The rush to modernize entire industries and adopt digital business models has seen organizations undergo rapid digital transformation throughout recent years. Major industrial, manufacturing, agriculture, and healthcare sectors are leveraging contemporary digital technologies to drive change and innovation.
One particular sector experiencing this change is the financial and banking sectors—which have successfully digitized the delivery of services thanks to accelerated digital banking adoption efforts. Digital adoption plays a pivotal role in the transition from brick-and-mortar banking to digital banking and has become a vital component of the transformation strategies of financial entities.
Previously, the only way for customers to complete critical financial errands was to physically visit their bank branch—which can involve long queues and unnecessary paperwork.
Now with online banking apps, e-wallets, and digital banking channels giving customers the ability to make e-payments, manage their funds remotely, and make instant financial decisions in real-time, the everyday use of digitized banking services has become widely exploited.
However, to address changing customer needs while navigating the chaos caused by COVID-19, financial service providers are embracing digital disruption to reinvigorate traditional business models.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about digital banking adoption in today’s zealous digital landscape—covering the latest trends, challenges, research, and solutions currently permeating the sector.
- What Is Digital Banking?
- What Is Digital Banking Adoption?
- Digital Banking Adoption Is Increasing Globally
- Digital Banking Vs. Traditional Banking
- The Emergence Of New Banking Models
- Digital Banking Opportunities
- The Biggest Challenges of Digital Banking Adoption
- What Is FinTech?
- The Role Of FinTech In Digital Banking Adoption
- Is Digital Banking The Future?
- What Role Will Branches Play In The Digital Banking Adoption Revolution?
- How Should Banks Rethink How They Engage With Customers?
- How Should Banks Position Themselves In The Future?
- Digital Banking Transformation: The Future Of Transactions
What Is Digital Banking?
Digital banking describes the complete digitization of end-to-end banking processes and is an umbrella term that encompasses both online and mobile banking.
This typically involves deploying web-based products and services alongside AI-empowered process automation to facilitate online and mobile banking app financial management. This allows customers to complete transactions and access banking services online via any device, browser, or app.
Statista reports that digital banking users in the U.S will grow from 197 million users in 2021 to almost 217 million users by 2025.
The digital banking model is often known as the “omnichannel” approach because customers can access their bank accounts 24/7, regardless of where they are. The need for digital banking solutions stems from increasing customer demand for digital solutions for accessing and managing their financial data.
Forbes says, “Together, online and mobile banking creates the digital banking umbrella, giving people access to banking wherever they may be—or, in some cases, wherever they’re graced with secure Wi-Fi and strong cell signal.“
What Is Digital Banking Adoption?
Digital banking adoption refers to the rate at which consumers, businesses, and organizations adopt new digital banking services. This can include the use of online and mobile banking platforms and apps, e-payments, money transfers, loan services, and other contemporary financial architecture offered through digital mediums (e.g., cryptocurrency).
Factors influencing digital banking adoption include consumer preferences, competition in the industry, technology advancements, regulatory requirements, and marketing strategies. Several digital adoption strategies can be used to accelerate digital banking transformation rates, including marketing and communications campaigns, developing partnerships with third-party providers, and improving overall customer experience.
With the recent global pandemic, there has been a sudden shift to digital banking for many people. This was likely accelerated by other existing trends—such as the growing use of digital channels for various transactions, including banking, and the wider use of teleconferencing/video calls instead of face-to-face meetings.
Digital Banking Adoption Is Increasing Globally
Digital banking adoption models have graduated from simplistic add-ons and online features that support physical visits to bank branches, into a predominantly digital-first ecosystem where financial management is mostly done online.
In developing economies, digital banking has become widespread ever since the rise of the internet in the late 90’s made it possible for consumers to access online financial services remotely. Statista reports that Transaction value in the Neobanking segment is projected to exceed 1 trillion U.S dollars in 2022.
Fast forward, digital banking adoption is now being embraced globally. McKinsey’s 2021 Personal Financial Services survey reveals that digital banking adoption rates in emerging Asia-Pacific markets have caught up with that of developed economies.
The survey reports that consumers in emerging Asia-Pacific markets actively using digital banking rose from 54% to 33% between 2017 and 2021—an increase of 21% over five years. The survey further details that emerging Asia-Pacific markets lead the use of fintech and e-wallets, which has resulted in enhanced digital banking solutions becoming adopted faster than developed markets.
Digital Banking Vs. Traditional Banking

Financial models are changing as consumer trends continue to shift towards an everything-online culture. Banking institutions now face the challenge of offering products across geographies and cultures connected by technology.
Borders and geography no longer limit the financial services industry, so adapting to a changing global demand has become more important than ever.
Today, modern digital banking solutions are adopted by both long-held financial institutions and financial technology (fintech) start-ups—either developing digital banking services to support physical branches or digital-only platforms (neobanks) for those offering online-only services.
Financial technology (fintech) simply refers to any organization that utilizes technology to deliver financial services—companies falling under the fintech umbrella include veteran platforms such as Venmo and emerging ones like Revolut.
Some of the most reputable financial institutions providing industry-leading digital banking services include Citi, Wells Fargo, and JP Morgan Chase—who hold the largest share of active mobile banking customers in the U.S.
These proprietary banking apps host a range of e-resources that enable customers to monitor and manage their financial assets, make financial health assessments, utilize predictive analytics, and receive tailored insights.
However, incumbent financial bodies are finding it increasingly necessary to re-assess the limitations of legacy architecture and source solutions that deliver faster innovation and operational efficiency.
The Emergence Of New Banking Models
To transition from traditional banking models into emerging digital models, financial institutions have begun collaborating with fintech companies to supplement legacy systems with agile architecture able to innovate as fast as competing providers.
Alternatively, traditional banks are leveraging their infrastructure and opening up their application programming interfaces (APIs) to host fintech stacks that deploy Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) solutions.
Along with BaaS, companies dedicated to developing financial technologies have enabled the rise of neobanks—sometimes referred to as challenger banks.
Neobanks—also known as digital-only banks—are fast becoming the go-to financial service providers best able to meet the demands of tech-conscious consumers. Insider Intelligence says there will be 40 million neobank account holders by 2025.
Neobanks provide digital-only web-based mobile services that generally require no/low fees or traditional physical branch networks. These online banks offer slimmed-down services compared to conventional banks and are often required to partner with an established bank to acquire a license permitting them to operate.
Neobanks that are fully licensed and offer wide-ranging financial services qualify as a new bank—their online-only operations differentiating them from traditional brick-and-mortar providers. Examples of these new banks include Monzo, Nubank, and Starling Bank.
The advent of new banks, decentralized finance (DeFi), peer-to-peer lending (P2P), software-as-a-service (SaaS), and other fintech models signify shifting societal and consumer demands towards more efficient and autonomous financial tools—and the prospective success of at least one of these emergent technologies appears likely.
In the UK, the number of challenger banks is cropping up after the country introduced new open banking regulations alongside robust regulations provisioned by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). These challenger banks allow customers to collaborate with fintech and third-party providers (TPP), ultimately giving them the final say on how their financial data is shared.
Traditional financial institutions must embrace and find a way to navigate digital disruptors to catch up with the rapid innovations fintech is delivering. This means embracing new technologies and being open to competition from a wide range of service providers with different business models.
Digital Banking Opportunities
Digital banking opportunities are emerging in a wide range of areas, including digital payments, personal finance management (PFM), lending and financing services, international commerce, wealth management, e-wallets, identity verification, AI-driven virtual assistants, and more.
As more consumers and businesses adopt digital banking services, the market for these offerings is expected to continue growing in the coming years. This presents a tremendous opportunity for organizations to develop innovative digital banking solutions and capture a share of the emerging market.
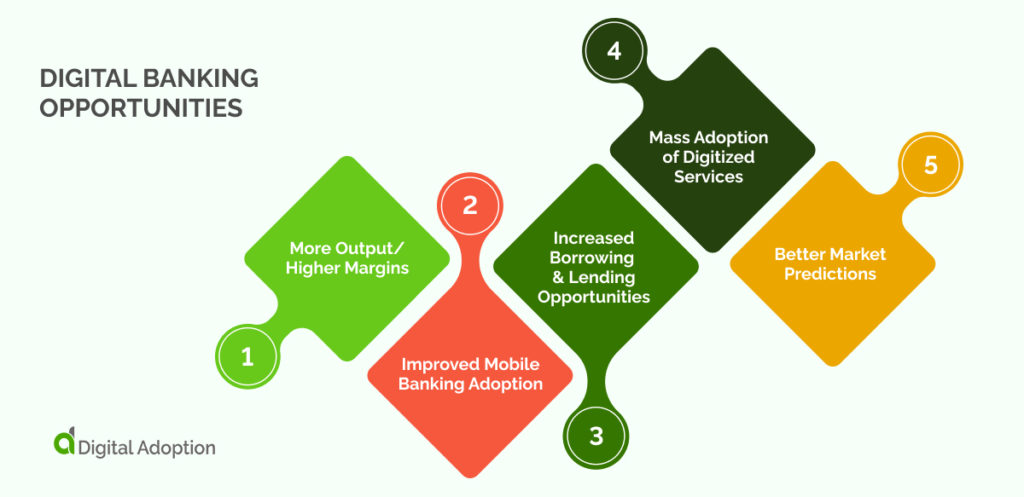
Digital banking opportunities are prospects for business growth and innovation in the financial services sector. These opportunities include:
1. More Output/Higher Margins
Customers no longer have to wait to deposit or withdraw money from their accounts or make online purchases during bank hours. Banks can now offer 24/7 services with digital banking, leading to increased profits.
2. Improved Mobile Banking Adoption
Mobile banking apps allow customers to access their bank accounts and perform various transactions, such as check deposits or online payments, at any time. This convenience can help drive higher digital banking adoption rates, especially among younger users who are more likely to use mobile devices for financial transactions.
3. Increased Borrowing & Lending Opportunities
Digital banking platforms can facilitate lending and financing services, allowing customers to apply for loans or other types of credit online. This gives businesses greater access to capital, which can drive growth and innovation in various industries.
4. Mass Adoption of Digitized Services
The mass adoption of digitized services is accelerating across the banking industry at a rapid rate. Banks that can implement digital banking solutions at scale will be better positioned to capitalize on the growing market for these offerings. Digitized services represent a significant opportunity for organizations to expand their customer base, increase revenues, and improve operational efficiency.
5. Better Market Predictions
Data is critical for any organization because it can be used to predict the market and offer better services to customers. Digital banking is backed up with an accurate data collection mechanism. Today, the data available in banks have not been utilized as they are supposed to be mainly because the format in which they exist makes them harder to access.
Though digital banking benefits both customers and banks, it’s safe to say that the future banker will be entirely digital. As we speak, AI for banking is already being implemented by other banks, with remarkable results in some cases. Eventually, bank queues will cease, which is a fair warning for any bank or financial institution wanting to maintain a strong market presence.
The Biggest Challenges of Digital Banking Adoption
When money is involved, security is naturally a top concern. It’s no surprise that statistics from DA’s ‘digital adoption in the banking industry’ report that most digital banking providers (38%) feel that ensuring data security and cybersecurity across the network and infrastructure is a top priority.
With digital banking and the wider digital economy growing each year, so does the threat of cyberattacks. As financial institutions continue to launch predominantly mobile and web-based services, achieving this without compromising their customers’ safety and security is challenging.
The six biggest challenges in digital banking for providers in 2021, according to our data, also include:
- Increasing competition from digital-first providers
- Building end-to-end customer journeys that integrate across partners
- Ensuring easy data interoperability and flow with external partners
- Relevant skills and talent capabilities
The digitization of traditional banking models allows long-held financial institutions to evolve alongside the very same technology enabling its transformation—but the adoption of new technologies and digitized services means particular attention must be placed on cybersecurity.
Phishing attacks, malware and ransomware attacks, identity theft, and fraudulent activity pose huge security risks for customers and providers alike. So banking institutions going digital emphasize enhanced cybersecurity solutions that fortify customer transactions with protective parameters.
This includes deploying antivirus and runtime application self-protection (RASP) solutions to protect core systems or two-factor authentication and biometric scanning for end-users. Digital banks are also using artificial intelligence to perform data analytics and create models that can recognize threats and anomalies. While machine learning can be taught to detect fraud by analyzing customer behavior and identifying changes using intelligent insights across large data sources.
What Is FinTech?
There is a growing number of financial technology companies revolutionizing how we bank and manage our finances. These innovative companies offer various products and services, including digital banking platforms, mobile payment systems, peer-to-peer lending networks, crowdfunding platforms, automated investment management tools, and more.
Fintech started to gain traction around the mid 90’s. At that time, it was used mainly by large financial institutions for things like back-end systems. But since then, there has been a shift toward more consumer-oriented services.
Now fintech encompasses different sectors and industries such as education, retail banking, fundraising and nonprofit organizations, and investment management.
The fintech startups that receive the most funding are designed to overtake traditional financial institutions by being more agile, appealing to underserved markets, or providing superior service.
For example, Affirm tries to remove credit card companies from the online shopping process by giving consumers a way to immediately take out short-term loans for purchases.
Although rates can be expensive, Affirm states that they offer an opportunity for people with no or poor credit to get loans and improve their credit scores.
The Role Of FinTech In Digital Banking Adoption
Although fintech can pose particular challenges to digital banking adoption, it also plays a crucial role in helping businesses stay competitive and relevant in the rapidly changing financial landscape.
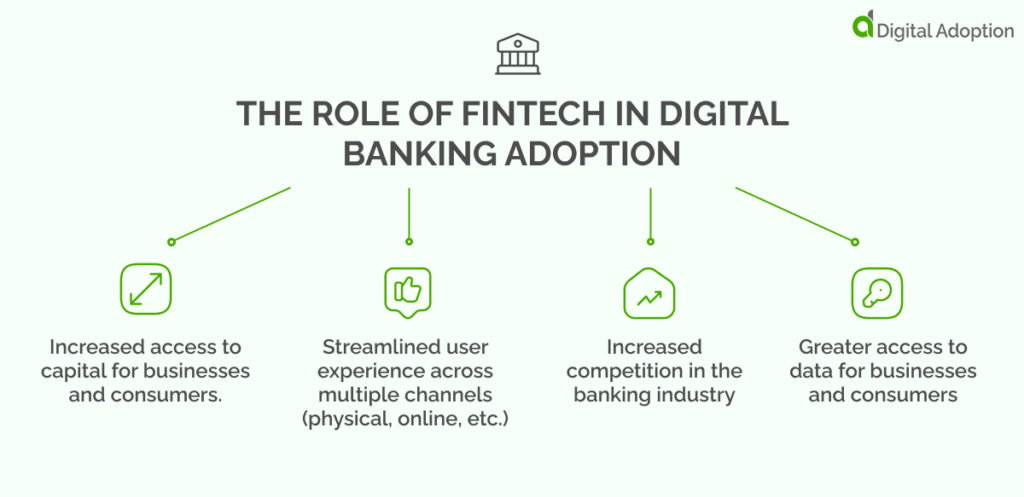
Some critical ways that fintech influences digital banking include:
1. Increased access to capital for businesses and consumers.
Many fintech companies offer new streamlined ways for people and businesses to access capital through online platforms, mobile apps, and more. Increased capital access helps reduce barriers to entry, allowing more people to take advantage of financial services and products.
2. Streamlined user experience across multiple channels (physical, online, etc.)
To remain competitive in the digital age, banks must provide a seamless consumer experience across all channels, including physical branches, websites, and mobile apps.
Fintech companies are helping to drive this transformation by introducing new technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning that make it easier to interact with customers in real-time.
3. Increased competition in the banking industry
The rise of fintech has led to increased competition among banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. This has led to faster innovation cycles and greater pressure on traditional players to keep up with the latest technologies and trends to remain competitive.
4. Greater access to data for businesses and consumers
Many fintech startups are generating huge amounts of data through their platforms and applications, which can improve customer experiences, reduce costs, and make data-driven business decisions.
Big data analytics tools have increased recently, particularly within the financial services industry.
Is Digital Banking The Future?
The rapidly-evolving fintech industry primarily arose as a recovery response to the economic fallout caused by the 2008 financial crash, which offered an alternative financial paradigm for those who wanted to branch away from traditional banking models.
Since then, the number of emerging fintech start-ups has risen yearly, and with advancements in financial technology continuing to rewrite industry norms—we expect this trend to continue.
The rapidly-evolving fintech industry mainly arose as a recovery response to the economic fallout caused by the 2008 financial crash, which offered an alternative financial paradigm for those who wanted to branch away from traditional banking models.
The components driving the development of financial technology can be characterized mainly by the rapid adoption of 4 key technologies often referred to as the “ABCDs of fintech” Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain Technology, Cloud Computing, and Big Data empower fintech innovation across sectors.
Let’s explore these technologies further:
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is improving digital banking adoption in various ways. Thanks to advancements in machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP), fintech and traditional financial service providers alike understand AI’s potential applications are plenty.
AI can leverage customer data to provide companies with distinct insights and predictions on customer and marketplace trends. AI’s analysis of consumer behavior using vast amounts of data from multiple sources means it’s able to make intelligent recommendations for improving the customer journey and evaluating risk scores.
The benefits of blockchain technology have been realized for some time, underpinning the nascent cryptocurrency market and the emergence of uniquely identifiable digital assets. Based on the principles of consensus, cryptography, and decentralization, this new technology penetrates global business and established financial sectors to enhance processes, increase efficiency, and deliver transparency across the organization.
Blockchain
Blockchain can transform the core of digital banking architecture by using its efficient and immutable processes. For example, traditional financial providers are eager to leverage digital currencies for more secure and faster transaction processes.
One of the primary benefits of blockchain technology is its ability to create tamper-proof records. This makes it an attractive solution for banks, who are constantly looking for ways to improve the security and efficiency of their transaction processes.
For example, many banks are now exploring digital currencies as a more secure alternative to traditional payment methods like credit cards. Digital currencies can offer faster transaction times, lower processing fees, and increased transparency compared to conventional payment methods.
Moreover, blockchain technology is inherently built with security embedded, which financial service providers can rely on to fortify security capabilities, keep secure records of ownership and utilize smart contracts to execute water-tight transactions on blockchain’s unchanging ledgers.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is transforming companies’ business through its on-demand infrastructure, application hosting, and software solutions. Digital banking adopters can leverage the cloud to accelerate their innovation cycles, improve customer engagement, optimize costs and ultimately enhance the customer experience.
The unique selling point of cloud computing is the flexibility and scalability it offers businesses. Software-as-a-service (SaaS), neobanks, Banking-as-a-service (BaaS), and other fintech providers empowered by the potential of cloud transformation, which helps avoid vendor lock-ins that require spending on costly software licenses. Rolling subscription models also means fintech providers face lower upfront costs when developing software hosted on the cloud, allowing them to experiment and scale business models.
Data
Data is considered “the new oil” and, much like the natural resource, is a highly sought-after ingredient fuelling the transformation of entire industries. Traditional banking institutions depend on large data sets to maintain essential operations. This data, however, has long been deposited in physical form, which can make for unwieldy organizational processes, forecasting capabilities, and decision-making.
Data has now been digitized and is readily accessible through cloud storage and processing tools. Providers can leverage big data and analytics to gain insights on customers’ online activities- like logging in to virtual banking, transactions, web browsing, eCommerce, and social media use.
Digital banks can collect massive amounts of customer data and use sophisticated AI algorithms to decode these trends into insights that can help identify customer needs, forecast marketplace changes and optimize operational efficiency.
Overall, the ABCDs of fintech – AI, blockchain technology, cloud computing, and data analytics – are transforming the digital banking landscape by enhancing efficiency, security, and customer experience. Digital banks that embrace this paradigm shift while focusing on their customers will be positioned to stay competitive and capture a share of the evolving market.
What Role Will Branches Play In The Digital Banking Adoption Revolution?

There is no clear answer to this question, as the role of branches in digital banking adoption is still evolving. On the one hand, some experts believe that traditional bank branches may become redundant as more consumers adopt digital banking solutions.
However, others argue that physical branches still play an important role in engaging customers and providing high service and support. In particular, many people still prefer to visit their local branch for complex tasks or in-person assistance.
As the digital banking revolution continues to unfold, it will be interesting to see how banks balance the need for both online and offline services to meet their customers’ changing needs.
How Should Banks Rethink How They Engage With Customers?

One key way banks can rethink how they engage with customers is by focusing on customer experience. Financial institutions can create personalized interactions that improve satisfaction and loyalty over time by using data analytics and other technologies to understand their customers’ needs and preferences.
Additionally, banks should consider investing in new digital tools and services that help enhance the customer journey. This might include offering more online banking products, such as personal finance apps or automated investment platforms, allowing users to easily manage their accounts from any device.
To succeed in this rapidly changing landscape, banks must also be willing to embrace innovation and experimentation to stay ahead of the competition. By continuously evaluating emerging trends and technologies, they can better understand the evolving needs of their customers and adapt accordingly.
How Should Banks Position Themselves In The Future?
To position themselves for success in the future, banks must be willing to embrace innovation and adapt to changing trends and technologies. This may involve investing in new digital tools and services that better meet the needs of their customers, as well as experimenting with new approaches to engaging with clients and improving customer experience.
At the same time, banks must also maintain a strong focus on delivering high-quality products and services to build customer trust and loyalty. By leveraging data analytics, machine learning, and other cutting-edge technologies, they can better understand their customers’ needs and create tailored experiences that drive satisfaction and engagement.
Digital Banking Transformation: The Future Of Transactions
The digital banking revolution is changing how financial institutions engage with customers, offering new tools and services that improve convenience and satisfaction. As such, banks must be willing to embrace innovation and experimentation to position themselves for success in the future.
Ultimately, meeting the needs of today’s digital consumers will be vital to ensuring long-term success in this rapidly evolving landscape.













