Data from multiple surveys show that U.S. consumers have quickly veered toward digital adoption in health apps and online doctor consultations after the advent of the Pandemic.
The share of U.S. patients who prefer virtual consultations has consistently increased after the pandemic. However, not all specializations have been impacted equally. Psychiatry has witnessed the most significant increase in online consultations, while disciplines needing invasive procedures are still understandably offline. There was a 70 times increase in tele claims from U.S. patients in April 2020 — immediately after the pandemic restrictions were announced.
Interestingly, the increase in teleconsultations has continued even after two years, despite relaxations in Covid-related movement restrictions. This shows that while the pandemic was the catalyst needed to boost online consults, people did not stop using it when the pandemic subsided. However, concerns remain with most consumers worried about data security and, more importantly, the privacy of their health data. While health apps continue to increase their customer base, U.S. patients are particular in their doctors approving the usage of such apps.
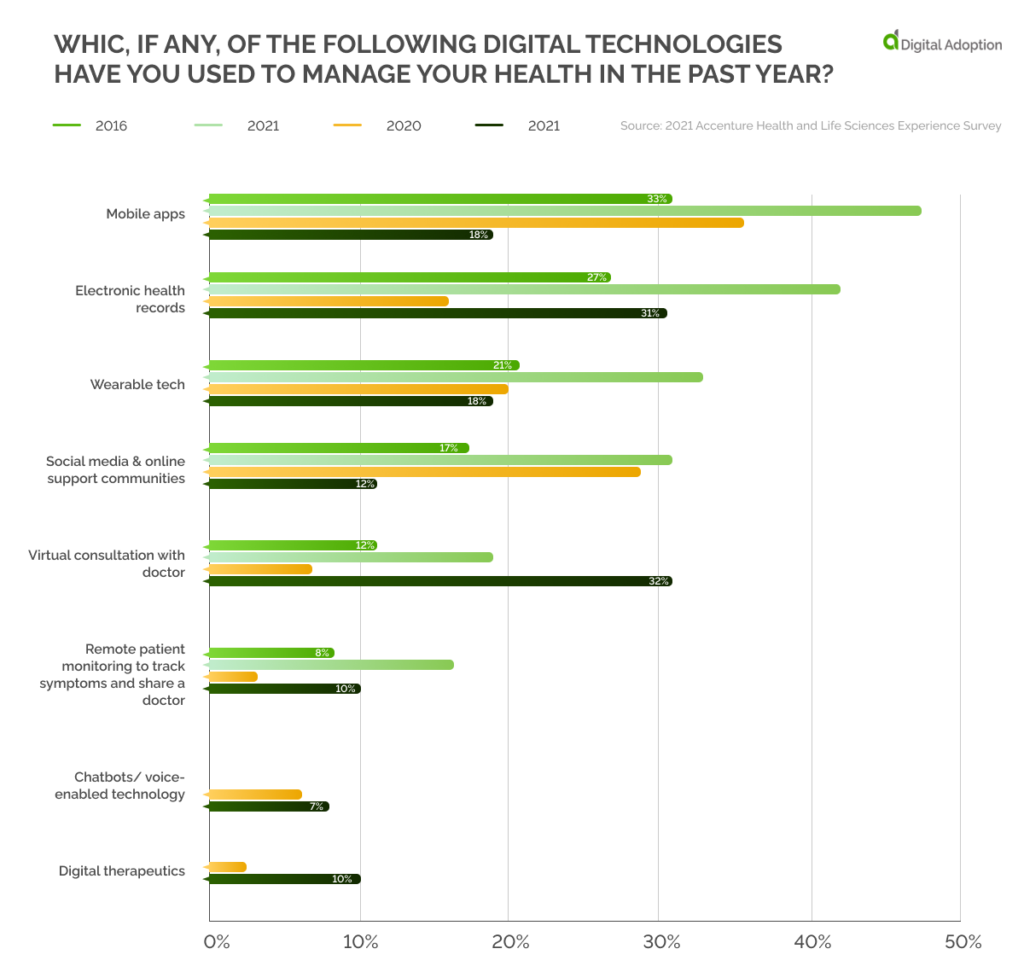
Digital Technologies Used
In 2016, when U.S. residents were asked about their preferred digital technology for monitoring their health, about 33% said they used mobile apps. In contrast, virtual consultation with the doctor was cited by only 12%.
In just over four years, things took a wild turn. In 2021, when the same set of residents was asked the question, only 18% said they relied on mobile apps, while 32% were interested in a virtual consultation.
The change is directly related to the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to a unique situation of an increasing number of patients, high restrictions on movements, and fear of getting the disease while in close contact.
The growing disease burden and reluctance to have physical contact meant that doctors and patients increasingly preferred digital consultation. As seen in the graph below, this led to a surge in such consults.
The sudden demand for digital health-based tools also led to innovations such as digital therapeutics and health chatbots.
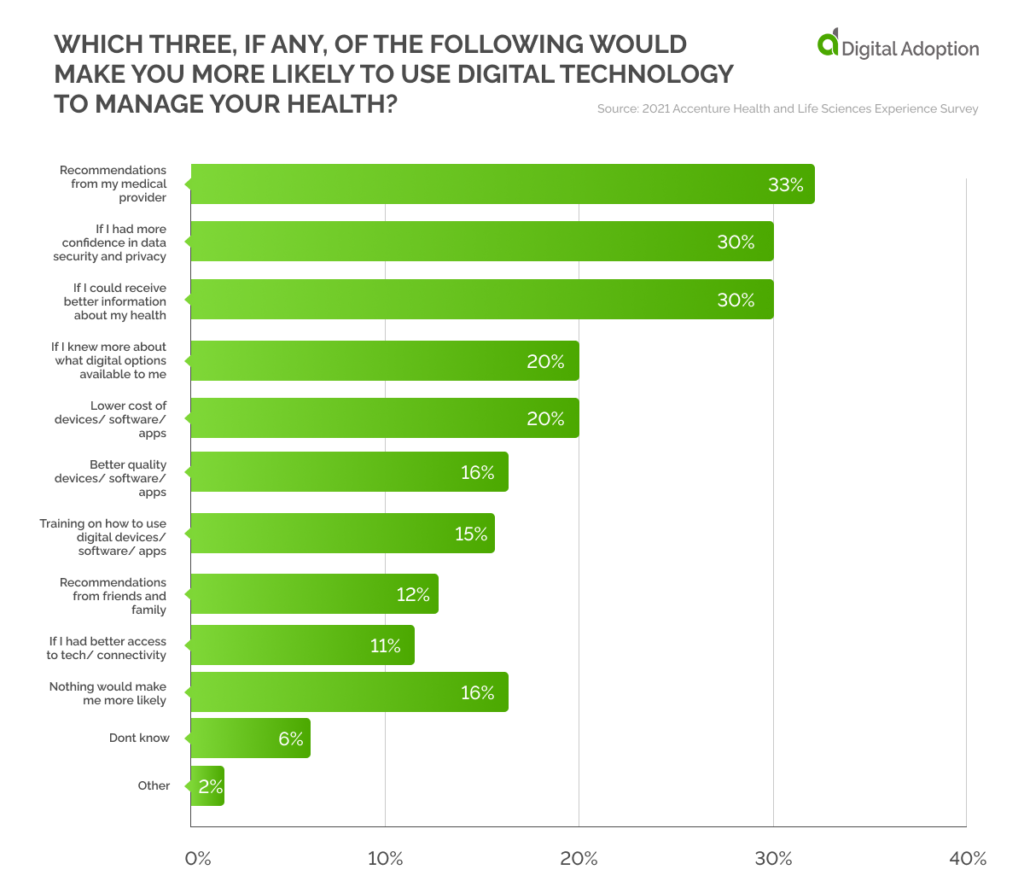
Reasons for Digital Adoption
While U.S. consumers quickly adapted to digital health, 33% said their medical provider should validate such technology. The proliferation of health apps and wearables has made U.S. consumers cautious about their choices.
This is also reflected in 30% of them insisting that confidence in data security and privacy will help them use digital technology more. It is important to note that consumers are least bothered about the software quality or cost of the device. Regarding health, their primary aim was to ensure that the apps had no security issues and that their physician recommended them.
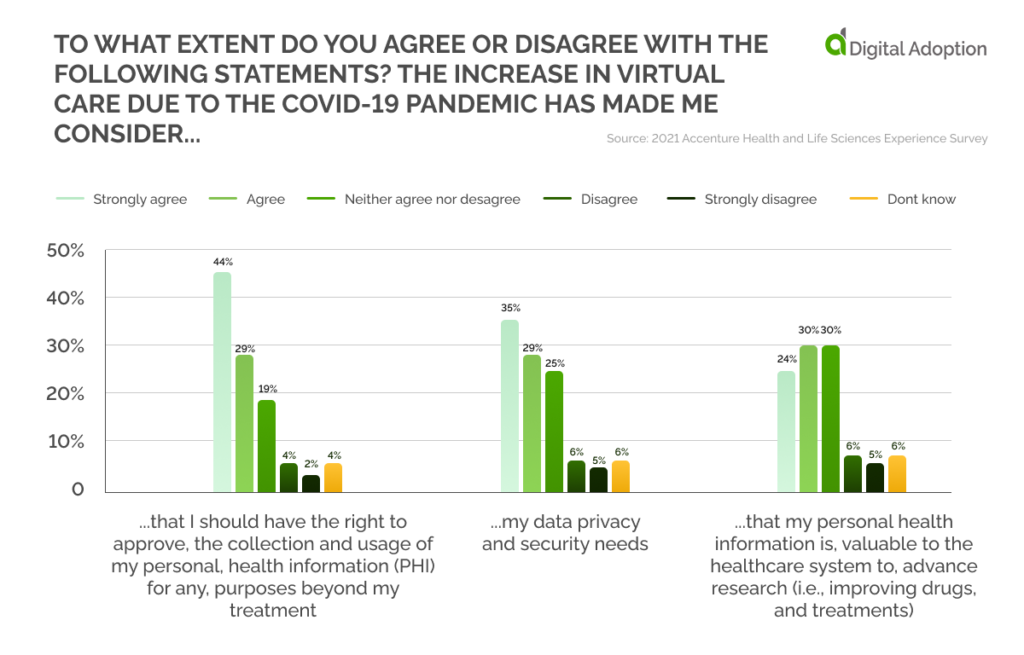
Digital Technologies Used
Concerns about digital security and privacy were chief issues for digital health enthusiasts in the U.S. About 44% of U.S. consumers strongly agreed in 2021 that they should have the right to approve collecting and using personal health information for purposes beyond their treatment.
About 35% strongly agreed that the increase in virtual care due to the Covid-19 pandemic has made them consider their data privacy and security needs.
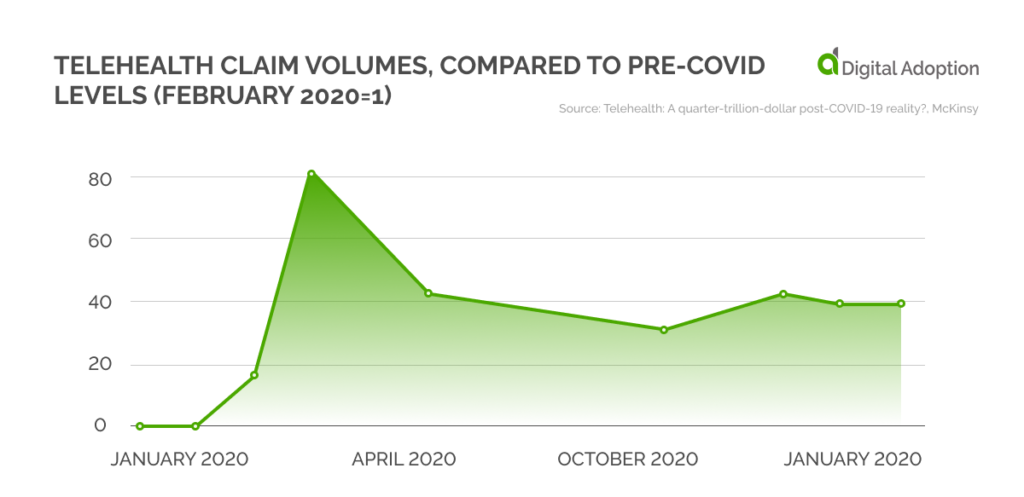
Telehealth Claims
An analysis of telehealth claim volumes in the U.S. showed that such claims had spiked to 78 times the pre-Covid levels in April 2020 after the cases started to spread like wildfire. The severe movement restrictions on the initial days and the sudden surge in ailments meant that tele-consults were the only way out. The safety of the patients and the doctors also played a vital part in this surge.
Though the restrictions eased and the fear of catching the virus subsided a bit in the following months, telehealth claims continue to be 38 times more than what they were before the pandemic.
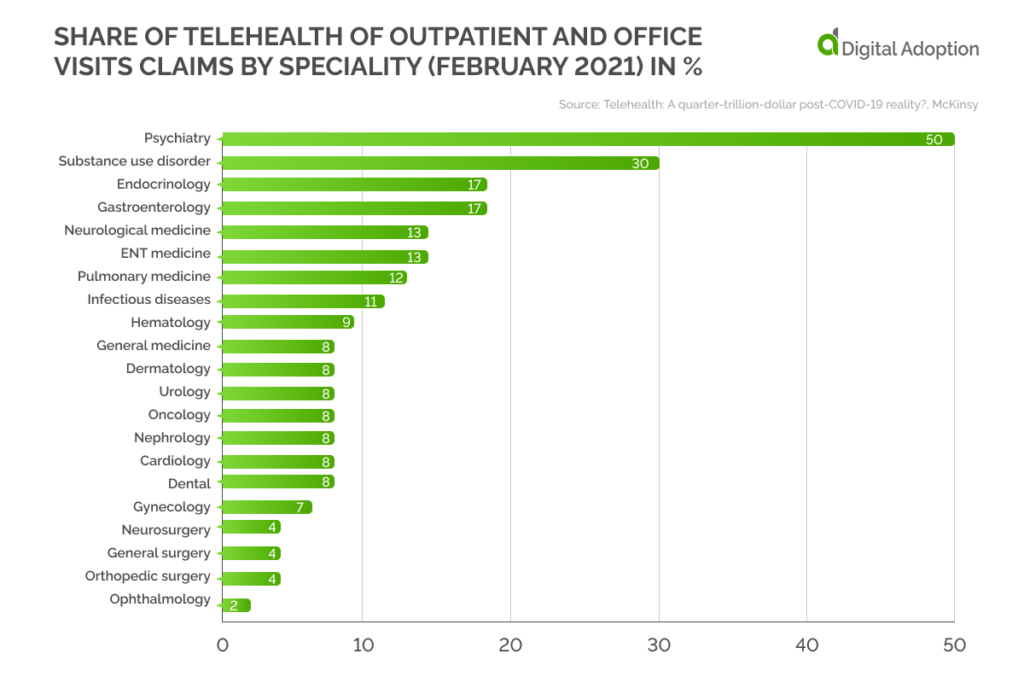
Specialization-wise Penetration
While telehealth consultations have drastically improved across the U.S. after the pandemic, the increase was not recorded across all specializations. The psychiatry specialization, which requires negligible physical contact, recorded the biggest surge in telehealth penetration. In February 2021, at least 50% of psychiatry outpatient claims were made online.
Telehealth penetration was higher among patients getting treated for substance use disorder. However, the share decreased to less than 5% when it came to specialties such as general surgery, orthopedic surgery, and ophthalmology, as physical examination of the patient is a must in such cases.
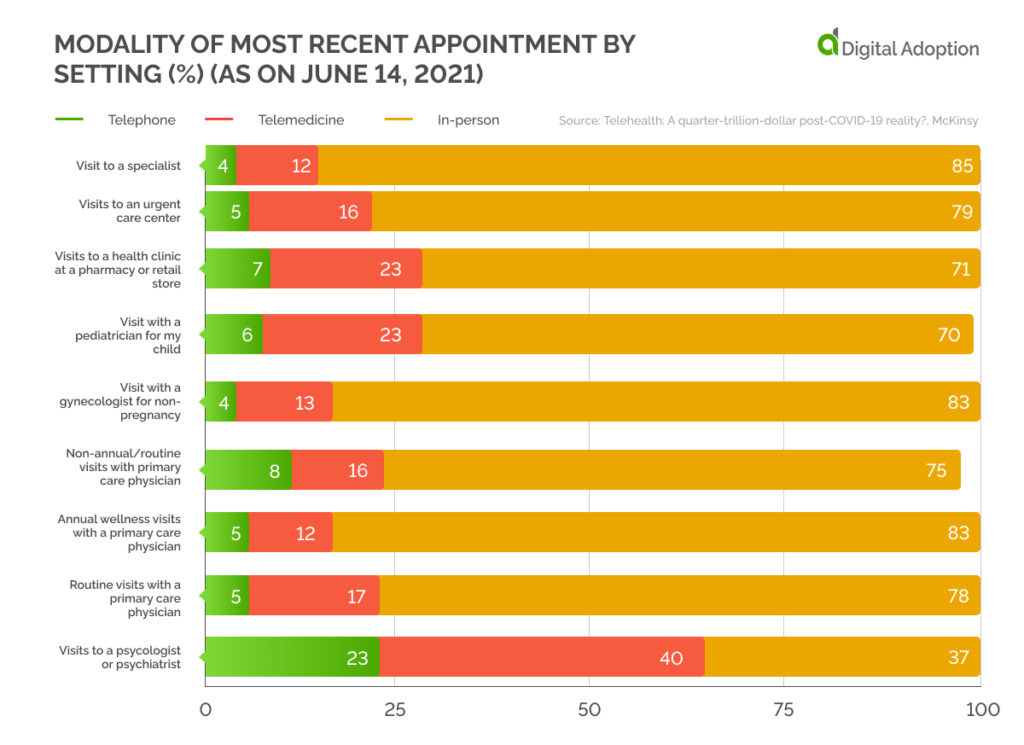
Modality of Appointments
When U.S. customers were asked about their most recent type of appointment on June 14, 2021, only 31% of psychiatric/psychological patients said they met their consultant in person. This further shows how the penetration of telehealth has been disproportionately higher in the psychiatry specialization.
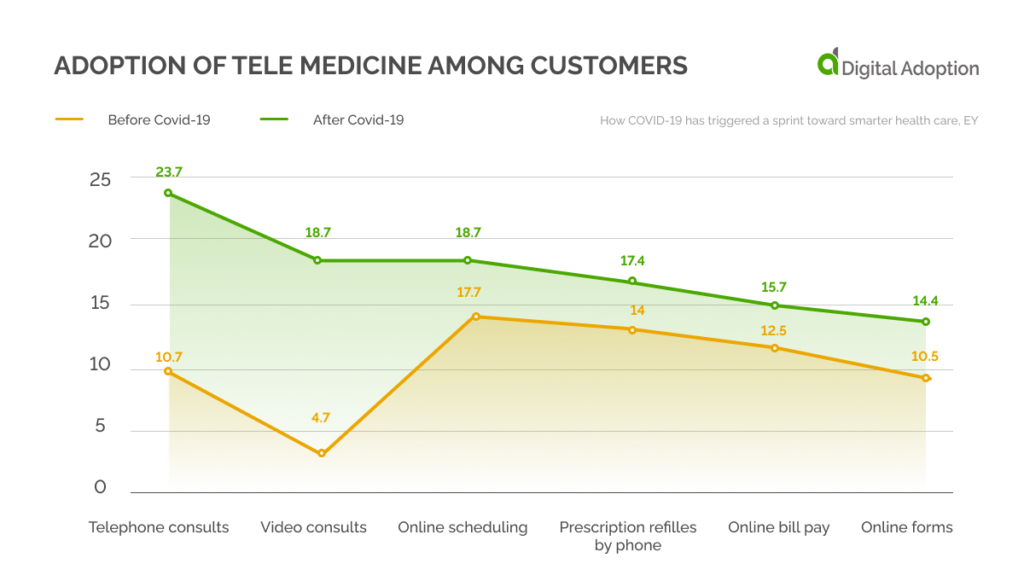
Digital Health Adoption Rates
When U.S. residents were asked about the adoption of telemedicine, only 4.7% of patients said they attempted it before COVID-19. The share increased to 18.7% after the pandemic. Before the pandemic, only 10.7% of patients consulted doctors over the telephone, while 23.7% made phone consults after the advent of the pandemic.
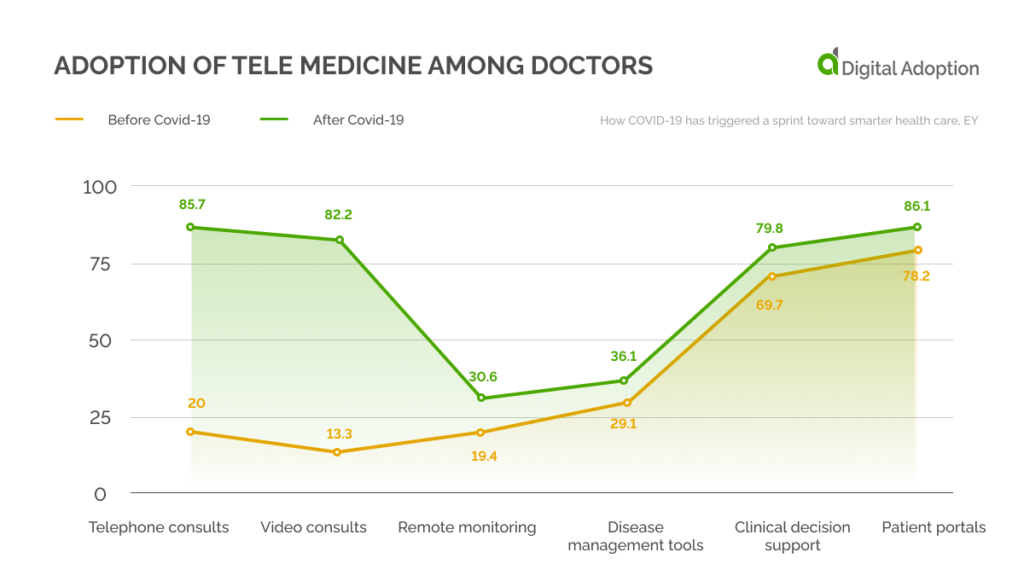
When a similar question was posed to doctors in the U.S., stark differences were observed before and after the pandemic. Only 20% of doctors consulted patients over the telephone before the pandemic, and the share increased to 85% after Covid-19. A similar sharp spike in doctor consults was also observed in video consults.
Top Reasons for Digital Adoption
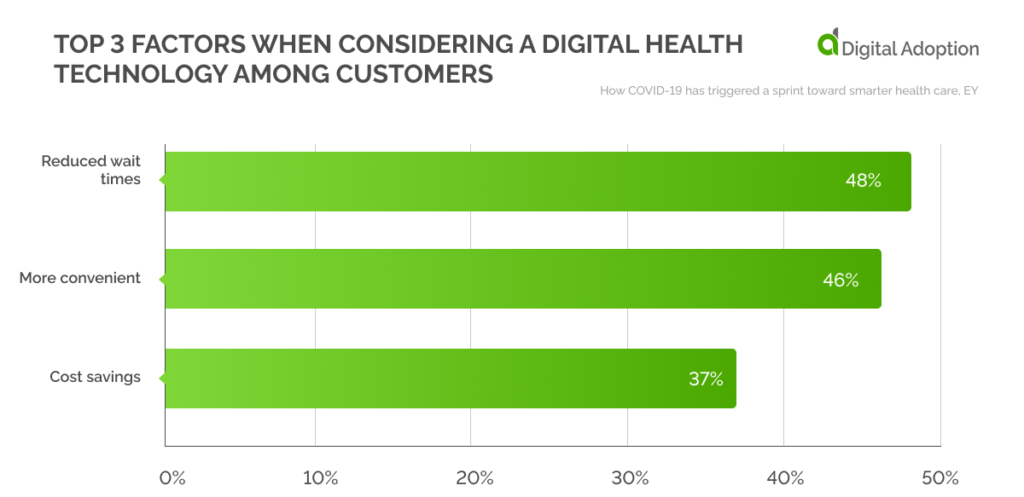
When asked to list the top three factors that helped U.S. customers consider digital health technology, 48% said they were drawn towards it as it helped reduce wait times. Convenience and cost savings were also quoted as the main reasons.
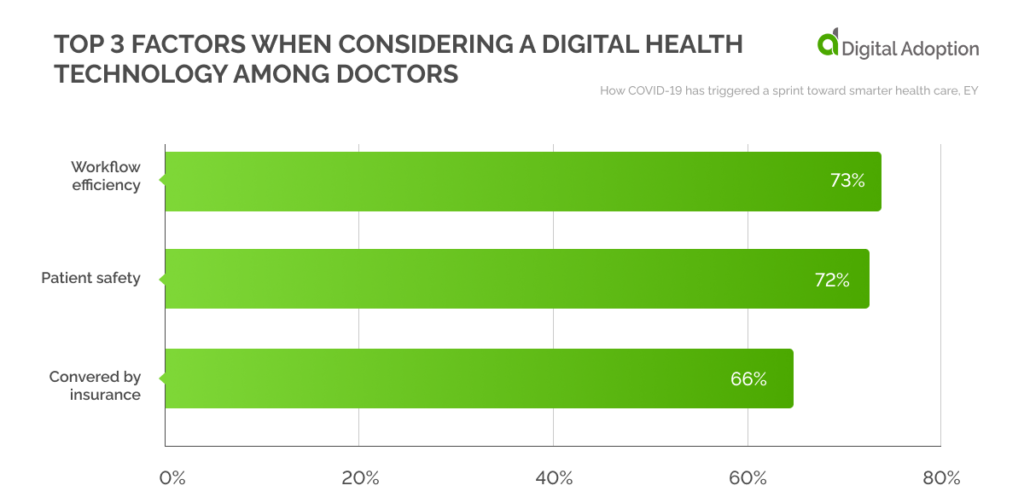
When the same question was posted to U.S. doctors, 73% cited workflow efficiency. Patient safety and insurance coverage were also among the top three reasons.
Conclusion
The survey results unequivocally indicate that most U.S. patients express satisfaction with transitioning to digital consultations and virtual disease management. Nonetheless, moving forward, addressing their apprehensions regarding data privacy and security is imperative.
Implementing robust policies and regulations is crucial to assuring U.S. citizens that their health information will remain confidential, not disclosed without consent, and not exploited for profit, thereby fostering even greater acceptance and adoption of digital healthcare solutions.




![4 Best AI Chatbots for eCommerce [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/4-Best-AI-Chatbots-for-eCommerce-2025-img-300x146.jpg)


![13 Digital Transformation Enablers [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/13-Digital-Transformation-Enablers-2025-img-300x146.jpg)



![4 Best AI Chatbots for eCommerce [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/4-Best-AI-Chatbots-for-eCommerce-2025-img.jpg)

