Research from McKinsey suggests that 2030 cloud adoption could lead to $3 trillion in EBITDA value. This shows that cloud platforms are essential for the success of modern enterprises.
Businesses today need to offer unique experiences across various channels. This helps engage audiences on their preferred platforms. They also must outpace their competitors.
Traditional methods no longer suffice for engaging customers, employees, and partners. These groups now expect immediacy and convenience.
Cloud adoption improves the customer and employee experience. It allows organizations to adapt to rapid changes. This keeps them competitive and agile.
In this article, we will focus on what cloud adoption is and how it works. Next, we will examine who it is for and the various types.
Then, we will look at how you can implement cloud adoption. Following this, we will go into when to use it and which sectors currently use it. Lastly, we will consider its benefits and challenges.
What Is Cloud Adoption?
Cloud adoption involves integrating cloud computing into business practices. Cloud computing stores, manages, and processes critical data using remote servers.
This transition can mean moving from traditional on-site infrastructure to cloud-based services. It can also involve using cloud solutions alongside existing in-house systems.
Adopting the cloud signifies the start of a digitally mature enterprise. It’s more than changing technology. It highlights a fundamental shift in how businesses operate.
This means that it affects organizational procedures and the workforce. In the first instance, it aims to enhance the scalability of data management systems. This change will also reduce costs and cut risks.
How Does Cloud Adoption Work?
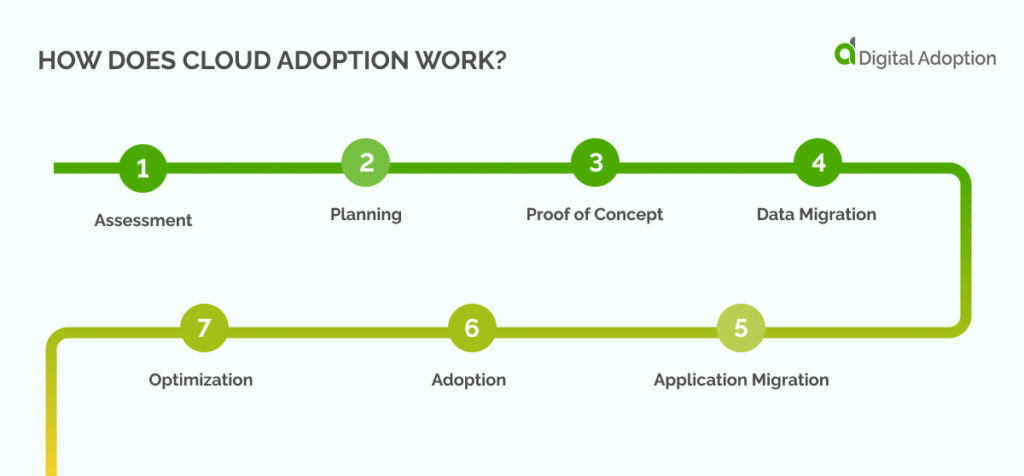
The process of cloud adoption takes place in the following steps:
Assessment: CIOs and IT leaders must assess the pros and cons of cloud adoption in their industry. They should explore well-known vendors within their field. Additionally, they must gather information about the experiences of early adopters. The focus needs to be on challenges and successes.
This stage will also involve evaluating current infrastructure and application interdependencies. This exercise can pinpoint potential risks and obstacles associated with migration.
Planning: Companies must engage in comprehensive research before crafting their cloud strategy. This step involves examining recognized cloud platforms and services. You also need to decide on the type of cloud adoption. This could be public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud.
Proof of Concept: This crucial stage involves creating a cloud adoption strategy. You can call this strategy a proof of concept (POC). You must introduce the POC to your team members and ensure their ongoing support.
Data Migration: Explore and choose from the available storage options. You also need to focus on security within your budget constraints. Once you’ve confirmed the integrity of your data, proceed with migrating it to the cloud.
Application Migration: Select the migration approach that best fits your organizational needs. Options may include lift-and-shift migration, re-platforming, repackaging, and retaining. This step is a vital component of your cloud adoption plan.
Adoption: Use these tools to automate the scaling of features and functions. Cloud services offer significant scalability and elasticity benefits.
Optimization: After the initial adoption phase, continuous improvement is essential. This process helps companies to maximize the return on their cloud investment.
Who Is Cloud Adoption For?
Cloud adoption is for any organization that wants to use cloud computing as a disruptor. It can also be a means to enhance its capabilities. It can also help organizations launch innovative products and services.
Transitioning to the cloud moves beyond focusing on cost reduction. Instead, it focuses on accelerating innovation to secure a competitive advantage.
Cloud adoption and migrating data are the starting points. This initial step facilitates the development of a cohesive data platform.
A modern data platform is crucial for exploring advancements in AI and ML, such as generative AI. Here, the cloud functions as the facilitator. Data acts as the catalyst. AI becomes the defining distinction.
Companies that need to adapt to the ever-changing world will also benefit. Cloud technology can drive digital transformation by providing tools for rapid digitization. It allows businesses to create impactful automation strategies.
This large-scale automation helps employees with complex tasks. It also improves efficiency and saves time. This then increases returns on investment. With cloud adoption, organizations avoid the cost and hassle of physical IT infrastructure. They can use services like virtual servers, storage, and databases on demand.
Types Of Cloud Adoption
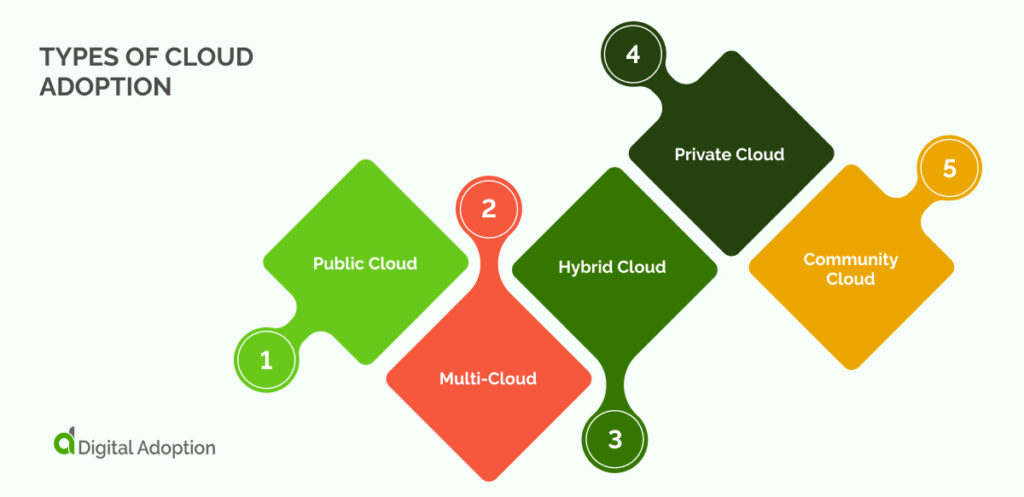
Before moving to the cloud, you need to be aware of the various types of cloud adoption models:
Public Cloud
The public cloud offers cloud services over a network for public use. Customers can’t control the infrastructure’s location.
Users share the cost model. It can be either free or based on a pay-per-use policy. This cloud type is ideal for organizations managing host and user applications.
Multi-Cloud
The multi-cloud approach uses services from various cloud providers. It allows organizations to select services that best meet their needs. This avoids reliance on a single vendor. Multicloud offers diversity in features and capabilities.
But, it introduces complexity in management and increases costs. There can be compatibility and interoperability challenges due to providers using different technologies.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds merge public and private cloud features into a heterogeneous cloud. They overcome the scalability limits of private clouds by using public cloud resources. Benefits include cost efficiency, quick data transfer, and improved security.
Yet, hybrid environments can be complex to create and manage. They pose challenges in security management and need specific expertise.
Private Cloud
A private cloud serves one organization, providing control over security and data. This cloud type suits organizations with high security and management needs.
Community Cloud
Community clouds target specific industries or communities. They integrate services from different clouds to meet shared goals. These clouds are cost-effective through shared infrastructure.
Despite their adaptability and scalability, managing shared responsibilities can be difficult. They offer a security level that is between public and private clouds. Community clouds support sectors like media, healthcare, energy, and scientific research.
How To Implement Cloud Adoption
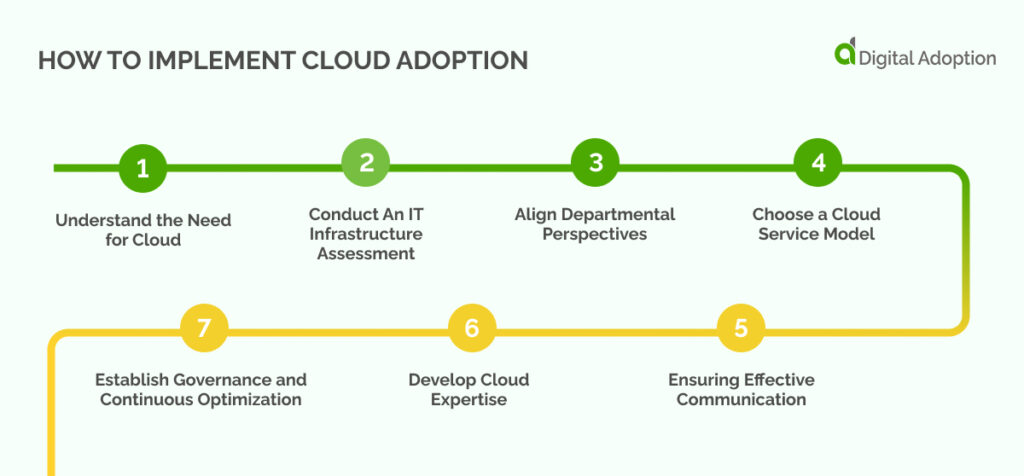
Embracing cloud adoption is not a decision to rush into. Understanding the technology is essential. You also need to know your current setup and future opportunities.
Below are steps to help your organization reap the benefits of embarking on a cloud journey:
Understand the Need for Cloud
Before moving to cloud implementation, consider its impact on your organization. Identify your motivations and goals. These factors will guide your planning and strategy. Understand the differences between on-premise and cloud servers. Know the cloud provider’s revenue model to optimize costs.
Conduct An IT Infrastructure Assessment
Assess your current digital infrastructure. This step helps develop a successful strategy for cloud adoption. Identifying potential obstacles and opportunities is crucial for efficient deployment.
Align Departmental Perspectives
Different departments have unique concerns and risks. Aligning these with business objectives is vital. Your cloud strategy should result from collaborative efforts. It should provide a unified vision of the cloud’s role.
Choose a Cloud Service Model
Analyze your infrastructure and business figures to select a suitable cloud service model. Consider the provider’s strategy to ensure alignment with your long-term goals. Choose IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS based on your company’s needs.
Ensuring Effective Communication
Maintain effective communication across the organization. Discuss the benefits and costs of cloud adoption. Broaden cloud evangelism as more stakeholders see its benefits.
Develop Cloud Expertise
Hire or train cloud experts to ensure successful cloud adoption. Integrate them into development teams and emphasize cloud development through regular training and coaching solutions.
Establish Governance and Continuous Optimization
- Put in place a governance model for using cloud services.
- Track performance and costs.
- Use automation to maintain agility as cloud usage expands.
When To Use Cloud Adoption
Various motivations can push businesses toward transformation via cloud adoption. Critical business events might trigger this shift.
These can include responding to regulatory compliance changes. It can also involve undergoing mergers, acquisitions, or divestitures. There might also be a need to manage the environmental impact of the business.
Businesses might also adopt the cloud to scale and meet geographic demands. They may also seek to optimize internal operations or boost business agility. For instance, cloud adoption could occur to protect against cyberattacks.
Finally, the desire to improve customer experiences can lead to cloud adoption. For instance, your organization might want to improve email communications through software. Developing new technical capabilities is another strong motivator.
Which Sectors Does Cloud Adoption Benefit?
Here are some examples of industries that cloud adoption can benefit:
Energy and Utilities
Cloud adoption is pivotal in transforming the energy and utilities sector. It supports smart grid technologies, improving grid performance and energy distribution. It also helps adapt to demand changes.
Cloud analytics and IoT devices enable predictive maintenance. This approach allows early equipment issue detection, preventive maintenance, and cost savings. It also improves operational reliability.
Agriculture
In agriculture, IoT and big data are driving innovation. They help us understand the environment and crop production better. Cloud technology provides detailed insights from soil, machinery, and livestock sensors. This optimizes agricultural practices and enhances decision-making.
Education
Education faces ongoing funding challenges. Cloud adoption offers a solution. It centralizes resources for students and streamlines assignment distribution for teachers. This improves collaboration and accessibility.
Healthcare
Cloud solutions have revolutionized healthcare. They secure patient data storage and ensure HIPAA compliance. Telemedicine, enabled by cloud technology, offers remote healthcare services. This improves access in remote areas and enhances patient care.
Retail
Retailers use cloud technology to analyze customer preference data. This enables personalized offerings and boosts sales. Cloud also simplifies vendor management by automating invoicing and payments. This makes operations more efficient.
Manufacturing
Cloud adoption provides a cost-effective alternative for manufacturing infrastructure. It supports product development, marketing, and smart manufacturing. Cloud tools aid in marketing, product planning, and supply chain integration. Cloud-based ERPs track production, stock, and sales.
Finance and Banking
In finance and banking, cloud adoption improves security and compliance. It includes measures like encryption and access controls. This protects financial data and aids regulatory compliance.
Cloud solutions enable real-time transaction processing, improving the efficiency of financial operations. Cloud-based machine learning models detect and prevent fraud, securing the economic ecosystem.
Benefits Of Cloud Adoption
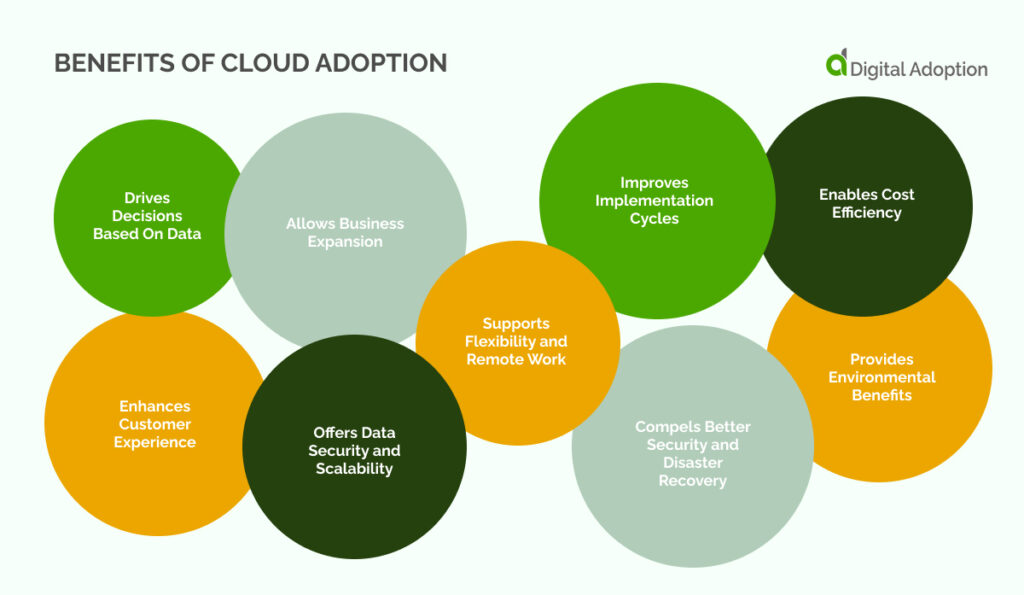
Cloud adoption offers organizations the opportunity to achieve their business objectives.
Here are some key advantages of embracing cloud technology:
Drives Decisions Based On Data
Businesses generate massive amounts of data daily. This data, known as big data, includes both structured and unstructured types. Extracting valuable insights from big data requires efficient and cost-effective processing methods.
Traditional storage systems may not keep up with the volume of data. Investing in infrastructure becomes necessary for supporting big data processing.
On-premises data warehouses often cannot support the rapid processing needed for advanced analytics. Migrating to the cloud allows organizations to better analyze data. This move enables data-driven decision-making.
Adopting cloud business intelligence is essential for staying competitive. It eliminates the need for physical infrastructure and enhances data accessibility.
Allows Business Expansion
Whether through mergers or diversification into new markets, cloud adoption streamlines these processes.
A strategic shift towards cloud computing can transform business operations. This leads to increased efficiency and facilitates new avenues for growth.
Enhances Customer Experience
In the digital age, customer satisfaction is paramount. Cloud technology offers businesses a significant advantage by enabling superior customer service.
Companies that use cloud-based customer support systems often resolve issues more quickly. This is because of the high availability and reliability of cloud services. Moreover, these systems allow for instant communication with customers. This enhances their experience and, by extension, their loyalty to the brand.
Offers Data Security and Scalability
Data loss, whether from natural disasters or technical failures, is a concern. Cloud adoption provides a secure, resilient environment for data storage and backup. This ensures business continuity even in the face of such challenges.
One of the most appealing aspects of cloud services is their scalability. As businesses grow, their IT needs change. You can adjust your cloud services requirements to fit evolving requirements. This removes the need for much upfront investment in physical infrastructure.
Supports Flexibility and Remote Work
The global shift towards remote work has highlighted the importance of flexibility. Cloud services enable employees to access critical systems and data from anywhere. This fosters a dynamic, agile organization.
Enables Cost Efficiency
Cloud adoption services operate on a pay-as-you-go pricing model. This means that businesses pay only for the resources they use.
This approach offers a more predictable, manageable cost structure. This is more cost-effective than on-premises IT infrastructure.
Furthermore, the provider can update and maintain cloud services. This reduces the burden of costly upgrades and maintenance on the business.
Improves Implementation Cycles
Organizations with on-premise software often face long lead times. It takes months to decide to install a product and then to determine its actual usage.
Cloud solutions offer a solution with quicker implementation cycles. Products go live in weeks, not months.
Moreover, cloud technology boosts team collaboration. It lets teams access, edit, and share documents and data anytime. This increases productivity and efficiency. Cloud-based apps provide real-time updates on workflows and file sharing.
Compels Better Security and Disaster Recovery
Cloud adoption enhances an organization’s ability to protect its data. It also helps a company recover from disasters. Personal devices and on-premises servers are vulnerable to security breaches and physical damage.
This is because they use robust encryption and many layers of backup to safeguard data. This minimizes downtime and the impact on business operations.
Provides Environmental Benefits
Adopting cloud technology benefits the environmental side of a business. By using the cloud, you can reduce waste and energy consumption. This contributes to a smaller carbon footprint.
Furthermore, cloud platforms ease seamless collaboration across departments and geographies. This breaks down data silos and drives efficiencies within the workplace.
Challenges of Cloud Adoption
Here are common challenges businesses might encounter during their transition to the cloud:
Security Concerns
A PwC survey reveals that 66% of IT professionals consider security a significant challenge in cloud adoption. But, cloud service providers can offer good security measures.
They use strong encryption, conduct regular audits, and have compliance certifications. This has enhanced data protection in the cloud.
So, overcoming this challenge involves a shift in organizational culture. Think about how your organization can become comfortable with cloud technologies. Start small, migrating a few workloads to the cloud and evaluating the results.
Understand your cloud provider’s security breach contingency plans. Appreciate how they can enhance security on your end.
Enhancing cybersecurity includes ensuring robust data encryption. It also involves adding extra authentication measures. You also need to foster clear communication among various teams.
The Organizational Impact of Cloud Migration
Cloud migration affects more than just the IT team. It may also have implications for legal, finance, and HR departments. All teams need to collaborate. This ensures all employees understand the cloud adoption model and workflows.
Security training and ongoing cloud education are vital to cut operational challenges. Introducing a new cloud system necessitates personnel training and an effective troubleshooting system.
Initial resistance from employees unfamiliar with cloud technology is common. However, clear communication of the benefits of the cloud can help enterprise digital adoption. Continuous learning can also act as employee training and fill any skill gaps.
Loss of Control
Adopting cloud solutions means less control over software, systems, and computing assets.
Reliability issues arise from internet dependency, which can disrupt business operations. Downtime and cloud service outages may lead to major productivity and revenue losses.
This poses challenges in assessing security system efficiency. It also makes implementing incident responses and monitoring data more difficult.
To address this, check each cloud provider’s visibility level. Also, look at their measures to prevent data breaches.
Next, look at what measures they have in place to cut the effect of downtime. Utilizing monitoring tools or setting up APIs can provide insights into your data. They can assist in reducing the risks associated with reduced oversight.
Next Steps For Cloud Adoption
Not moving to the cloud can make you fall behind competitors and lose your competitive edge. A strong cloud adoption strategy is crucial for growth and future-proofing your business.
Buying a cloud subscription isn’t enough. Your teams need to use the cloud in their daily tasks to see a real return on investment. Cloud adoption success depends on your teams’ willingness to adopt and use new tools.
For long-term success, you need an effective cloud adoption plan. Cloud adoption projects are complex, and developing the necessary skills can take time. Assessing your current infrastructure, business needs, and goals is important.
This assessment helps you create a strategic plan and make informed decisions. Sharing knowledge across the company builds a community that supports your strategic goals.
Achieving success with cloud technology requires continuous planning, monitoring, and optimization. Following cloud adoption best practices reduces risk and avoids common pitfalls.













