Innovation management is vital in today’s dynamic business environment. This is especially because of COVID-19. This period highlighted the importance of adaptability, change management, and forward planning. But, it’s often reduced to a buzzword when companies merely adopt new technology and claim innovation. This can breed complacency and impede real progress.
Genuine innovation management demands risk-taking and creative thinking. It focuses on purpose-driven change to deliver meaningful value.
This article will detail what innovation management is and its components. It will then go through the different types of innovation management and their key frameworks. Next, it will look at successful innovation management and how to measure it.
You will learn how to implement innovation management. You will also explore its benefits and challenges. We will also look at some examples of innovation management tools.
- What is Innovation Management?
- What are the Components of Innovation Management?
- What are the Different Types of Innovation Management?
- Key Frameworks of Innovation Management
- What Does Successful Innovation Management Look Like?
- How to Measure Innovation Management
- How to Implement Innovation Management
- What are Innovation Management Tools?
- Benefits of Innovation Management
- Challenges/Risks of Innovation Management
- What’s Next For Innovation Management?
What is Innovation Management?
Innovation management is a structured approach designed to nurture, assess, and select new ideas. You do it to put the most promising ones into practice. Then, it aims to propel the value of a business or organization. This method unfolds in four critical steps. The first step involves generating ideas.
You can do this through brainstorming sessions and soliciting employee contributions. Next comes the capturing of these ideas. This step ensures that you document ideas in a manner that allows for easy sharing with important stakeholders.
The third step after this is evaluating the ideas. This involves discussing and critiquing the innovative concepts to assess their suitability for an organization. The fourth and final step is prioritizing the ideas. This is where decisions are made on which innovations to pursue, with the aim of optimizing the use of time and resources within the company.
Innovation management uses the organizational framework to enhance the employees’ capacity for generating new ideas. The effective practice of innovation management requires the engagement of every employee.
What are the Components of Innovation Management?
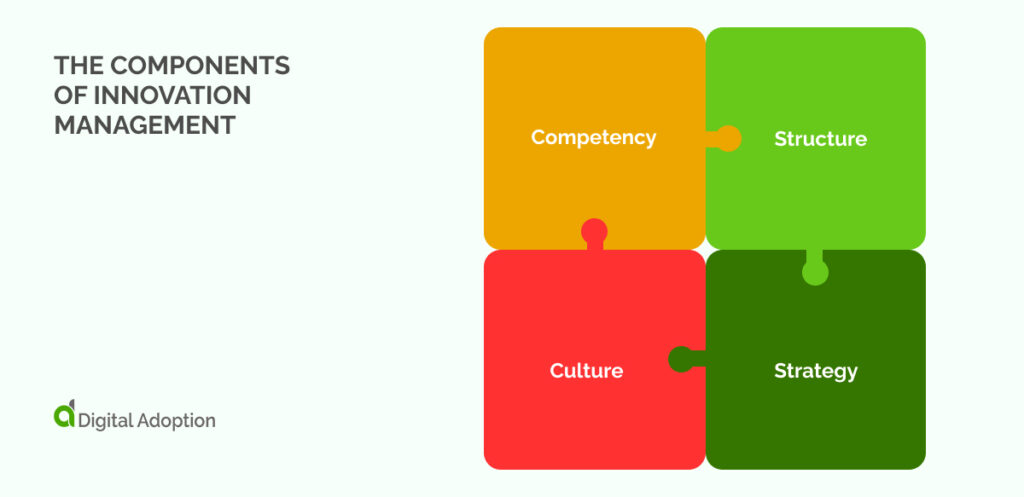
There are four components of innovation management which are:
Competency
Competency encompasses an organization’s various abilities and resources for initiating and overseeing innovation. This concept primarily focuses on human resources. Innovation is heavily reliant on the skills and collective efforts of both individuals and teams. It includes the knowledge, insights, and practical expertise of those within the organization.
Additionally, competency extends to the organization’s informational and tacit knowledge. It also includes financial resources, all critical for fostering innovation. Moreover, the capacity for innovation, such as having the time, willingness, and authority to act, is vital.
Structure
Structure pertains to the systems and processes within an organization that ease innovation. A robust organizational structure is key for managing innovation. It enables the organization to operate with greater efficiency and produce impactful ideas. For example, how management responds to employee suggestions can illustrate this point.
If management views these suggestions as calls for significant changes, they might dismiss them. So, a structure that removes barriers to innovative ideas can enhance innovation.
Culture
Culture significantly impacts an organization’s innovative capabilities. A culture that fails to encourage creativity and innovation might lead employees to suppress their ideas. Or, they might leave the organization. Corporate culture often starts at the top with leaders and managers. But, employees have a role in shaping it too.
Discussing this with management can lead to a more innovation-friendly culture. This is especially if employees see a need for more innovation. An innovation-supportive culture is marked by vision-driven leadership.
It prioritizes speed, learning through experimentation. It also gives employees the autonomy to explore new ideas. It also values employees who seek improvement. It does not penalize failure, viewing it instead as a part of the innovation journey.
Strategy
Strategy is crucial for outlining and achieving an organization’s long-term goals. A well-defined strategy allows an organization to introduce new ideas and select the best courses of action. The lack of a definite strategy can lead to inefficiency. It can also result in pursuing initiatives that don’t align with the organization’s long-term objectives.
It also involves allocating resources in a way that supports the innovation process. Over time, the allocation of resources may need adjustments. This could be to focus more on developing new ideas. Or you might want to focus on changes in resource availability.
What are the Different Types of Innovation Management?
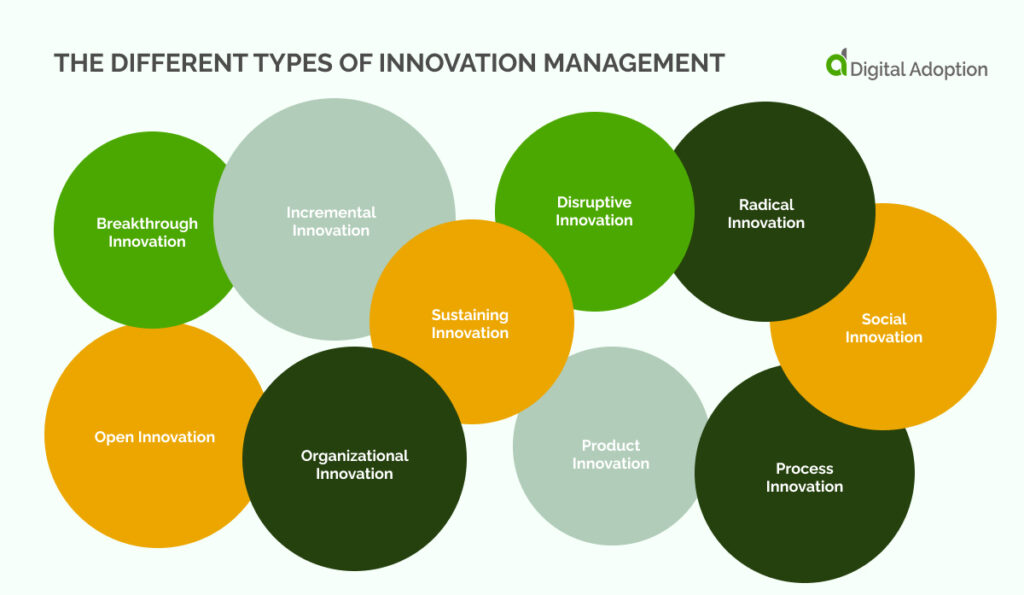
Innovation management encompasses a range of types.
Recognizing the specific category your innovation management effort aligns with is crucial:
Breakthrough Innovation
Breakthrough innovation allows a company to alter its products or services within its industry. This is especially common in technology, where competition is fierce and innovation fast-paced. Breakthroughs are valued for their potential to stand out.
Incremental Innovation
This type of innovation involves continuous improvements or changes to a company’s existing products and services. It is less risky and generally less costly. It’s vital for differentiation, enhancing current offerings, and increasing brand value.
Open Innovation
Open innovation is based on the philosophy of being open to external ideas, not just those generated internally. It involves collaboration with external business partners, entrepreneurs, and talents across industries. This approach can lead to strategic growth. Intellectual property sharing with vendors and partners can be mutually beneficial. Access to a wider idea pool and expertise provides a significant competitive advantage.
Organizational Innovation
This innovation adjusts business practices to optimize, automate, or modify operations. The aim is to benefit the company as a whole.
Sustaining Innovation
Sustaining innovation focuses on gradually improving products, services, or processes. It is crucial for staying competitive and often represents a large part of innovation budgets.
Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation creates a significant market shift, introducing a gap difficult for competitors to match. While offering great potential, achieving it is challenging.
Radical Innovation
Radical innovation creates solutions for previously unidentified needs. It has the potential to change the world and significantly impact daily life.
Product Innovation
Product innovation enhances the performance or attributes of products. It may involve new technology or combine existing technologies in new ways. Not all product innovations require technology.
Social Innovation
Social innovation focuses on improving social and workplace environments. It aims to enhance teamwork and group wellbeing.
Process Innovation
Process innovation gives new or significantly improved production or delivery methods. It often involves new technologies or methods to save time, money, or improve customer service. It may need a change in culture or structure.
Key Frameworks of Innovation Management
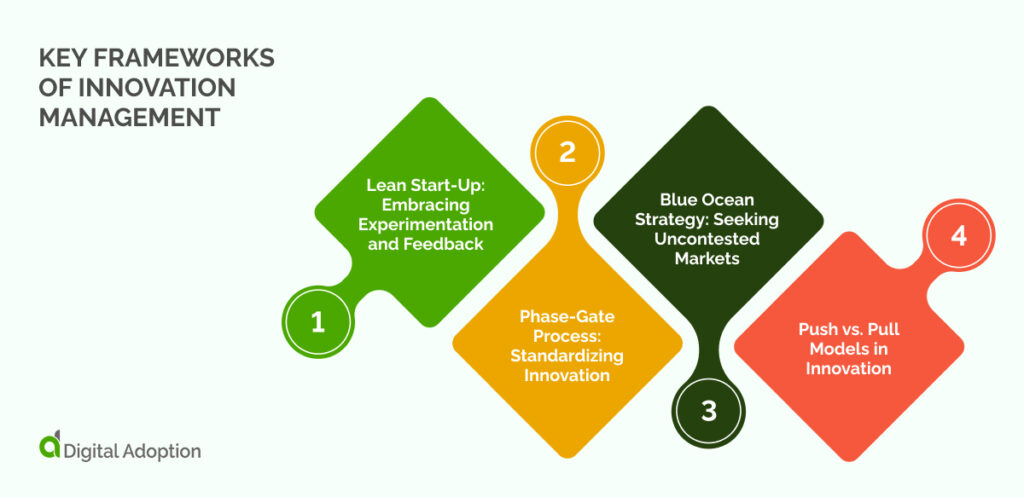
The key frameworks that guide leaders towards successful innovation management are:
Lean Start-Up: Embracing Experimentation and Feedback
The lean start-up methodology aligns closely with agile principles. It favors experimentation, customer feedback, and iterative design over detailed planning and traditional development. It challenges the notion of a perfect business plan. It advocates instead for a build-test-improve cycle for products.
This approach starts with developing a minimum viable product (MVP) to address a problem. The MVP is then tested in the market or with beta testers to identify flaws and determine market viability. The underlying belief of this methodology is that testing cannot occur without a tangible product. So, it encourages the rapid development of a lean product to begin testing.
Phase-Gate Process: Standardizing Innovation
The Phase-Gate, or stage-gate or waterfall model, is a recognized framework for product innovation. This framework operates on the principle that the abundance of ideas exceeds available resources. This requires a phased development approach.
Each idea progresses through designated phases. It concludes with a ‘gate’ where it’s evaluated against set criteria. Ideas that pass this assessment receive further investment and move to the subsequent phase. This process aims to streamline decision-making. It also allows the focus of resources on viable ideas by standardizing the progression and assessment of ideas.
However, the emphasis on standard criteria may inadvertently favor incremental, easily understandable ideas. This could potentially leading to innovation stagnation. Despite its traditional association with the waterfall approach, you can adapt the phase-gate model for use with agile methodologies. This allows for a more iterative innovation process.
Blue Ocean Strategy: Seeking Uncontested Markets
Blue Ocean Strategy inspires businesses to venture beyond the competitive confines of ‘red oceans’ filled with rivals. Instead, they should enter ‘blue oceans’ of uncharted market spaces.
It suggests developing a new value curve through four strategic questions that assess which industry factors to enhance, reduce, eliminate, or create. This approach highlights that many organizational behaviors are reactionary to competition. It proposes that innovation lies in not competing but in defining a unique market space.
Push vs. Pull Models in Innovation
You can divide innovation strategies into push-based and pull-based models. Push-based models are driven by internal and technological insights. They focus on addressing known market and user challenges with new solutions.
In contrast, pull-based models are guided by customer and market needs. They adapt to changing demands through engagement and rapid response. Pull-based approaches typically demand less upfront investment. This makes them attractive for startups due to quicker market entry and lower marketing costs.
What Does Successful Innovation Management Look Like?

A successful innovation management process is made up of these facets:
Using Agile Methodologies
Agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban improve innovation management. They support flexible and iterative product development approaches, enabling organizations to quickly adapt to changes and feedback. This results in faster innovation cycles.
Tracking Innovation Success
Measuring the success of innovation initiatives requires specific metrics. These include the number of new ideas generated and the rate at which these ideas are implemented. It also includes revenue from new products or services and employee engagement levels.
Building a Culture of Innovation
An innovation-friendly culture starts with a growth mindset at all organizational levels. Encouraging collaboration across departments and fostering interdisciplinary interactions can enhance knowledge sharing and creative problem-solving.
Applying Design Thinking
Design thinking principles help identify and address unmet customer needs. This approach, centered on understanding users, involves steps like empathy, defining problems, ideation, prototyping, and testing. It leads to products and services that truly meet customer expectations.
Promoting a Learning Culture
A learning culture is vital within any organization. It is key to encourage employees to develop their skills through training, workshops, and conferences. Opportunities for experimentation and learning from failures contribute to an adaptable workforce.
Encouraging Creative Imagination
For innovation to flourish, it’s essential to remove barriers to free thinking. Conformity and a fixed mindset hinder creativity. Businesses should encourage an environment where they reward productive behaviors and innovative ideas.
Leading By Example
Leaders with a clear vision for the future inspire innovative thinking. Such leaders build trust through their expertise and creates an environment that values teamwork and collaboration.
Capturing and Evaluating Ideas
Implementing a robust system is crucial to capture, evaluate, and prioritize ideas effectively. This system should integrate various methods. These include idea management platforms, suggestion boxes, hackathons, and innovation challenges. These systems allow for the efficient collection and assessment of ideas from employees, customers, and other stakeholders.
Leveraging Emerging Technologies
Organizations can drive innovation by leveraging digital technologies. For instance, artificial intelligence and virtual/augmented reality offer new growth and efficiency opportunities. Adopting these technologies can transform how businesses operate and compete.
How to Measure Innovation Management
There are two types of innovation management metrics you need to take into account.
These are:
Input Metrics: Measuring Innovation Effort
Input metrics encompass the resources and activities that fuel innovation. These include investment in talent, collaboration, training, and research.
They are crucial for evaluating an organization’s effort and commitment to innovation. Important indicators include the innovation budget as a percentage of revenue or profit and the number of employees engaged in innovation projects. It also includes the volume of ideas generated or screened and the time allocated to innovative activities.
For example, timesheets can provide insight into how many hours are spent on new projects or creative thinking. This emphasizes the need for allocating actual work hours to innovation every week.
Financial metrics are another aspect of input metrics. It shows what is invested in innovation and how innovation teams manage their budgets. It also highlights the company’s overall spending on innovation to promote innovation.
Output Metrics: Evaluating Innovation Outcomes
Output metrics focus on the tangible results of innovation efforts. These include new products, services, processes, or business models. These metrics are vital for gauging the real impact and value of innovation.
They help assess an organization’s success in implementing innovation. It also looks at its effectiveness in meeting customer and stakeholder needs.
Examples of output metrics include revenue or profit from new offerings or market share changes. It could also include customer satisfaction rates and the opportunities created by innovative efforts.
Other measures include the return on investment (ROI) from innovation activities and comparing actual versus planned breakeven times for new products.
The time-to-market metric is also important. It quantifies the period from conception to commercial availability. This reflects the innovation process’s speed and effectiveness in seizing market opportunities.
How to Implement Innovation Management
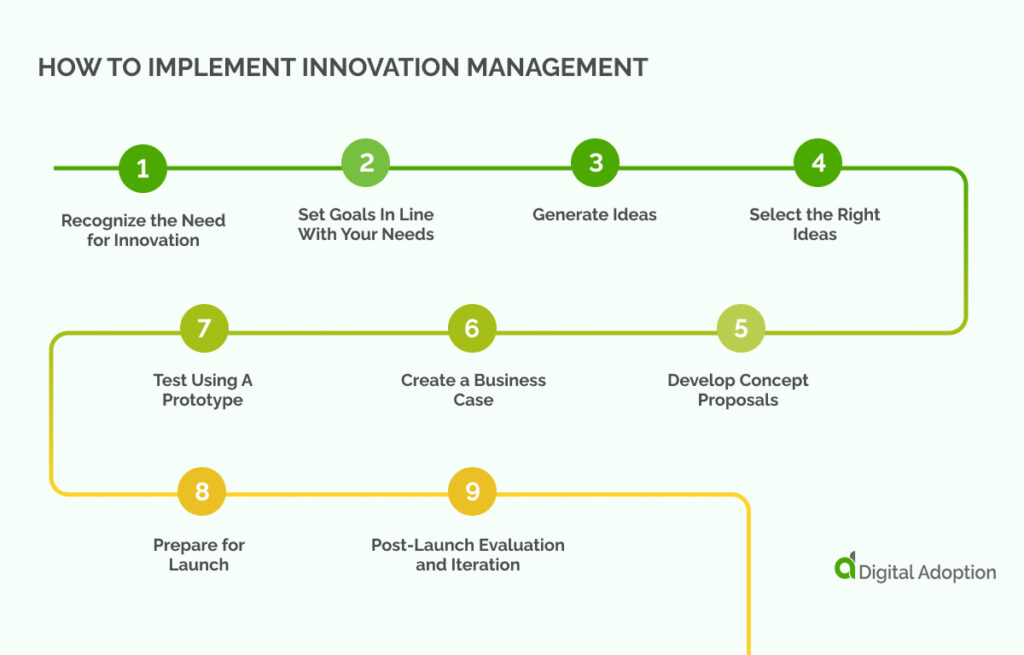
Implementing innovation typically progresses through various steps or stages. The exact steps can differ, reflecting each organization’s unique needs and context.
Here are the general steps that you can use to implement innovation management:
Recognize the Need for Innovation
Grasping the reason behind starting a new innovation project is crucial. Every company can improve, as the market is reshaped by new technologies and changing consumer habits. The initial step is to identify a specific problem that needs solving. This could range from creating new products to overhauling internal processes or management structures.
Identifying problems requires a comprehensive approach. It involves collecting detailed insights through customer surveys or interviews and getting feedback from staff on improving work conditions or fostering innovation.
You should get ideas from employees, customers, or the public. Analyzing internal data is key to uncovering issues such as declining sales or low employee engagement. Additionally, keeping an eye on industry trends is vital for identifying shifts in consumer behavior that could lead to new innovation opportunities.
Set Goals In Line With Your Needs
After pinpointing a need, it’s essential to set clear project goals. This includes deciding on the outcomes you’re aiming for, like new products or business models, and evaluating the resources and talent at your disposal. The list of needs can expand quickly, particularly when venturing into new areas such as open innovation competitions.
Generate Ideas
You can generate ideas through various methods. These include brainstorming sessions, idea contests, and customer feedback. At this stage, the aim is to generate a broad range of ideas without immediate judgment or selection.
Select the Right Ideas
Choosing the right ideas from the pool requires a systematic process. Considerations include the idea’s clarity, usability, stability, scalability, and stickiness. It also looks at how well it integrates within the organization and its profitability. The goal is to select ideas that match the organization’s needs and capabilities.
Develop Concept Proposals
The chosen ideas are then developed into detailed concept proposals. This involves conducting market research, creating prototypes, and assessing technical feasibility. The aim is to detail the innovation’s value proposition and target market. It also looks at competitive advantages and key features.
Create a Business Case
Developing a business case involves evaluating the innovation’s potential return on investment and viability. This analysis looks at market size, revenue potential, cost estimates, and financial projections. The business case aids in deciding whether the innovation is aligned and worth pursuing.
Test Using A Prototype
The next step is to develop the approved concept into a tangible product, service, or process. Creating a prototype at this stage helps pinpoint and address significant project challenges. It also helps refine the concept based on feedback from real-world use.
Prepare for Launch
This phase gets the innovation ready for market launch. It covers finalizing product design, setting up production processes, and developing marketing and sales strategies. It also deals with intellectual property protection and regulatory compliance.
Post-Launch Evaluation and Iteration
Following the launch, you can evaluate the innovation’s performance. Gather customer feedback, and meaure success against the initial objectives. You can make changes based on this feedback. Innovation management is a continuous, iterative process, where each cycle informs future initiatives.
What are Innovation Management Tools?
Companies need a robust system to track, check, and guide their innovation efforts. You could apply this system to a single project or across the entire organization. It includes tools that assist in managing, tracking, and controlling various aspects of innovation initiatives. Such initiatives might involve product development processes or cost-saving sprints.
Innovation management tools are essential for supporting innovation activities. They offer organizations a range of current strengths and weaknesses. They aid businesses and organizations in planning, monitoring, and executing their innovation strategies more effectively.
Examples of innovation management tools are:
- Ideawake
- Inno360
- Ideascale
- Ideanote
- Brightidea Innovation Cloud
- Accept Mission
- Braineet Workflow
- Viima
- Exago
Benefits of Innovation Management

The main benefits of innovation management for your workforce is that it allows them to:
Embrace Risk in Innovation
Innovation management recognizes the risks inherent in trying new things. It focuses on minimizing these risks and choosing the concepts with the highest potential for success. This approach enables businesses to dedicate their efforts to the most promising innovations.
Retain and Attract the Right Talent
Attracting and keeping talented employees is essential for an organization’s success. Innovation management provides opportunities for employees to offer their ideas, be creative, and have a meaningful impact. This nurtures a culture of innovation and continuous learning. It also makes the organization attractive to top talent seeking a dynamic workplace.
Address Recurring Issues
Organizations often grow accustomed to recurring problems, relying on inefficient workarounds or accepting losses. Innovation management advocates for fresh approaches to these issues. It helps businesses find and put in place more effective solutions.
Adapt to External Changes
Innovation management assists organizations in adjusting to external changes. These include evolving customer preferences, technological advancements, or regulatory shifts. Being proactive and innovative allows companies to handle market disruptions. It also allows them to handle emerging challenges, maintaining their relevance.
Improve Cost Efficiency
Ineffective processes and outdated ideas are typically not cost-effective. Innovation management enables businesses to take a closer look at their operations. It also helps identify areas of overspending. They can then replace these areas with more efficient, profitable solutions.
Gain a Competitive Edge
Organizations must innovate to stay competitive in today’s rapidly changing business landscape. Innovation management helps companies create distinctive products, services, or processes. This differentiates them from competitors and establishes a sustainable competitive advantage.
Collect and Organize Ideas
One of the benefits of innovation management is its ability to efficiently collect and organize new ideas. With the right tools, organizations can centralize insights. They can also streamline the review and implementation process.
Enhance Customer Satisfaction
Understanding and addressing customer needs is crucial. Innovation management plays a key role in improving customer experiences and satisfaction. This focus ensures companies remain customer-centric, meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
Involve All Employees
Innovation cannot happen without involving the entire workforce. Soliciting ideas from employees provides unique insights. It also makes them feel valued and included in decision-making. This promotes a forward-thinking culture, enhancing employee engagement and satisfaction.
Ensure Long-term Sustainability
Organizations that embrace innovation management position themselves for long-term success. By continually innovating, they can adapt to changing market conditions. They can also stay relevant, and avoid becoming stagnant. This approach fosters resilience and ensures ongoing growth.
Drive Growth and Expansion
Innovation is essential for entering new markets and driving growth. Continuous innovation allows organizations to launch new products or services. It also allows them to attract new customers and expanding their market share. Innovation management supports the exploration of new opportunities and industry entry. This expands the company’s footprint.
Challenges/Risks of Innovation Management
Mastering innovation presents a complex challenge. Every organization can encounter obstacles as they try to improve their innovative capabilities.
Below are the key challenges faced in innovation management:
Lack of a Growth Mindset
There’s a clear distinction between company cultures satisfied with “things are fine just the way they are” and those that embrace a growth mindset. Without a growth mindset in your organization, this outlook seeps into every action and decision. Employees might show little interest in improving themselves or the products they work on.
This mindset can also affect how the marketing team perceives and approaches the target audience. Establishing that a growth mindset is not merely an option. It is an essential need when it comes to innovation.
Hierarchical Structures
Organizations characterized by a top-down management approach tend to foster passivity among frontline employees. This issue becomes apparent when employees make statements such as ‘I just work here’. You could also hear employees stating that an action is not within their job specification.
Such remarks show a workforce that does only what is expected, never going beyond. Yet, innovation involves going beyond current expectations and limitations.
No Strategy or Lack of Focus
Innovation is often driven by the vision to create something that doesn’t yet exist. Organizations with a clear and inspiring vision attract individuals who want to innovate.
Having a vision is one thing. Communicating it effectively so everyone is on board is another challenge. A well-articulated vision increases the likelihood of implementing innovative ideas.
Lack of focus can lead to resources being spread too thinly. This creates too much overhead and diluting the effectiveness of initiatives. A scattered approach can mean that the organization’s capabilities do not implement ideas properly. Talking about innovation alone is not enough. It requires concrete investment in the infrastructure needed to capture and test new ideas.
Unsupportive Leadership
The responsibility to foster an innovative environment still lies with the organization’s leaders. They must provide their teams with the necessary resources. This includes technology, and opportunities for innovation. Leadership support is crucial for turning innovative ideas into practical, impactful solutions.
What’s Next For Innovation Management?
Innovation challenges and improves existing frameworks, confronting established norms that can hinder progress. This creates a dynamic of new ideas clashing with traditional practices.
Many companies focus on innovation, recognizing its complexities. To navigate these challenges, an organization must define its desired innovations. They must also foster a culture supportive of innovation. Then, they need to put in place a strategic approach to innovation management.
Effective innovation management necessitates a forward-looking attitude that confronts inevitable obstacles. It requires a flexible management strategy that balances organizational goals with innovation possibilities.
There must also be a commitment to persistence, ready to refine and retry ideas as needed. The journey begins with assessing the current state of the organization. You also need to identify bottlenecks that limit innovation efforts.
Some aspects, like specific processes, might be easier to address than others. For instance, changing the organizational culture is likely to be more time-consuming. Once you address bottlenecks, the next step is to enhance capabilities in all critical areas identified at the outset.
It’s essential not to focus only on fixing weaknesses. Innovation arises from excelling in particular areas and being distinct, rather than being average across the board.




![4 Best AI Chatbots for eCommerce [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/4-Best-AI-Chatbots-for-eCommerce-2025-img-300x146.jpg)


![13 Digital Transformation Enablers [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/13-Digital-Transformation-Enablers-2025-img-300x146.jpg)



![4 Best AI Chatbots for eCommerce [2025]](https://www.digital-adoption.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/4-Best-AI-Chatbots-for-eCommerce-2025-img.jpg)

