As businesses grow, scaling sales becomes a top priority.
Yet, only 39% of a sales rep’s time is actually spent selling, indicating that there’s significant room for improvement in sales productivity.
Having a structured approach to sales is essential to unlocking more value. Research from HBR reveals that 50% of top-performing sales teams adhere to well-defined processes, while only 28% of underperforming teams do the same.

As your company expands, adapting your sales department structure becomes crucial to meet evolving demands.
This article will explore modern sales department structures, discussing different types, key roles, and functions within sales teams. We’ll also provide guidance on building a structure that aligns with your business’s size and industry requirements.
- What is a sales department structure?
- What are the different types of sales department structures?
- What are the different roles in a sales department structure?
- What are the functions of a sales department structure?
- How to build a sales department structure
- Tailoring your sales structure for success
- People Also Ask
What is a sales department structure?
A sales department structure is a framework that outlines the hierarchy, roles, and responsibilities of a sales team.
A good sales structure does more than increase sales. It unifies communication and makes things run smoothly. When everyone knows their role, they understand what to do and can help make decisions.
What are the different types of sales department structures?
Sales department structures can take many forms depending on a business’s specific needs.
It’s important to find the problem you want to solve before creating a new structure. Once you know the issues, the structures below can help you shape your sales department to meet those needs.
Let’s take a look at the sales department structures that most businesses use:
Island sales department structure
In the island sales team structure, sales representatives manage the whole sales process. This setup promotes independence and helps build strong client relationships. Sales reps work alone, creating a flexible environment to meet client needs.
Advantages
- Personalized service
- Clear accountability
- Creative problem-solving
Disadvantages
- Limited collaboration
- Inconsistent sales approaches
- Risk of knowledge silos
Assembly line department team structure
An assembly line sales department has a more organized structure. Teams have specific roles and focus on individual tasks. This setup improves efficiency and creates clear processes that match workers with their skills.
Advantages
- Increased efficiency
- Consistent sales processes
- Specialization of tasks
Disadvantages
- Limited creativity
- Delayed communication
- Reduced client interaction
Pod sales department structure
A pod sales team structure combines different sales methods. In this setup, sales reps share tasks and collaborate on projects. It lets employees use their strengths and adjust as needed. Each pod works semi-independently to achieve shared sales goals.
Advantages
- Enhanced collaboration
- Shared expertise
- Increased motivation
Disadvantages
- Conflicting priorities
- Potential for uneven workload
- Dependence on group dynamics
Outside sales department structure
An outside sales team structure focuses on reps who meet clients away from the office. This model is important for teams that create personalized client relationships. Sales reps often visit clients at their locations, which boosts service quality and improves how clients view the company’s value.
Advantages
- Strong client relationships
- Personalized sales experiences
- Flexibility in meeting locations
Disadvantages
- Limited support resources
- Potential isolation
- Higher travel costs
Inside sales department structure
An inside sales team structure has salespeople who work from the office. They connect with clients through emails, video calls, and phone calls. Many companies prefer this setup because it is efficient and allows for quick responses.
Advantages
- Cost-effective
- Quick response times
- Streamlined communication
Disadvantages
- Limited personal interaction
- Potential for disengagement
- Dependence on technology
Geographical sales department structure
A geographical sales department structure gives each sales representative a specific region to manage. They focus on building a chain of command and making sales in their assigned areas. This setup is helpful for larger companies entering new markets. Sales reps can better understand local clients and their needs.
Advantages
- Local market knowledge
- Tailored sales strategies
- Reduced travel time
Disadvantages
- Unbalanced territories
- Potential for competition
- Limited collaboration across regions
Product-specific sales team structure
The product sales team structure has salespeople who focus on product management. This is often used in IT companies where understanding the product is important. It helps salespeople become experts. They can then provide better solutions to customers. This structure leads to stronger relationships with clients.
Advantages
- Deep product knowledge
- Targeted sales strategies
- Effective client solutions
Disadvantages
- Limited flexibility
- Potential gaps in support
- Reduced cross-selling opportunities
What are the different roles in a sales department structure?
A sales department structure has many different roles. As technology evolves, new roles are created, and others are transformed.
Understanding the roles and responsibilities of your sales department is important. It gives you a clear line of accountability and guarantees everyone is aligned with sales targets.
Let’s take a closer look at the different roles in a sales department structure:
- Sales director: A sales director leads sales operations. They make plans to help the team reach sales goals and work together to earn more money.
- Account manager: An account manager helps clients after they buy something. They build strong relationships, understand client needs, and help clients get the best use from the product or service.
- Sales engineer: A sales engineer knows the product well and helps the sales team understand how it works. They explain the product’s features to customers and show how it can solve their problems.
- Customer success manager: A customer success manager checks to make sure clients are happy with the product. They help clients reach their goals and fix any issues to keep customers satisfied.
- Sales enablement manager: A sales enablement manager gives the sales team resources and training. They make sure salespeople have what they need to do well in their jobs.
- Sales coach: A sales coach helps salespeople improve their skills. They give advice and training to help the team do better and meet their sales goals.
- Sales development representative (SDR): An SDR finds potential customers and checks if they are interested in the product. They reach out to leads and gather information before passing them to the sales team.
- Business development representative: A business development representative looks for new ways to boost sales. They research potential clients, reach out, and build relationships to help the company grow.
- Sales operations manager: A sales operations manager makes the sales process better. They analyze data and provide insights to help improve sales team performance.
- Regional sales manager: A regional sales manager is in charge of sales in a certain area. They lead a team of sales representatives and make sure they meet their goals.
- Channel sales manager: A channel sales manager builds relationships with partner companies that sell the product. They help partners with the resources they need to drive sales.
- Territory sales manager: A territory sales manager is responsible for sales in a specific area. They work to find new business and create plans to boost sales in that region.
What are the functions of a sales department structure?
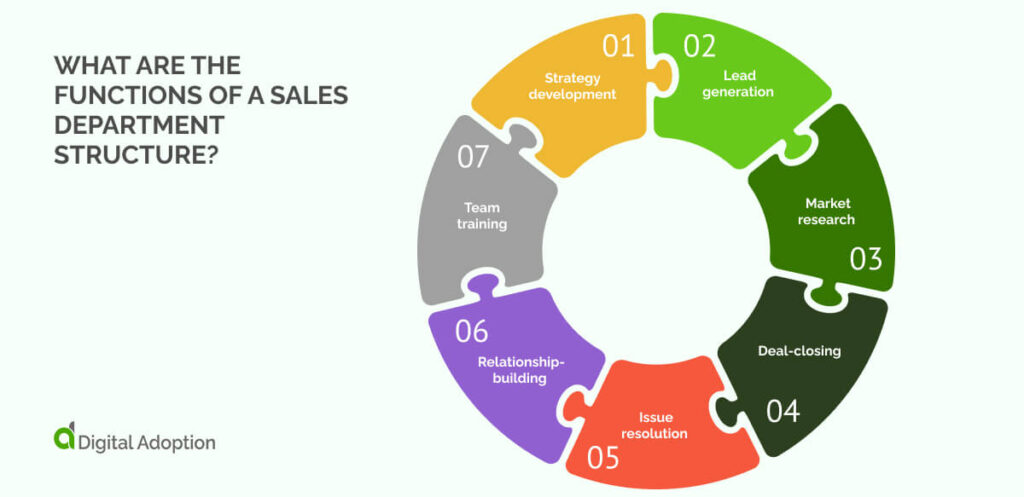
Sales departments are often large and have many different functions. Understanding the roles of each team will help you create an efficient sales structure.
Let’s take a look at the most common functions of a sales department structure:
Strategy development
One key function in sales is strategy development. Senior sales managers create strategies that align with the company’s goals. They analyze sales data to understand market trends and adjust strategies to drive product-led growth. This ensures the sales team remains competitive and responsive to changing customer needs and market conditions.
Lead generation
Lead generation is another important function of a sales department. It involves finding customers interested in the company’s products or services. Sales teams use various methods to identify leads. This can include online research, networking, and referrals. Generating leads helps businesses grow and secures future opportunities.
Market research
Market research helps sales teams make sense of their market. It’s a vital function that is often overlooked within the sales process. Sales teams gather and analyze data about customers and competitors. This information helps them make better decisions. With these insights, teams can adjust their strategies to improve their sales efforts and achieve success.
Deal-closing
The deal-closing reps work closely with the lead generation team to ensure sales are finalized. This team is responsible for following up on leads and closing the deal. Throughout the latter stages, they support quality assurance and customer satisfaction. Their goal is to turn potential leads into customers.
Issue resolution
The issue resolution team identifies and fixes customer problems. They respond to concerns and find appropriate solutions. These teams deal directly with sales-related issues and help customers feel supported. Quickly resolving problems boosts customer satisfaction and builds positive relationships.
Relationship-building
The relationship-building team focuses on creating and maintaining strong connections with customers. They engage with clients to understand their needs and preferences. This team works to breed trust and loyalty and ensure customers feel valued. Strong relationships lead to repeat business and long-term partnerships for businesses.
Team training
Sales training is another important function of the sales department. Investing in team training ensures that employees are updated with the latest processes. The team uses sales training software to provide interactive resources and track progress.
How to build a sales department structure
Now that you have a better grasp of the roles in a sales department, it’s time to learn how to build one of your own.
We will explore creating an effective sales department structure for different business sizes.
Let’s look at the specific strategies for small, medium, and large companies:
Small business
Small-sized businesses should focus on the following:
Versatile sales roles
In a small business, sales roles should be versatile. Team members should handle multiple tasks, like selling and customer support. This flexibility allows the team to adapt to changes. Employees can learn new skills, making them more valuable. Versatile roles help the business respond better to customer demands.
Scalable sales processes
Sales processes must be scalable for growth. Start with basic steps, such as lead generation and follow-up. As the business expands, these processes can develop. Documenting procedures helps the team maintain consistency. A scalable approach ensures that sales efforts remain efficient as the company increases its sales volume.
Focus on customer relationships
Building strong customer relationships is vital. Prioritize listening to customer needs and feedback. A strong connection leads to repeat business, and regular communication helps build trust. Focusing on relationships creates loyal customers who can contribute to long-term business growth.
Medium business
Medium-sized businesses should focus on the following:
Specialized sales functions
Specialized sales functions are crucial in medium-sized businesses. Teams focus on areas such as lead generation, closing deals, and maintaining relationships. This helps employees develop their skills and expertise, leading to better performance. This approach ensures that each sales function contributes to overall success.
Sales enablement and training
Sales enablement is essential for a medium business. Providing digital onboarding and training means that sales teams are updated on best practices and industry trends. Regular training sessions improve skills and boost confidence. Empowering the team with the right tools improves cogency and leads to better sales.
Data-driven performance management
Data-driven performance management identifies trends and measures individual performance. This information enables managers to make informed decisions about training and resource allocation. A focus on data ensures that medium-sized businesses continually improve and meet goals.
Large business
Large-sized businesses should focus on the following:
Complex, multi-tiered structure
Large businesses should use a complex, multi-tiered sales structure. This structure includes various teams responsible for different functions, such as lead generation and account management. Each tier focuses on specific goals, allowing for better coordination. This structure supports large-scale operations and drives overall effectiveness.
Global and regional alignment
For large businesses, global and regional alignment is essential. It assures sales teams understand local markets while adhering to a unified strategy. Virtual collaboration across regions promotes consistent messaging and brand integrity. Meeting local demands enhances customer relationships and success in diverse markets.
Advanced sales operations and analytics
Advanced sales operations and product analytics are crucial for large businesses. These tools offer real-time data on sales performance and market trends. Analyzing this data helps companies make informed decisions. A data-driven approach leads to better strategies and improved resource allocation.
Tailoring your sales structure for success
Sales department structures are complex, but investing in the right one is essential for success.
Start by understanding your sales goals. Consider potential challenges and how to address them. Identifying the right structure will help you customize your sales department effectively.
Once you understand your purpose, think about what problems you might face.
How can you troubleshoot these problems before they arise? Is there a structure that suits your needs or challenges?
Answering these questions allows you to create a structure that aligns with your specific requirements and supports your objectives.
Remember, the best structure adapts to your unique challenges and stimulates growth. Tailoring this aspect of your business can improve performance and outcomes.
People Also Ask
-
What is a sales department?A sales department is responsible for selling products or services. Its main goal is to generate revenue. The team manages customer relationships and develops effective sales strategies. It also analyzes market trends. This ensures the business meets its objectives and enhances overall performance.
-
What is the best way to structure a sales team?The best way to structure a sales team depends on the companys size and goals. Common options include functional, geographic, and product-based structures. Each type has advantages. Choosing the right structure aligns with business strategies and meets customer needs, improving overall sales performance.
-
What is the functional structure of a sales organization?A functional structure organizes a sales team by specialized roles. These roles can include account management, lead generation, and customer support. This setup promotes efficiency and expertise in each area. It ultimately leads to improved sales performance and increased customer satisfaction across the organization.













