” in healthcare. But how can AI support healthcare? What are the risks?
Let’s take a look.
Examples of AI adoption in healthcare
AI tools have some very interesting possibilities in the healthcare sector. In the background, AI can accelerate scientific discovery, and on the client side, it can support healthcare professionals to make informed decisions.
It can sometimes improve medical advice given to patients. And “under the bonnet” can alleviate the onerous burden of administrative tasks and paperwork.
Risks
In healthcare, the transition to AI-driven solutions comes with high risks. The “switchover disruption” phenomenon is not just an inconvenience – it’s about safeguarding patient lives and data.
Moreover, doctors, nurses, and other support staff may resist any new technology that might threaten their patients.
As a result, shadow AI must be treated very carefully. Uncertain risks such as AI hallucinations and privacy breaches can have life-or-death consequences, depending on their position within the healthcare system.
The future
Since healthcare faces similar technical challenges to finance, companies must carefully monitor their AI systems.
Companies in this position could use a digital adoption platform capable of handling AI. However, AI adoption in healthcare must also navigate the resistance to change in a compassionate field.
This is a “human” challenge – not a technical one. Leaders must give staff a clear narrative about AI’s role and actively reassure patients that their safety and privacy are their highest concerns.
AI Adoption in Retail
In retail, adopting AI will change business processes and customer experience. There’s no “life or death” in retail. It’s just a matter of profit, efficiency, and good business.
All businesses will be keen to implement AI in at least one function. Consumer retailers are currently approaching AI adoption with caution.
The US National Retail Federation has produced a particularly useful report on how the retail sector handles it.
Examples
Fully implemented case studies for the use of AI in retail are still emerging. The sector-changing plans are still speculative.
These prospects include many possibilities. AI-driven inventory tracking across the supply chain, personalized customer styling recommendations, and generating AI models tailor-made for specific applications are all on the horizon of global retail.
AI also proves its worth in predicting in-store foot traffic, facilitating customer engagement through responses to reviews, enabling dynamic pricing strategies, and tailoring marketing communications on a customer-by-customer basis.
Risks
In retail, as in the entertainment industry, the shift from creative human work to AI-generated output has sparked significant criticism.
A critical concern is the potential for mass unemployment if AI counterparts supplant human roles.
The sector leaders must strike a delicate balance. On the one hand, they should leverage AI’s efficiency – and, on the other, safeguard employment among the global workforce. That’s a big challenge!
The future
The future of AI in retail hinges on identifying the “right” opportunities, especially when existing systems function smoothly. Many businesses are cautious, waiting to see how AI can seamlessly integrate into their business models.
The most promising applications often emerge in multi-site businesses, requiring substantial infrastructure investment. Initiatives like the NRF working group are poised to bolster the adoption of industry-wide AI applications, providing a supportive ecosystem for the retail sector’s AI-driven transformation.
As the industry navigates this transformative path, collaboration and innovation will be key to harnessing AI’s potential for enhanced customer experiences and operational efficiency.
AI adoption – what do we do now?
In this article, we’ve focussed on the ins and outs of different industries- rather than AI adoption statistics, the range of digital technologies available, or the demands of natural language processing. Those are topics for another day.
Undoubtedly, many of the challenges and opportunities for generative “AI adoption” cut across businesses and sectors. That’s why many third-party app developers are making good money from AI-driven software.
But as soon as you go deeper, many factors make a difference in AI adoption practices. As we’ve seen, the opportunities and challenges are different across sectors – but the specific business units, locations, and job roles will all make a difference, too.
As a result, tech-savvy business leaders should not be adopting AI solutions without the appropriate level of diligence. After all, we still don’t have a fully mature ecosystem of AI tools. At the end of 2022, a Gartner analysis suggested that Generative AI was just a phase at the start of a “peak of inflated expectations” in AI’s hype cycle.
Now is not the time to sit still – but it’s also not the time to go crazy. Now’s the time to prepare, listen, adapt, and implement when appropriate. And then, as the right solutions come, you can implement them for maximum business results.













