Major developments in AI have seen it take the world by storm. AI is no longer reserved for far-flung sci-fi plots on the silver screen; it’s making real-world impacts across every industry.
Finance and accounting are two sectors particularly focused on capturing value through AI. Research shows that the financial services industry invested $35 billion U.S. in AI during 2023.
Today, machines can be trained on data to perform complex actions traditionally executed by humans. These advances in AI have ushered in a new era in accounting, and their diverse applications have sparked innovations across various domains.
This translates to increased agility and productivity across the board, with access to analytical insights, financial forecasting, pattern detection, and automation capabilities, to name a few.
This article examines AI’s role in accounting, its impact on accountants’ roles, and strategies for accountants to thrive in an AI-driven future.
- What is artificial intelligence (AI) in accounting?
- How can accountants use artificial intelligence (AI)?
- Can artificial intelligence (AI) replace accountants?
- Artificial intelligence (AI) in accounting advantages
- Artificial intelligence (AI) in accounting disadvantages
- How can accountants stay relevant with Artificial intelligence (AI)?
What is artificial intelligence (AI) in accounting?
Artificial intelligence (AI) in accounting refers to the use of advanced technologies like machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), computer vision (CV), and natural language processing to automate, enhance, and optimize various financial tasks and processes.
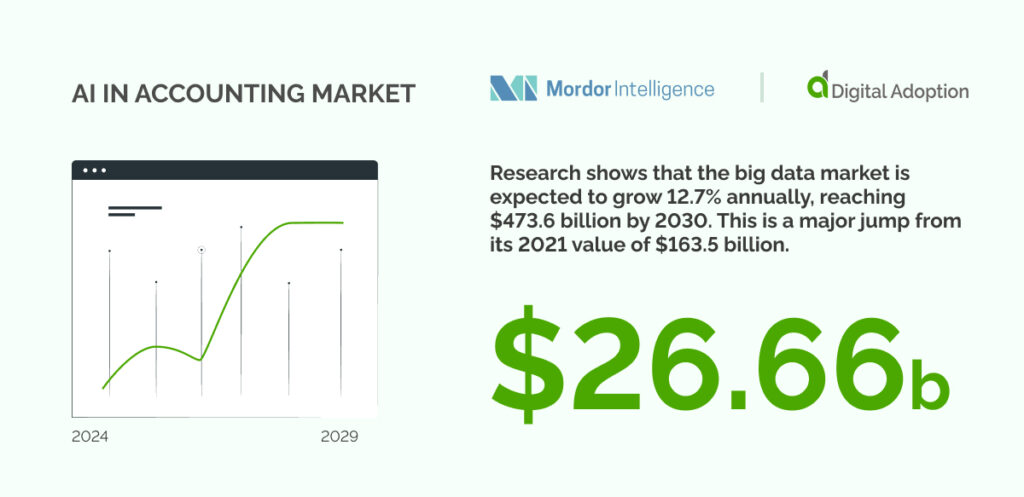
According to Mordor Intelligence, the AI in accounting market is expected to expand significantly, growing from USD 4.73 billion in 2024 to USD 26.66 billion by 2029. This represents a robust annual growth rate of 41.27% during this period.
As the market grows, AI will transform accounting practices across various financial tasks. These advanced technologies are just some examples of how AI drives innovation in the field.
Machine learning in accounting focuses on teaching algorithms to identify patterns in financial data. Training these models on historical records and transaction details enables computers to independently generate insights, detect anomalies, and predict economic trends based on the data they analyze.
Deep learning in accounting is an advanced form of Machine Learning that utilizes interconnected algorithms resembling the human brain’s neural network. This approach allows DL models to learn and adapt from complex financial data, enhancing their ability to perform nuanced tasks such as automating invoice processing, detecting fraudulent activities, and interpreting unstructured financial documents.
Computer vision in accounting utilizes advanced image recognition technologies to automate the extraction and processing of financial documents. This technology enables systems to read and interpret various forms of financial paperwork, such as invoices, receipts, and bank statements, converting them into structured data for further analysis.
Natural language processing in accounting enhances the ability to analyze and interpret textual data from financial documents and communications. NLP enables systems to extract relevant information from unstructured data sources such as contracts, emails, and financial reports, transforming it into structured, actionable insights.
How can accountants use artificial intelligence (AI)?
Integrating AI in accounting is transforming key processes and introducing new ideas and concepts that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity across the industry.
Let’s take a closer look.
Document review
AI is revolutionizing document review in accounting by automating the evaluation of contracts and financial documents. Traditional manual review processes are labor-intensive, time-consuming, prone to human error, and often inconsistent.
AI-powered platforms use natural language processing and machine learning to analyze large volumes of documents, identify key information, and flag anomalies. This automation allows accountants to focus on higher-value tasks, ensuring compliance and accuracy while reducing the risk of oversight and improving overall efficiency.
Auditing
In auditing, AI is enabling more thorough and efficient data analysis. Traditional audits often rely on sampling and manual checks, which can miss crucial details and are susceptible to errors. By embedding AI technology into the audit process, accountants can analyze and extract data from unstructured sources and scrutinize large datasets with precision.
AI also helps auditors detect patterns, identify anomalies, and more effectively assess risks of material misstatement due to fraud. This technological enhancement improves audit quality and accuracy, allowing auditors to provide clients with deeper insights and strategic advice.
IT
AI enhances IT processes within accounting firms by significantly boosting productivity and innovation. Customized AI software applications can automate data synthesis, code completion, documentation generation, and code reviews, streamlining development processes. These tools can analyze and correct code, predict errors, and offer optimization suggestions, leading to 20% to 50% productivity gains.
Additionally, enterprise versions of AI models like ChatGPT-4 assist professionals in both routine and complex tasks, facilitating better decision-making and faster problem-solving, thereby enhancing overall IT efficiency within accounting practices.
Client Solutions
AI is improving client solutions in accounting by providing sophisticated, reliable, and scalable tools. Frameworks like KPMG’s Trusted AI help design, build, deploy, and maintain AI-driven solutions tailored to client needs. AI enhances the ability to analyze vast amounts of financial data, generate actionable insights, and automate routine processes, leading to more informed decision-making and improved efficiency.
These AI-driven client solutions ensure compliance, reduce risk, and can be customized to address specific industry challenges. They empower businesses to leverage advanced technologies and achieve better financial outcomes.
Can artificial intelligence (AI) replace accountants?
As AI technology advances and integrates into the accounting industry, it’s important to consider its impact on routine tasks, complex operations, and ethical standards and whether it will ultimately replace human accountants in these areas.
Let’s take a closer look.
Routine accounting tasks with AI
AI is highly effective at performing routine accounting tasks such as data entry and transaction processing. This allows AI to manage large volumes of data quickly and accurately, freeing human accountants to focus on more strategic and complex work. While AI can significantly enhance efficiency in these areas, it does not possess the critical thinking and problem-solving skills that human accountants bring.
While AI will likely replace many routine tasks, human accountants will still be necessary for tasks requiring interpretation, strategic advice, and professional judgment to ensure the accuracy and integrity of financial information.
AI in complex accounting operations
AI still struggles with complex accounting operations that require significant judgment and expertise, such as tax planning, auditing, and specialized financial advice. These areas necessitate a deep understanding of legal and regulatory requirements, industry-specific knowledge, and client-specific circumstances, which AI currently lacks.
Human accountants excel at analyzing complex data, identifying trends, and making informed recommendations. They also provide a personalized touch in client interactions.
AI is unlikely to replace human accountants in complex operations, but it can enhance their efficiency and effectiveness by handling more routine aspects.
Addressing ethical concerns with AI in accounting
As AI continues to develop in accounting, addressing ethical concerns becomes crucial. AI systems may not always align with human moral values, raising issues of data privacy, security, bias, and fairness.
Human accountants play a vital role in maintaining ethical standards and accountability. They are trained to identify and address potential biases in financial reporting and can critically analyze data to challenge assumptions and inconsistencies.
This scrutiny is essential for ensuring reliable, unbiased financial information and maintaining stakeholder trust. While AI can assist with ethical concerns, it cannot replace human accountants’ fundamental role in upholding ethical standards.

Artificial intelligence (AI) in accounting advantages
As AI technology advances, businesses and accounting firms must proactively explore and implement AI solutions to stay competitive.
They should research the potential applications and benefits to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making in their financial operations.
Let’s take a closer look.
Fraud detection
AI enhances fraud detection in accounting by using machine learning algorithms to analyze transaction patterns and identify anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity. These systems can continuously monitor large volumes of data in real-time, flagging suspicious transactions for further review.
Businesses and accounting firms must understand that AI improves the accuracy and speed of fraud detection compared to traditional methods, reducing the risk of financial loss. However, combining AI with human oversight is crucial to validate findings and ensure that the AI system is trained on diverse and comprehensive data sets to avoid false positives.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics leverages AI to analyze historical data and forecast future trends, helping businesses make informed financial decisions. By applying statistical models and machine learning algorithms, AI can predict cash flow, market trends, and economic performance, allowing firms to proactively address potential issues.
Accounting firms should integrate predictive analytics into their strategic planning to enhance decision-making accuracy and risk management. It’s important to ensure that the data used is relevant and up-to-date, as the quality of predictions depends on the quality of the input data.
Automated data entry
Automated data entry uses AI to streamline inputting of financial information into accounting systems. This technology reduces the need for manual data entry, minimizing errors and increasing efficiency. AI systems can quickly process invoices, receipts, and other documents, accurately transferring data into accounting software.
Businesses should implement automated data entry to save time and reduce administrative costs. However, they must also ensure proper validation mechanisms are in place to handle any discrepancies or exceptions that the AI might not resolve.
Invoice processing
AI-driven invoice processing automates invoice data extraction, validation, and entry into accounting systems. This technology speeds up the accounts payable process, reduces human error, and improves accuracy. Using optical character recognition (OCR) and machine learning, AI can handle various invoice formats and detect discrepancies.
Accounting firms should adopt AI for invoice processing to enhance operational efficiency and accelerate payment cycles. Integrating these systems with existing ERP solutions and ensuring that the AI is trained to recognize the specific invoice structures used by different vendors is crucial.
Account reconciliation
AI assists in account reconciliation by automating and comparing financial records across different accounts and systems. This technology identifies discrepancies and matches transactions with high precision, significantly reducing the time and effort required for reconciliation.
Businesses should leverage AI to ensure their financial statements are accurate and up-to-date. Effective account reconciliation with AI improves transparency and compliance. Firms should periodically review AI-generated results and ensure the system is calibrated to handle complex reconciliation scenarios.
Data analysis
AI-powered data analysis enables firms to extract actionable insights from large datasets by identifying patterns, trends, and correlations. This advanced analysis supports strategic decision-making by better understanding financial performance and business operations.
Accounting firms should utilize AI for data analysis to enhance their analytical capabilities and deliver more valuable insights to clients. To maximize benefits, businesses must ensure that the AI tools are tailored to their specific data needs and that users are trained to interpret and act on the insights generated effectively.
Artificial intelligence (AI) in accounting disadvantages
If businesses aren’t careful and tactful in their approach to integrating AI into accounting, they risk encountering substantial challenges. These issues could undermine operational efficiency, compromise data security, and impact overall effectiveness.
Without a thoughtful strategy, companies may face significant drawbacks that affect their competitive position and long-term success in the industry.
Let’s take a closer look.
Job displacement
AI’s integration into accounting can lead to job displacement for those performing routine tasks. Automating activities such as data entry and transaction processing reduces the need for human intervention, potentially resulting in layoffs or reduced hiring for entry-level positions.
This shift necessitates that employees acquire new skills to remain relevant in the evolving job market. As traditional roles become obsolete, there is an urgent need for strategic workforce planning and investment in employee retraining programs to help displaced workers transition into more complex or supervisory roles within the industry.
High implementation costs
Adopting AI solutions in accounting often involves substantial initial costs, including software purchase, system integration, and comprehensive staff training. These expenses can be particularly burdensome for small and medium-sized enterprises, which may struggle to allocate resources effectively.
Ongoing maintenance and updates also contribute to long-term financial commitments. The high costs associated with AI technology can create a disparity between larger organizations that can afford these investments and smaller firms that may lag behind in leveraging advanced tools, potentially impacting their competitive edge.
Data privacy and security risks
AI systems necessitate access to extensive financial data, which raises significant concerns regarding data privacy and security. If these systems are compromised through cyberattacks or other breaches, sensitive information could be exposed or misused. Protecting against such vulnerabilities requires robust security measures, including encryption and regular audits.
Failure to secure data adequately can result in severe legal repercussions, financial penalties, and damage to an organization’s reputation. Ensuring that AI systems comply with stringent data protection regulations is crucial to safeguarding confidential client information.
Algorithmic bias
AI algorithms can inadvertently reinforce existing biases present in historical data, leading to biased decision-making and recommendations. This issue arises when the training data reflects prejudiced patterns or discriminatory practices, which AI systems then perpetuate. For instance, financial recommendations or risk assessments could be skewed against certain groups or demographics.
Identifying and correcting these biases demands continuous oversight and adjustments, which can be complex and resource-intensive. Ensuring fairness and equity in AI applications requires ongoing vigilance and involvement from diverse stakeholders to mitigate potential adverse impacts.
Loss of human judgment
AI systems excel in processing vast amounts of data but lack the human judgment needed for nuanced decision-making. Critical accounting tasks often involve ethical considerations, contextual understanding, and professional insight that AI cannot replicate. Relying solely on automated solutions might undermine the ability to address complex scenarios or provide personalized client support.
Human accountants bring a depth of expertise and experience that complements AI’s capabilities. Balancing technology with human oversight is essential to maintain the quality and integrity of financial analysis and advisory services.
System dependence and errors
Heavy reliance on AI systems can lead to complacency and decreased manual oversight. If AI tools malfunction or produce erroneous outputs due to misconfiguration or data issues, errors might go undetected without sufficient human intervention. This over-dependence can diminish the quality of financial reporting and decision-making if professionals do not actively monitor and validate AI-generated results.
Ensuring accuracy requires a balanced approach, incorporating regular checks and maintaining skilled personnel to oversee and correct potential system errors, safeguarding against inaccuracies, and maintaining operational integrity.
How can accountants stay relevant with Artificial intelligence (AI)?
To remain relevant in an era of AI, accountants should embrace technology while honing their unique human skills.
Understanding AI’s capabilities allows accountants to identify and fill gaps where technology falls short, such as advanced data analysis and client interactions. Professionals can enhance their efficiency and client engagement by upskilling in these areas.
Cultivating soft skills is equally important. While AI excels at processing data, it lacks human intuition, judgment, and interpersonal skills. To stand out, accountants should focus on developing communication, problem-solving, critical thinking, and relationship-building abilities.
Moreover, AI’s automation of routine tasks presents an opportunity for accountants to shift their focus to higher-value activities. AI allows accountants to focus on strategic financial analysis, risk management, and personalized insights.
This transforms accountants from mere number crunchers into trusted business advisors.




![4 Best AI Chatbots for eCommerce [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/4-Best-AI-Chatbots-for-eCommerce-2025-img-300x146.jpg)


![13 Digital Transformation Enablers [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/13-Digital-Transformation-Enablers-2025-img-300x146.jpg)



![4 Best AI Chatbots for eCommerce [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/4-Best-AI-Chatbots-for-eCommerce-2025-img.jpg)

